|
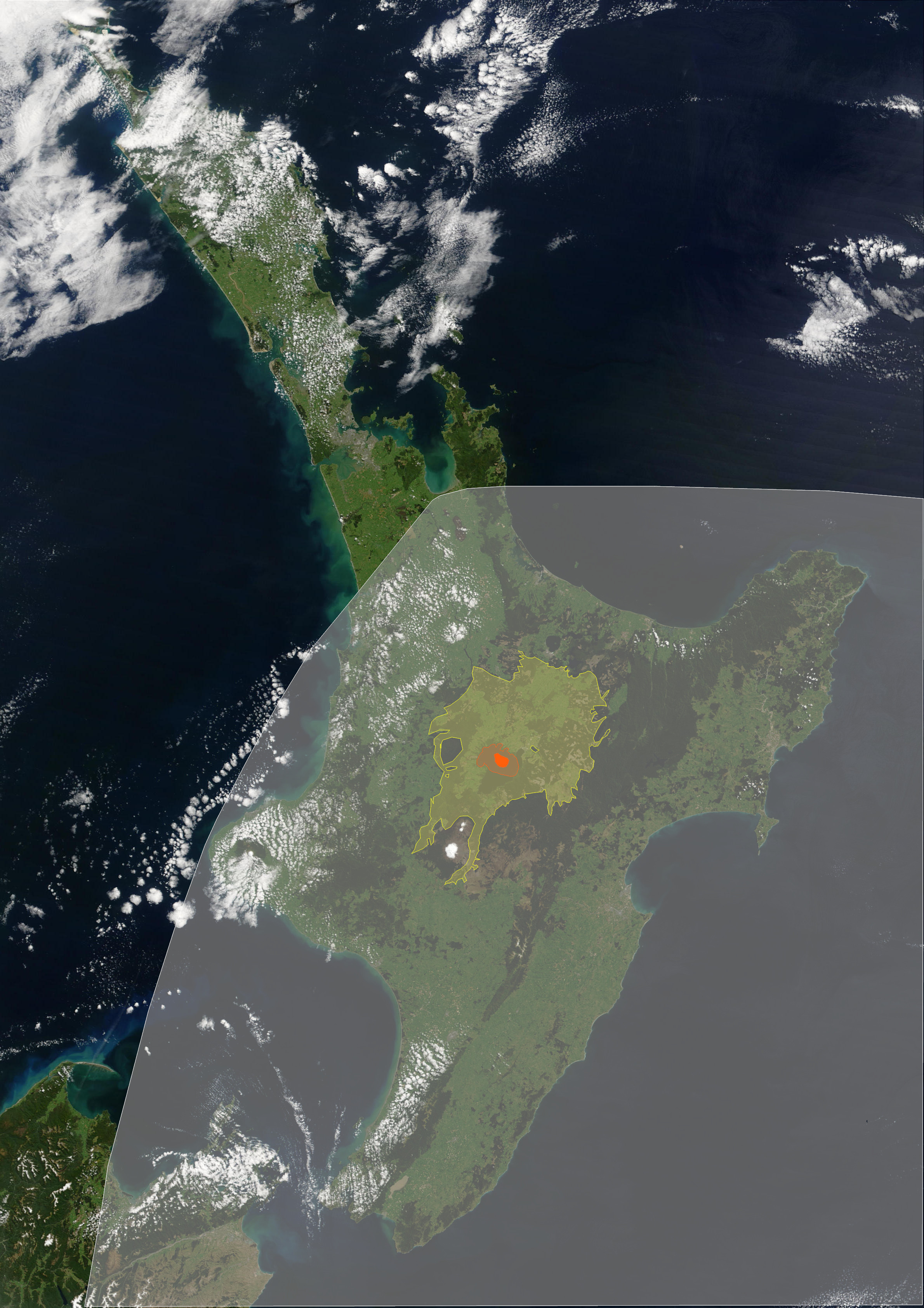
Oruanui Eruption
The Oruanui eruption (also known as the Kawakawa eruption or Kawakawa/Oruanui event) of Taupō Volcano in New Zealand around 25,700 years before present was the world's most recent supereruption, and its largest phreatomagmatic eruption characterised to date. Geography At the time of the eruption, the sea level was much lower than at present, and for over 100,000 years the Taupō Volcano had been mainly under Lake Huka, a larger lake than the present Lake Taupō. Lake Huka was destroyed in the eruption, and other features of the local geography were changed significantly as outlined below. Eruption With a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 8, it is one of the largest eruptions ever to occur in New Zealand and the most recent supereruption. It occurred years BP in the Late Pleistocene. It generated approximately of pyroclastic fall deposits, of pyroclastic density current (PDC) deposits (mostly ignimbrite), and of primary intracaldera material, equivalent to of rhyolitic m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Before Present
Before Present (BP) or "years before present (YBP)" is a time scale used mainly in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events occurred relative to the origin of practical radiocarbon dating in the 1950s. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use 1January 1950 as the commencement date (epoch) of the age scale, with 1950 being labelled as the "standard year". The abbreviation "BP" has been interpreted retrospectively as "Before Physics", which refers to the time before nuclear weapons testing artificially altered the proportion of the carbon isotopes in the atmosphere, which scientists must account for when using radiocarbon dating for dates of origin that may fall after this year. In a convention that is not always observed, many sources restrict the use of BP dates to those produced with radiocarbon dating; the alternative notation "RCYBP" stands for the explicit "radio carbon years before present". Usage The BP scale is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma (sometimes colloquially but incorrectly referred to as ''lava'') is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural satellites. Besides molten rock, magma may also contain suspended crystals and volcanic gas, gas bubbles. Magma is produced by melting of the mantle (geology), mantle or the Crust (geology), crust in various tectonics, tectonic settings, which on Earth include subduction zones, continental rift (geology), rift zones, mid-ocean ridges and Hotspot (geology), hotspots. Mantle and crustal melts migrate upwards through the crust where they are thought to be stored in magma chambers or trans-crustal crystal mush, crystal-rich mush zones. During magma's storage in the crust, its composition may be modified by Fractional crystallization (geology), fractional crystallization, contaminati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Maroa Caldera
The Maroa Caldera (Maroa Volcanic Centre) is approximately in size and is located in the north-east corner of the earlier Whakamaru caldera in the Taupō Volcanic Zone in the North Island of New Zealand. Volcanic activity in the caldera commenced over 300,000 years ago and the most recent volcanic eruption within in it was 9,400 years BCE. Geography Its northern rim is to the south of the Waikato River at Ātiamuri. At Ātiamuri the Ohakuri Caldera which had a paired eruption with the Rotorua Caldera is to its immediate north. The eastern boundary is also defined by the present Waikato River and it extends as far south as probably opposite Orakei Korako on the river. The southern boundary is somewhat ill defined given the subsequent deep deposits from the Taupō Volcano but includes a number of domes of which the highest is Maroanui at . Eruptive history The Maroa Caldera's last major eruption produced of tephra about 230,000 years ago (230 ka). Its earliest eruption was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dike (geology)
In geology, a dike or dyke is a sheet of rock that is formed in a fracture of a pre-existing rock body. Dikes can be either magmatic or sedimentary in origin. Magmatic dikes form when magma flows into a crack then solidifies as a sheet intrusion, either cutting across layers of rock or through a contiguous mass of rock. Clastic dikes are formed when sediment fills a pre-existing crack.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak Magmatic dikes A magmatic dike is a sheet of igneous rock that cuts across older rock beds. It is formed when magma fills a fracture in the older beds and then cools and solidifies. The dike rock is usually more resistant to weathering than the surrounding rock, so that erosion exposes the dike as a natural wall or ridge. It is from these natural walls that dikes get their name. Dikes preserve a record of the fissures through which most mafic magma (fluid magma low in silica) reaches the surface. They are studied by geologists for the clues they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Detrital Zircon Geochronology
Detrital zircon geochronology is the science of geochronology, analyzing the age of zircons deposited within a specific sedimentary rock, sedimentary unit by examining their inherent radioisotopes, most commonly the uranium–lead dating, uranium–lead ratio. Zircon is a common Accessory mineral, accessory or trace mineral constituent of most granite and felsic igneous rocks. Due to its hardness, durability and chemical inertness, zircon persists in sedimentary deposits and is a common constituent of most sands. Zircons contain trace amounts of uranium and thorium and can be dated using several modern analytical techniques. Detrital zircon geochronology has become increasingly popular in geological studies from the 2000s mainly due to the advancement in radiometric dating techniques. Detrital zircon age data can be used to constrain the maximum depositional age, determine provenance (geology), provenance, and reconstruct the tectonic setting on a regional scale. Detrital zirco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Zircon
Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of the range of substitution in zircon is (Zr1–y, REEy)(SiO4)1–x(OH)4x–y. Zircon precipitates from silicate melts and has relatively high concentrations of high field strength incompatible elements. For example, hafnium is almost always present in quantities ranging from 1 to 4%. The crystal structure of zircon is tetragonal crystal system. The natural color of zircon varies between colorless, yellow-golden, red, brown, blue, and green. The name derives from the Persian ''zargun'', meaning "gold-hued". This word is changed into " jargoon", a term applied to light-colored zircons. The English word "zircon" is derived from ''Zirkon'', which is the German adaptation of this word. Yellow, orange, and red zircon is also known as " hyacint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), but different nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have similar chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is derived from the Greek roots isos (wikt:ἴσος, ἴσος "equal") and topos (wikt:τόπος, τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd (doctor), Margaret Todd in a 1913 suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy, who popularized the term. The number of protons within the atomic nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Volcanic Ash Aggregation
Volcanic ash aggregation occurs when particles of volcanic ash collide and stick together during transport. This process modifies the size distribution of airborne particles, which affects both atmospheric dispersal and fallout patterns on the ground. Aggregation also impacts the dynamics of volcanic plumes, pyroclastic density currents, and their associated hazards A hazard is a potential source of harm. Substances, events, or circumstances can constitute hazards when their nature would potentially allow them to cause damage to health, life, property, or any other interest of value. The probability of that .... Numerical models There are two main approaches to include the effects of ash aggregation in numerical models of ash injection and dispersal. One is to initialize the model with an aggregated grain size distribution, by moving fractions of the erupted mass into larger size bins (for example, the Cornell model). A second approach is a full theoretical description of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wairakei
Wairakei is a small settlement and Geothermal activity, geothermal area 8-kilometres (5 mi) north of Taupō, in the centre of the North Island of New Zealand, on the Waikato River. It is part of the Taupō Volcanic Zone and features several natural geysers, hot pools, boiling mud pools, and the Wairakei Power Station, a major geothermal electric power generating station. The station was the second large-scale geothermal facility worldwide, and was commissioned in 1958. It was listed in the book ''70 Wonders Of The Modern World'' published in 2000 by Reader's Digest to record ''The Eventful 20th Century''. The settlement, referred to as Wairakei Village, was constructed to house the workers of both the power station and the neighbouring Aratiatia hydro power station. From 31 October 2022 it had buses to Taupō, Mondays to Fridays. Demographics Statistics New Zealand describes Wairakei Village as a rural settlement, which covers . and had an estimated population of as of with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mount Tauhara
Mount Tauhara is a dormant lava dome volcano in New Zealand's North Island, reaching above sea level. It is situated in the area of caldera rim overlap of the Whakamaru Caldera and Taupō Volcano towards the centre of the Taupō Volcanic Zone, which stretches from Whakaari / White Island in the north to Mount Ruapehu in the south. It is east of the town of Taupō, next to the northeastern shore of Lake Taupō. Formed about 65,000 years ago, Mount Tauhara was not a violently explosive vent, instead slowly oozing a viscous dacitic lava. It is the largest mass of dacite within the Taupō volcano, whose material is 98% rhyolitic. Little evidence of its volcanic past remains today; the peak is covered in dense native bush. There is a steep walking track to the top of Mount Tauhara, starting at Mountain Road. On a clear day, the summit offers views over the Volcanic Plateau, encompassing the entirety of Lake Taupō in the southwest. The hike is relatively strenuous and takes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pyroclastic Flow
A pyroclastic flow (also known as a pyroclastic density current or a pyroclastic cloud) is a fast-moving current of hot gas and volcanic matter (collectively known as tephra) that flows along the ground away from a volcano at average speeds of but is capable of reaching speeds up to . The gases and tephra can reach temperatures of about . Pyroclastic flows are the deadliest of all volcanic hazards and are produced as a result of certain explosive eruptions; they normally touch the ground and hurtle downhill or spread laterally under gravity. Their speed depends upon the density of the current, the volcanic output rate, and the gradient of the slope. Origin of term The word ''pyroclast'' is derived from the Greek (''pýr''), meaning "fire", and (''klastós''), meaning "broken in pieces". A name for pyroclastic flows that glow red in the dark is (French, "burning cloud"); this was notably used to describe the disastrous 1902 eruption of Mount Pelée on Martinique, a Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Breccia
Breccia ( , ; ) is a rock composed of large angular broken fragments of minerals or Rock (geology), rocks cementation (geology), cemented together by a fine-grained matrix (geology), matrix. The word has its origins in the Italian language, in which it means "rubble". A breccia may have a variety of different origins, as indicated by the named types including sedimentary breccia, fault (geology), fault or tectonics, tectonic breccia, igneous breccia, Impact event, impact breccia, and Hydrothermal circulation, hydrothermal breccia. A megabreccia is a breccia composed of very large rock fragments, sometimes kilometers across, which can be formed by landslides, impact events, or caldera collapse. Types Breccia is composed of coarse rock fragments held together by cement or a fine-grained matrix. Like Conglomerate (geology), conglomerate, breccia contains at least 30 percent of gravel-sized particles (particles over 2mm in size), but it is distinguished from Conglomerate (geol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |