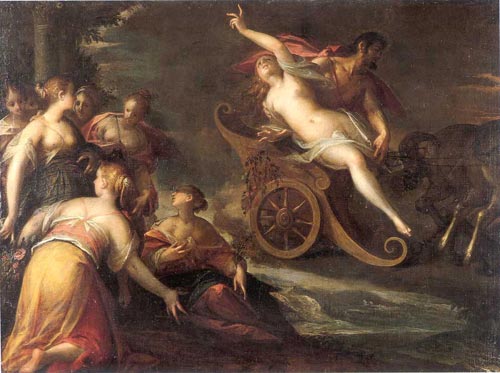|
Orphée Aux Enfers
''Orpheus in the Underworld'' and ''Orpheus in Hell'' are English names for (), a comic opera with music by Jacques Offenbach and words by Hector Crémieux and Ludovic Halévy. It was first performed as a two-act " opéra bouffon" at the Théâtre des Bouffes-Parisiens, Paris, on 21 October 1858, and was extensively revised and expanded in a four-act " opéra féerie" version, presented at the Théâtre de la Gaîté, Paris, on 7 February 1874. The opera is a lampoon of the ancient legend of Orpheus and Eurydice. In this version Orpheus is not the son of Apollo but a rustic violin teacher. He is glad to be rid of his wife, Eurydice, when she is abducted by the god of the underworld, Pluto. Orpheus has to be bullied by Public Opinion into trying to rescue Eurydice. The reprehensible conduct of the gods of Olympus in the opera was widely seen as a veiled satire of the court and government of Napoleon III, Emperor of the French. Some critics expressed outrage at the libretti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1878 Poster For Jacques Offenbach's Orphée Aux Enfers
Events January * January 5 – Russo-Turkish War: Battle of Shipka Pass IV – Russian and Bulgarian forces defeat the Ottoman Empire. * January 9 – Umberto I becomes King of Italy. * January 17 – Russo-Turkish War: Battle of Philippopolis – Russian troops defeat the Ottoman Empire. * January 23 – Benjamin Disraeli orders the British fleet to the Dardanelles. * January 24 – Russian revolutionary Vera Zasulich shoots at Fyodor Trepov, Governor of Saint Petersburg. * January 28 – In the United States: ** The world's First Telephone Exchange begins commercial operation in New Haven, Connecticut. ** ''The Yale News'' becomes the first daily college newspaper in the U.S. * January 31 – Turkey agrees to an armistice at Adrianople. February * February 2 – Greece declares war on the Ottoman Empire. * February 7 – Pope Pius IX dies, after a 31½ year pontificate (the longest definitely confirmed). * February 8 – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folies Bergère
150px, Stanisław Julian Ignacy Ostroróg">Walery, 1927 The Folies Bergère () is a cabaret music hall in Paris, France. Located at 32 Rue Richer in the 9th Arrondissement, the Folies Bergère was built as an opera house by the architect Plumeret. It opened on 2 May 1869 as the Folies Trévise, with light entertainment including operettas, comic opera, popular songs, and gymnastics. It became the Folies Bergère on 13 September 1872, named after nearby Rue Bergère. The house was at the height of its fame and popularity from the 1890s' ''Belle Époque'' through the 1920s. Revues featured extravagant costumes, sets and effects, and often nude women. In 1926, Josephine Baker, an African-American expatriate singer, dancer and entertainer, caused a sensation at the Folies Bergère by dancing in a costume consisting of a skirt made of a string of artificial bananas and little else. The institution is still in business, and is still a strong symbol of French and Parisia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lise Tautin
Lise Tautin, known on the stage by the pseudonym Mademoiselle (Mlle) Cor, (born Louise Vaissière, Yon, Jean-Claude. ''Jacques Offenbach.'' Editions Gallimard, Paris, 2000. Yvetot in 1834, died Bologna, May 1874), was a French soprano, associated with the opéra-bouffe in Paris in the middle of the 19th century, particularly the works of Offenbach.Gänzl K. ''The Encyclopaedia of the Musical Theatre.'' Blackwell, Oxford, 1994. Life and career Having been spotted by Offenbach at the Grand Théâtre de Lyon, Tautin made her debut with the Bouffes-Parisiens as Aspasie in '' Une demoiselle en loterie'' in July 1857 and was a big success with critics and the audiences. She also sang Fanchette in '' Le mariage aux lanternes'' (1857), Crout-ou-pôt in '' Mesdames de la Halle'' (1858), Minette in '' La chatte métamorphosée en femme'' 1858 - her incarnation of both girl and cat was praised, and Eurydice in ''Orphée aux Enfers'' (1858 and 1860 revival), where her ‘Hymne a Bacchus� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Léonce (actor)
Édouard-Théodore Nicole (c. 1823 – 19 February 1900), known as Léonce, was a 19th-century French actor and singer. Biography Léonce was born in Paris. After studying law, he made his stage debut at the Théâtre de Belleville. He also played the cello. In the 1850s, he was engaged at the Théâtre des Bouffes-Parisiens by Jacques Offenbach and sang many roles in the works of Offenbach and Hervé. After some time at the Théâtre de l'Athenée, he played in the premieres of '' Tromb-al-ca-zar'', '' Croquefer'', ''Orphée aux Enfers'', '' Mesdames de la Halle'' and '' Monsieur Choufleuri''. For several years, he appeared at the Théâtre des Variétés including in '' Les brigands'', '' Le docteur Ox'', '' La Vie parisienne'' and ''La Périchole''. After an unwise investment in a café, he ended his life in poverty. He died at Raincy on 19 February 1900. Theatre ; Comedian-singer *1858: '' Mesdames de la Halle'', une opérette bouffe de Jacques Offenbach - created ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Désiré (baritone)
Amable Courtecuisse (; 29 December 1823 – 7 September 1873), whose stage name was Désiré (), was a French baritone, who is particularly remembered for creating many comic roles in the works of the French operetta composer Jacques Offenbach.Karl-Josef Kutsch, Kutsch, K. J.; Leo Riemens, Riemens, Leo. ''Großes Sängerlexikon'' (fourth edition, in German), p. 1130. K. G. Saur, Munich, 2003. .Gänzl K. ''The Encyclopedia of the Musical Theatre.'' Blackwell, Oxford, 1994. . Life and career He was born in Lille or a nearby village of it, and studied the bassoon, singing, and declamation at the Lille Conservatory. His first appearances were at small theatres in Belgium and northern France beginning in 1845. In 1847, he arrived at the Théâtre Montmartre in Paris where he met Hervé (composer), Hervé. He asked Hervé to provide him with a musical sketch (drawn from Cervantes' novel ''Don Quixote''), in which the tall and thin Hervé as the Don was pitted against the short and pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proserpina
Proserpina ( ; ) or Proserpine ( ) is an ancient Roman goddess whose iconography, functions and myths are virtually identical to those of Greek Persephone. Proserpina replaced or was combined with the ancient Roman fertility goddess Libera, whose principal cult was housed in the Aventine temple of the grain-goddess Ceres, along with the wine god Liber. Each of these three deities occupied their own '' cella'' at the temple. Their cults were served or supervised by a male public priesthood. Ceres was by far the senior of the three, one of the '' Dii Consentes'', Rome's approximate equivalent to the Greek Twelve Olympians. She was identified with Greek Demeter and Liber was identified with Bacchus and Dionysus. Libera is sometimes described as a female version of Liber Pater, concerned with female fertility. Otherwise she is given no clear identity or mythology by Roman sources, and no Greek equivalent. Nothing is known of her native iconography: her name translates as a femin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurydice
Eurydice (; Ancient Greek: Εὐρυδίκη 'wide justice', classical pronunciation: ) was a character in Greek mythology and the wife of Orpheus, whom Orpheus tried to bring back from the dead with his enchanting music. Etymology Several meanings for the name ''Eurydice'' have been proposed such as "true judgment" or "profound judgment" from the Greek language, Greek: ''eur dike''. Fabius Planciades Fulgentius, Fulgentius, a mythographer of the late 5th to early 6th century AD, gave the latter etymological meaning. Adriana Cavarero, in the book ''Relating Narratives: Storytelling and Selfhood'', wrote that "the etymology of Eurydice seems rather to indicate, in the term ''eurus'', a vastness of space or power, which, joining to ''dike'' [and thus ''deiknumi'', to show], designates her as 'the one who judges with breadth' or, perhaps, 'she who shows herself amply.'" Mythology Marriage to Orpheus, death and afterlife Eurydice was the wife of musician Orpheus, who loved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter (mythology)
Jupiter ( or , from Proto-Italic language, Proto-Italic "day, sky" + "father", thus "sky father" Greek: Zeus, Δίας or Zeus, Ζεύς), also known as Jove (nominative case, nom. and genitive case, gen. ), is the sky god, god of the sky and god of thunder, thunder, and king of the gods in ancient Roman religion and Roman mythology, mythology. Jupiter was the chief deity of Roman state religion throughout the Roman Republic, Republican and Roman Empire, Imperial eras, until Constantine the Great and Christianity, Christianity became the dominant religion of the Empire. In Roman mythology, he negotiates with Numa Pompilius, the second king of Rome, to establish principles of Roman religion such as offering, or sacrifice. Jupiter is thought to have originated as a sky god. His identifying implement is the thunderbolt and his primary sacred animal is the eagle, which held precedence over other birds in the taking of auspices and became one of the most common symbols of the Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libretto
A libretto (From the Italian word , ) is the text used in, or intended for, an extended musical work such as an opera, operetta, masque, oratorio, cantata or Musical theatre, musical. The term ''libretto'' is also sometimes used to refer to the text of major liturgical works, such as the Mass (liturgy), Mass, requiem and sacred cantata, or the story line of a ballet. The Italian language, Italian word (, ) is the diminutive of the word ''wiktionary:libro#Italian, libro'' ("book"). Sometimes other-language cognates, equivalents are used for libretti in that language, ''livret'' for French works, ''Textbuch'' for German and ''libreto'' for Spanish. A libretto is distinct from a synopsis or scenario of the plot, in that the libretto contains all the words and stage directions, while a synopsis summarizes the plot. Some ballet historians also use the word ''libretto'' to refer to the 15- to 40-page books which were on sale to 19th century ballet audiences in Paris and contained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comédie-Française
The Comédie-Française () or Théâtre-Français () is one of the few state theatres in France. Founded in 1680, it is the oldest active theatre company in the world. Established as a French state-controlled entity in 1995, it is the only state theatre in France to have its own permanent troupe of actors. The company's primary venue is the Salle Richelieu, which is a part of the Palais-Royal complex and located at 2, Rue de Richelieu on Place André-Malraux in the 1st arrondissement of Paris. The theatre has also been known as the Théâtre de la République and popularly as "La Maison de Molière" (The House of Molière). It acquired the latter name from the troupe of the best-known playwright associated with the Comédie-Française, Molière. He was considered the patron of French actors. He died seven years before his troupe became known as the Comédie-Française, but the company continued to be known as "La Maison de Molière" even after the official change of name. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Théâtre Des Folies-Marigny
The Théâtre des Folies-Marigny (), a former theatre with a capacity of only 300 spectators, was built in 1848 by the Paris, City of Paris for a magician named Lacaze and was originally known as the Salle Lacaze. It was located at the east end of the Carré Marigny of the Champs-Élysées, close to the Avenue Marigny, but faced west toward the Cirque National on the other side of the square. In 1855 the Salle Lacaze became the home of Jacques Offenbach's Théâtre des Bouffes-Parisiens, where he first built his reputation as a theatre composer. It was subsequently used unsuccessfully by several companies until 1864, when it again became a profitable operetta theatre called the Folies-Marigny. When this company diminished in popularity, the theatre was closed. It was demolished in 1881 and replaced with the Panorama Marigny which was converted into the Théâtre Marigny in 1893. Salle Lacaze The first recorded entertainment use of the site dates to 1835, when a showman set up att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Operettas By Jacques Offenbach
This is a complete list of the 98 operettas of Jacques Offenbach (1819–1880). Subgenres The stage works of Offenbach (with the two exceptions of the opéras '' Die Rheinnixen'' and ''The Tales of Hoffmann'') are broadly referred to as 'operettas' in English references, even though only 16 of them were designated as opérettes by the composer. Offenbach called a further 8 opérette bouffe, and there is a single 'opérette fantastique'. There are 24 opéras comiques, and 24 opéras bouffes, together with 2 ' opéras bouffes féeries'. Other minor subgenres include opéra bouffon (5), bouffonnerie musicale (3), saynète (2) pièce d'occasion (2) and revue (2). Offenbach invented names for some individual works: 'anthropophagie musicale', 'chinoiserie musicale', 'comédie à ariettes', 'conversation alsacienne', 'légende bretonne', and 'légende napolitaine'. There are also one each of the following; 'fantasie musicale', 'opéra féerie', 'tableau villageois', and 'valse'. Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |