|
Operation Praying Mantis
Operation Praying Mantis was the 18 April 1988 attack by the United States on Iranian naval targets in the Persian Gulf in retaliation for the mining of a U.S. warship four days earlier. On 14 April, the American guided missile frigate struck a mine while transiting international waters as part of Operation Earnest Will, the 1987–88 effort to protect reflagged Kuwaiti oil tankers from Iranian attacks during the Iran–Iraq War. The explosion pierced the hull and broke the keel of the ''Samuel B. Roberts'', which nearly sank but was saved by its crew with no loss of life. After the serial numbers of mines recovered in the area were found to match those of mines seized on an Iranian barge the previous September, U.S. military officials planned a retaliatory operation. On 18 April, the attack destroyed, damaged, or sank two Iranian oil platforms, three warships, several armed boats, and two fighter jets. Two U.S. Marine aviators died when their helicopter crashed into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War, also known as the First Gulf War, was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. Active hostilities began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for nearly eight years, until the acceptance of United Nations Security Council Resolution 598 by both sides. Iraq's primary rationale for the attack against Iran cited the need to prevent Ruhollah Khomeini—who had spearheaded the Iranian revolution in 1979—from exporting the new Iranian ideology to Iraq. There were also fears among the Iraqi leadership of Saddam Hussein that Iran, a theocratic state with a population predominantly composed of Shia Muslims, would exploit sectarian tensions in Iraq by rallying Iraq's Shia majority against the Baʽathist government, which was officially secular but dominated by Sunni Muslims. Iraq also wished to replace Iran as the power player in the Persian Gulf, which was not seen as an achievable objective prior to the Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZU-23
The ZU-23-2, also known as ZU-23, is a Soviet towed 23×152mm anti-aircraft twin-barreled autocannon. ZU stands for ''Zenitnaya Ustanovka'' (Russian: Зенитная Установка) – anti-aircraft mount. The GRAU index is 2A13. Development history The ZU-23-2 was developed in the late 1950s. It was designed to engage low-flying targets at a range of 2.5 km as well as armoured vehicles at a range of two kilometres and for direct defence of troops and strategic locations against air assault usually conducted by helicopters and low-flying airplanes. In 1955, KBP presented the single-barrel ZU-1 and the twin-barrel ZU-14. While the former was eventually dropped, the ZU-14 was selected and, after some modifications, entered series production. In the Soviet Union, some 140,000 units were produced. The ZU-23 has also been produced under licence by Bulgaria, Poland, Egypt and the People's Republic of China. Development of this weapon into a self-propelled anti-aircraft gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Amity, Economic Relations And Consular Rights
The Treaty of Amity, Economic Relations and Consular Rights between the United States and Iran was signed in Tehran on August 15, 1955, received the consent of the U.S. Senate on July 11, 1956 and entered into force on 16 June 1957. The treaty is registered by the United States to the United Nations on 20 December 1957. The official texts are in English and Persian. It is sealed by plenipotentiaries Selden Chapin (U.S.) and Mostafa Samiy (Iran). The Treaty has served as the jurisdictional basis for various international legal disputes between the United States and Iran, including the International Court of Justice (ICJ) cases ''Oil Platforms'' and '' Alleged Violations of the 1955 Treaty of Amity, Economic Relations and Consular Rights''. In October 2018, the United States provided notice that it would be withdrawing from the Treaty following Iran's use of the Treaty as a basis to challenge the U.S. imposition of sanctions under the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Platform
An oil platform (also called an oil rig, offshore platform, oil production platform, etc.) is a large structure with facilities to extract and process petroleum and natural gas that lie in rock formations beneath the seabed. Many oil platforms will also have facilities to accommodate the workers, although it is also common to have a separate accommodation platform linked by bridge to the production platform. Most commonly, oil platforms engage in activities on the continental shelf, though they can also be used in lakes, inshore waters, and inland seas. Depending on the circumstances, the platform may be fixed to the ocean floor, consist of an artificial island, or float. In some arrangements the main facility may have storage facilities for the processed oil. Remote subsea wells may also be connected to a platform by flow lines and by umbilical connections. These sub-sea facilities may include one or more subsea wells or manifold centres for multiple wells. Offshore drillin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barge
A barge is typically a flat-bottomed boat, flat-bottomed vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. Original use was on inland waterways, while modern use is on both inland and ocean, marine water environments. The first modern barges were pulled by tugs, but on inland waterways, most are pushed by Pusher (boat), pusher boats, or other vessels. The term ''barge'' has a rich history, and therefore there are many types of barges. History of the barge Etymology ''Barge'' is attested from 1300, from Old French ''barge'', from Vulgar Latin ''barga''. The word originally could refer to any small boat; the modern meaning arose around 1480. ''Bark'' "small ship" is attested from 1420, from Old French ''barque'', from Vulgar Latin ''barca'' (400 AD). A more precise meaning (see Barque) arose in the 17th century and often takes the French spelling for disambiguation. Both are probably derived from the Latin ''barica'', from Greek language, Greek ''baris'' "Eg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element of a watercraft, important for stability. On some sailboats, it may have a fluid dynamics, hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose as well. The keel laying, laying of the keel is often the initial step in constructing a ship. In the British and American shipbuilding traditions, this event marks the beginning date of a ship's construction. Etymology The word "keel" comes from Old English language, Old English , Old Norse , = "ship" or "keel". It has the distinction of being regarded by some scholars as the first word in the English language recorded in writing, having been recorded by Gildas in his 6th century Latin work ''De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae'', under the spelling ''cyulae'' (he was referring to the three ships that the Saxons first arrived in). is the Latin word for "keel" and is the origin of the term careening, careen (to clean a keel and the hull in general, often by rolling the ship on its side). An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Tanker
An oil tanker, also known as a petroleum tanker, is a ship designed for the bulk cargo, bulk transport of petroleum, oil or its products. There are two basic types of oil tankers: crude tankers and product tankers. Crude tankers move large quantities of unrefined petroleum, crude oil from its point of extraction to oil refinery, refineries. Product tankers, generally much smaller, are designed to move refined products from refineries to points near consuming markets. Oil tankers are often classified by their size as well as their occupation. The size classes range from inland or coastal tankers of a few thousand metric tons of deadweight tonnage, deadweight (DWT) to ultra-large crude carriers (ULCCs) of . Tankers move approximately of oil every year.UNCTAD 2006, p. 4. Second only to pipeline transport, pipelines in terms of efficiency,Huber, 2001: 211. the average cost of transport of crude oil by tanker amounts to only US. Some specialized types of oil tankers have evolved. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuwait
Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is a country in West Asia and the geopolitical region known as the Middle East. It is situated in the northern edge of the Arabian Peninsula at the head of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Kuwait border, the north and Saudi Arabia to Kuwait–Saudi Arabia border, the south. With a coastline of approximately , Kuwait also shares a maritime border with Iran, across the Persian Gulf. Kuwait is a city-state, most of the country's population reside in the urban area, urban agglomeration of Kuwait City, the capital and largest city. , Kuwait has a population of 4.82 million, of which 1.53 million are Kuwaiti nationality law, Kuwaiti citizens while the remaining 3.29 million are Expatriates in Kuwait, foreign nationals from over 100 countries. Kuwait has the world's third List of sovereign states by immigrant and emigrant population, largest number of foreign nationals as a percentage of the population, where its citizens make up less th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
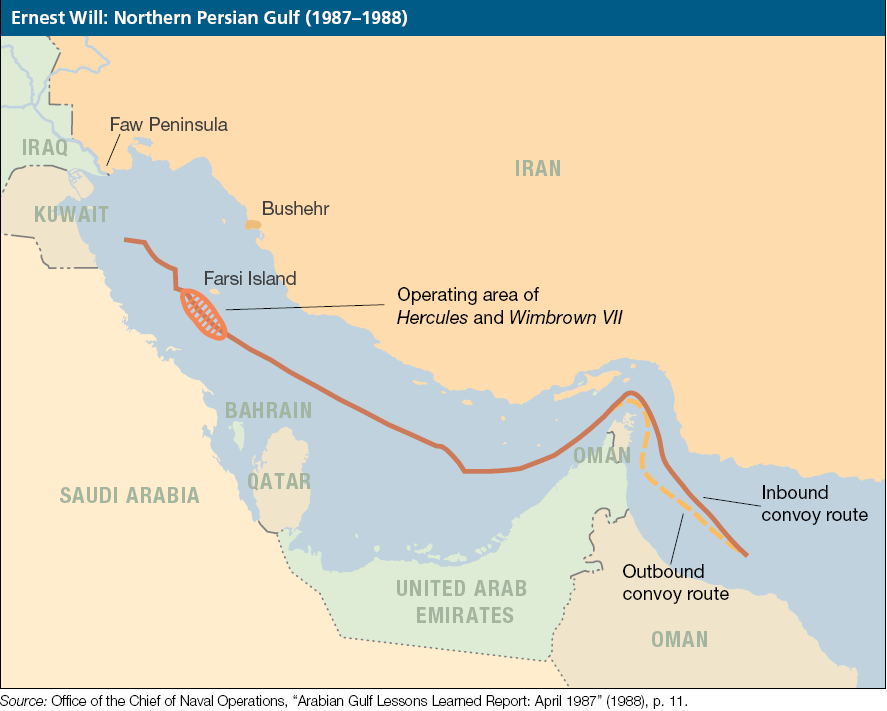
Operation Earnest Will
Operation Earnest Will (24 July 1987 – 26 September 1988) was an American military protection of Kuwaiti-owned tankers from Iranian attacks in 1987 and 1988, three years into the Tanker War phase of the Iran–Iraq War. It was the largest naval convoy operation since World War II, and flowed from Resolution 598 which had been adopted three days earlier. The U.S. Navy warships that escorted the tankers, part of U.S. Naval Forces Central Command, were the operations' most visible part. U.S. Air Force AWACS radar planes provided surveillance and U.S. Army special-operations helicopters hunted for possible attackers. Other U.S. Navy vessels participated in Operation Earnest Will. They were then under the command of the U.S. Navy's Seventh Fleet which had primary responsibility for combat operations in the Persian Gulf. The numerous ships used in Operation Earnest Will mostly consisted of Carrier Battle Groups, Surface Action Groups and ships from the Pacific's Third and Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Waters
The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water (or their drainage basins) transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed regional seas and estuaries, rivers, lakes, groundwater systems (aquifers), and wetlands. "International waters" is not a defined term in international law. It is an informal term, which sometimes refers to waters beyond the "territorial sea" of any country. In other words, "international waters" is sometimes used as an informal synonym for the more formal term "high seas", which under the doctrine of ''mare liberum'' (Latin for "freedom of the seas"), do not belong to any state's jurisdiction. As such, states have the right to fishing, navigation, overflight, laying cables and pipelines, as well as scientific research. The Convention on the High Seas, signed in 1958, which has 63 signatories, defined "high seas" to mean "all parts of the sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, what is now generally regarded as the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), a type of powerful ironclad warships was developed, and because they had a single gun deck, the term 'frigate' was used to describe them. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the 'frigate' designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |