|
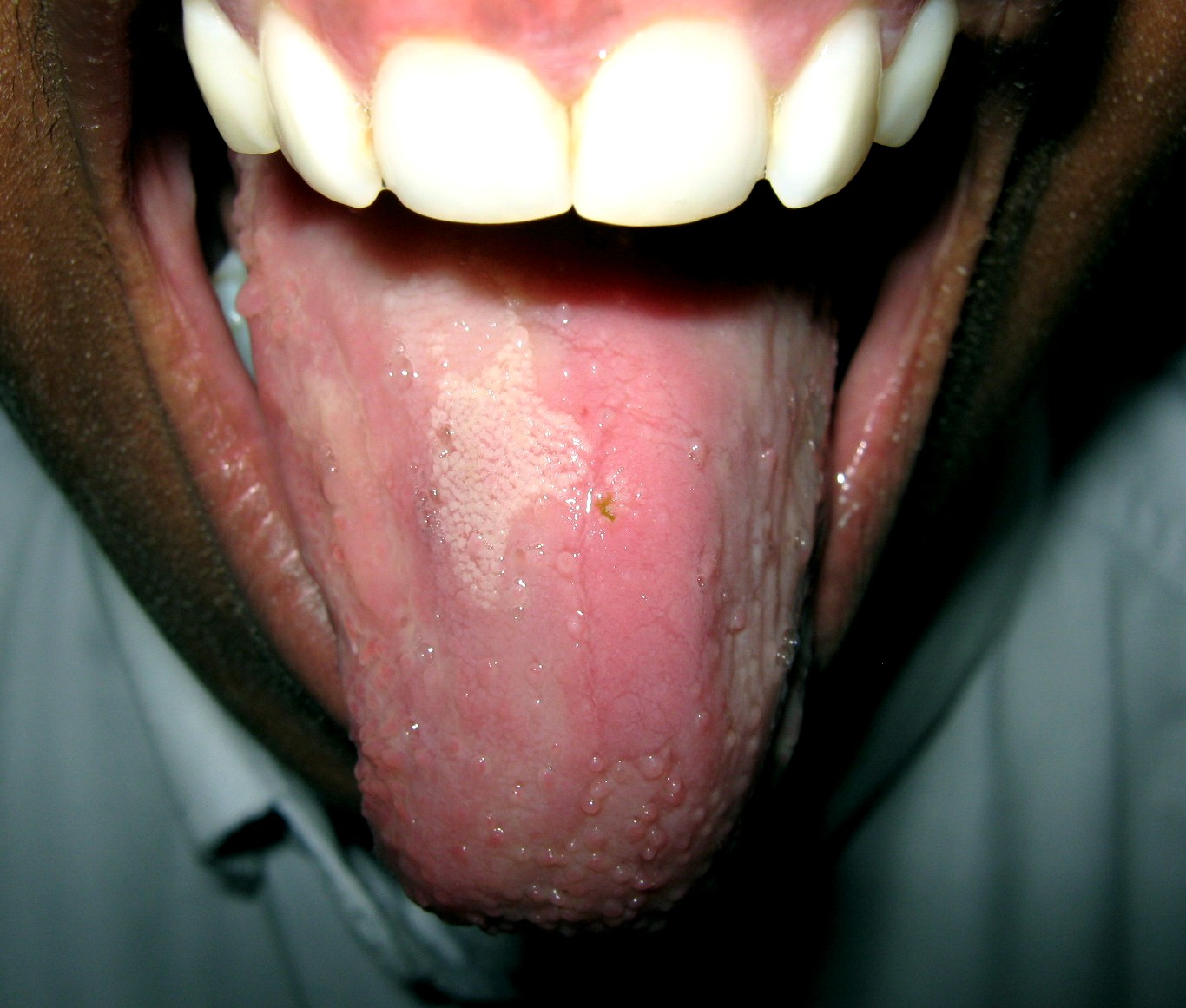
Oral Candidiasis
Oral candidiasis (Acute pseudomembranous candidiasis), also known among other names as oral thrush, is candidiasis that occurs in the mouth. That is, oral candidiasis is a mycosis (yeast/fungal infection) of ''Candida'' species on the mucous membranes of the mouth. '' Candida albicans'' is the most commonly implicated organism in this condition. ''C. albicans'' is carried in the mouths of about 50% of the world's population as a normal component of the oral microbiota. This candidal carriage state is not considered a disease, but when ''Candida'' species become pathogenic and invade host tissues, oral candidiasis can occur. This change usually constitutes an opportunistic infection by normally harmless micro-organisms because of local (i.e., mucosal) or systemic factors altering host immunity. Classification Oral candidiasis is a mycosis (fungal infection). Traditionally, oral candidiasis is classified using the Lehner system, originally described in the 1960s, into acute and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Infectious Disease (medical Specialty)
Infectious diseases (ID), also known as infectiology, is a medical specialty dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of infections. An infectious diseases specialist's practice consists of managing nosocomial (Hospital-acquired infection, healthcare-acquired) infections or community-acquired infections. An ID specialist investigates and determines the cause of a disease (bacteria, virus, parasite, fungus or prions). Once the cause is known, an ID specialist can then run various tests to determine the best drug to treat the disease. While infectious diseases have always been around, the infectious disease specialty did not exist until the late 1900s after scientists and physicians in the 19th century paved the way with research on the sources of infectious disease and the development of vaccines. Scope Infectious diseases specialists typically serve as consultants to other physicians in cases of complex infections, and often manage patients with HIV/AIDS and other forms of immuno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Glossitis
Glossitis can mean soreness of the tongue, or more usually inflammation with depapillation of the dorsal surface of the tongue (loss of the lingual papillae), leaving a smooth and erythematous (reddened) surface, (sometimes specifically termed atrophic glossitis). In a wider sense, glossitis can mean inflammation of the tongue generally. Glossitis is often caused by nutritional deficiencies and may be painless or cause discomfort. Glossitis usually responds well to treatment if the cause is identified and corrected. Tongue soreness caused by glossitis is differentiated from burning mouth syndrome, where there is no identifiable change in the appearance of the tongue, and there are no identifiable causes. Symptoms Depending upon what exact meaning of the word glossitis is implied, signs and symptoms might include: * Smooth, shiny appearance of the tongue, caused by loss of lingual papillae. * Tongue color changes, usually to a darker red color than the normal white-pink color of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Edentulous
Toothlessness or edentulism is the condition of having no teeth. In organisms that naturally have teeth, it is the result of tooth loss. Organisms that never possessed teeth can also be described as edentulous. Examples are the members of the former zoological classification order of '' Edentata'', which included anteaters and sloths, as they possess no anterior teeth and no or poorly developed posterior teeth. In naturally dentate species, edentulism is more than just the simple presence or absence of teeth. It is biochemically complex because the teeth, jaws, and oral mucosa are dynamic. Processes such as bone remodeling (loss and gain of bone tissue) in the jaws and inflammation of soft tissue in response to the oral microbiota are clinically important for edentulous people. For example, bone resorption in the jaw is frequently how the teeth were able to detach in the first place. The jaw in an edentulous area undergoes further resorption even after the teeth are gone; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Denture
Dentures (also known as false teeth) are prosthetic devices constructed to replace missing teeth, supported by the surrounding soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity. Conventional dentures are removable (removable partial denture or complete denture). However, there are many denture designs, some of which rely on bonding or clasping onto teeth or dental implants (fixed prosthodontics). There are two main categories of dentures, the distinction being whether they fit onto the mandibular arch or on the maxillary arch. Medical uses Dentures can help people via: * Mastication: chewing ability is improved by the replacement of edentulous (lacking teeth) areas with denture teeth. * Aesthetics: the presence of teeth gives a natural appearance to the face, and wearing a denture to replace missing teeth provides support for the lips and cheeks and corrects the collapsed appearance that results from the loss of teeth. * Pronunciation: replacing missing teeth, especially the anteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Denture Related Stomatitis
Denture-related stomatitis is a common condition where mild inflammation and redness of the oral mucous membrane occurs beneath a denture. In about 90% of cases, ''Candida (fungus), Candida'' species are involved, which are normally a harmless component of the oral microbiota (microbiology), microbiota in many people. Denture-related stomatitis is the most common form of oral candidiasis (a yeast infection of the mouth). It is more common in elderly people, and in those who wear a complete upper denture (a denture which replaces all the upper teeth, worn by someone with no natural teeth in their upper jaw). Denture-related stomatitis is more likely to develop when the denture is left constantly in the mouth, rather than removing it during sleep, and when the denture is not cleaned regularly. Signs and symptoms Despite the alternative name for this condition, "denture sore mouth", it is usually painless and asymptomatic. The appearance of the involved mucosa is erythematous (red) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |