|
Old Town Hall, Newton Stewart
The Old Town Hall is a former municipal building on Victoria Street in Newton Stewart, Scotland. The building, which was previously the meeting place of the burgh council, is a Category B listed building. History Following significant population growth, largely associated with the new cotton mills established by Sir William Douglas, the local laird, John Stewart, 7th Earl of Galloway, whose seat was at Galloway House, decided to commission a town hall for the area. The site he chose was on the corner of Victoria Street and Riverside Road, backing onto the River Cree. The building was designed in the Italianate style, built in painted rubble masonry and was completed in around 1800. The design involved an asymmetrical main frontage of four bays facing onto Victoria Street. The main block of three bays, on the left, featured three round-headed openings, formed by pilasters supporting imposts and arches with raised keystones; there were three Venetian windows on the first floor. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton Stewart
Newton Stewart (Scottish Gaelic language, Gd: ''Baile Ùr nan Stiùbhartach'') is a former burgh town in the historical county of Wigtownshire in Dumfries and Galloway, southwest Scotland. The town is on the River Cree with most of the town to the west of the river, and is sometimes referred to as the "Gateway to the Galloway Hills". The main local industries are agriculture, forestry and tourism. The town hosts a local market, and a number of services to support the farming industry. There are many mountain biking trails in the area. Newton Stewart lies on the southern edge of the Galloway Forest Park, which supplies many jobs to the town. Newton Stewart is from Scotland's book town Wigtown. History The town was founded in the mid 17th century by William Stewart, fourth and youngest son of the 2nd Earl of Galloway. The "New Town of Stewart" was granted burgh status by charter from King Charles II of England, Charles II, allowing a weekly market and two annual fairs to be he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
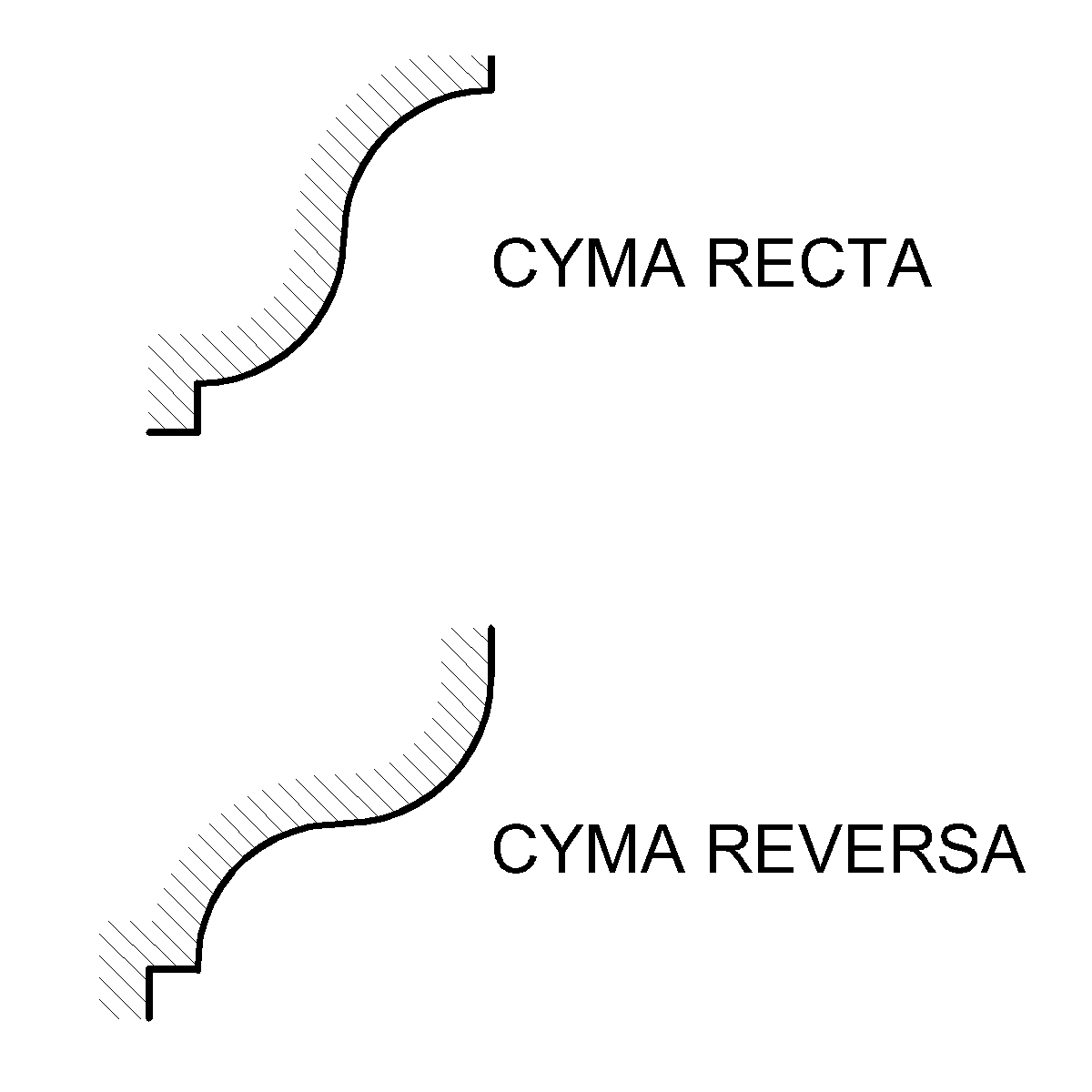
Ogee
An ogee ( ) is an object, element, or curve—often seen in architecture and building trades—that has a serpentine- or extended S-shape (Sigmoid curve, sigmoid). Ogees consist of a "double curve", the combination of two semicircle, semicircular curves or arc (geometry), arcs that, as a result of a inflection point, point of inflection from concave function, concave to convex function, convex or ''vice versa'', have ends of the overall curve that point in opposite directions (and have tangents that are approximately parallel). First seen in textiles in the 12th century, the use of ogee elements—in particular, in the design of arches—has been said to characterise various Gothic architecture, Gothic and Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic Revival architectural styles. The shape has many such uses in architecture from those periods to the present day, including in the ogee arch in these architectural styles, where two ogees oriented as mirror images compose the sides of the ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Chambers And Town Halls In Scotland
A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agreed definition of the lower boundary for their size. In a narrower sense, a city can be defined as a permanent and densely populated place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organizations, and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving the efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Listed Buildings In Newton Stewart, Dumfries And Galloway
This is a list of listed buildings in the town of Newton Stewart, in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. List Key Notes References * All entries, addresses and coordinates are based on data froHistoric Scotland This data falls under thOpen Government Licence {{DEFAULTSORT:List of listed buildings in Newton Stewart, Dumfries and Galloway Newton Stewart Newton Stewart (Scottish Gaelic language, Gd: ''Baile Ùr nan Stiùbhartach'') is a former burgh town in the historical county of Wigtownshire in Dumfries and Galloway, southwest Scotland. The town is on the River Cree with most of the town to ... Newton Stewart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumfries And Galloway Council
Dumfries and Galloway (; ) is one of the 32 unitary council areas of Scotland, located in the western part of the Southern Uplands. It is bordered by East Ayrshire, South Ayrshire, and South Lanarkshire to the north; Scottish Borders to the north-east; the English county of Cumbria, the Solway Firth, and the Irish Sea to the south, and the North Channel to the west. The administrative centre and largest settlement is the town of Dumfries. The second largest town is Stranraer, located to the west of Dumfries on the North Channel coast. Dumfries and Galloway corresponds to the historic shires of Dumfriesshire, Kirkcudbrightshire, and Wigtownshire, the last two of which are collectively known as Galloway. The three counties were combined in 1975 to form a single region, with four districts within it. The districts were abolished in 1996, since when Dumfries and Galloway has been a unitary local authority. For lieutenancy purposes, the area is divided into three lieutenanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMillan Hall, Newton Stewart
The McMillan Hall is a municipal building in Dashwood Square in Newton Stewart, Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. The structure, which is used as a community events venue, is a Category B listed building. History The first municipal building in the town was the old town hall in Victoria Street, which was completed in around 1800. In the early 1880s, the burgh leaders found that the old town hall was inadequate for their needs and, after the local grocers, Peter and William McMillan, left £10,000 in their wills towards the cost of a new town hall, the burgh leaders decided to commission a new structure. The foundation stone for the new building was laid by Alan Stewart, 10th Earl of Galloway in August 1884. It was designed by a local architect, Richard Park, in the French Renaissance style, built by local contractors, T. & J. Agnew, in ashlar stone and was completed in 1885. It appears that John Dick Peddie was involved in the design as well. The design involved a symmetrical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanics' Institute
Mechanics' institutes, also known as mechanics' institutions, sometimes simply known as institutes, and also called schools of arts (especially in the Australian colonies), were educational establishments originally formed to provide adult education, particularly in technical subjects, to working men in Victorian-era Britain and its colonies. They were often funded by local industrialists on the grounds that they would ultimately benefit from having more knowledgeable and skilled employees. The mechanics' institutes often included libraries for the adult working class, and were said to provide them with an alternative pastime to gambling and drinking in pubs. Many of the original institutes included lending libraries, and the buildings of some continue to be used as libraries. Others have evolved into parts of universities, adult education facilities, theatres, cinemas, museums, recreational facilities, or community halls. Few are still referred to as mechanics' institutes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the List of English districts by population, largest local authority district in England by population and the second-largest city in Britain – commonly referred to as the second city of the United Kingdom – with a population of million people in the city proper in . Birmingham borders the Black Country to its west and, together with the city of Wolverhampton and towns including Dudley and Solihull, forms the West Midlands conurbation. The royal town of Sutton Coldfield is incorporated within the city limits to the northeast. The urban area has a population of 2.65million. Located in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands region of England, Birmingham is considered to be the social, cultural, financial and commercial centre of the Midland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village Lock-up
A village lock-up is a historic building once used for the temporary detention of people in England and Wales, mostly where official prisons or criminal courts were beyond easy walking distance. Lockups were often used for the confinement of drunks, who were usually released the next day, or to hold people being brought before the local magistrate. The archetypal form comprises a small room with a single door and a narrow slit window, grating or holes. Most lock-ups feature a tiled or stone-built dome or spire as a roof and are built from brick, stone and/or timber. Such a room was built in many shapes; many are round, which gives rise to a sub-description: the punishment or village round-house (). Village lock-ups, though usually freestanding, were often attached to walls, tall pillar/tower village crosses or incorporated into other buildings. Varying in architectural strength and ornamentation, they were all built to perform the same function. Nicknames and forms They have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Vane
A wind vane, weather vane, or weathercock is an instrument used for showing the direction of the wind. It is typically used as an architectural ornament to the highest point of a building. The word ''vane'' comes from the Old English word , meaning "flag". Although partly functional, wind vanes are generally decorative, often featuring the traditional cockerel design with letters indicating the points of the compass. Other common motifs include ships, arrows, and horses. Not all wind vanes have pointers. In a sufficiently strong wind, the head of the arrow or cockerel (or equivalent) will indicate the direction from which the wind is blowing. Wind vanes are also found on small wind turbines to keep the wind turbine pointing into the wind. History The oldest known textual references to weather vanes date from 1800-1600 BCE Babylon, where a fable called ''The Fable of the Willow'' describes people looking at a weather vane "for the direction of the wind." In China, the ''Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a matter of controversy and there are a wide variety of forms and specialized terms to describe them. A dome can rest directly upon a Rotunda (architecture), rotunda wall, a Tholobate, drum, or a system of squinches or pendentives used to accommodate the transition in shape from a rectangular or square space to the round or polygonal base of the dome. The dome's apex may be closed or may be open in the form of an Oculus (architecture), oculus, which may itself be covered with a roof lantern and cupola. Domes have a long architectural lineage that extends back into prehistory. Domes were built in ancient Mesopotamia, and they have been found in Persian architecture, Persian, Ancient Greek architecture, Hellenistic, Ancient Roman architecture, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |