|
Olancha, California
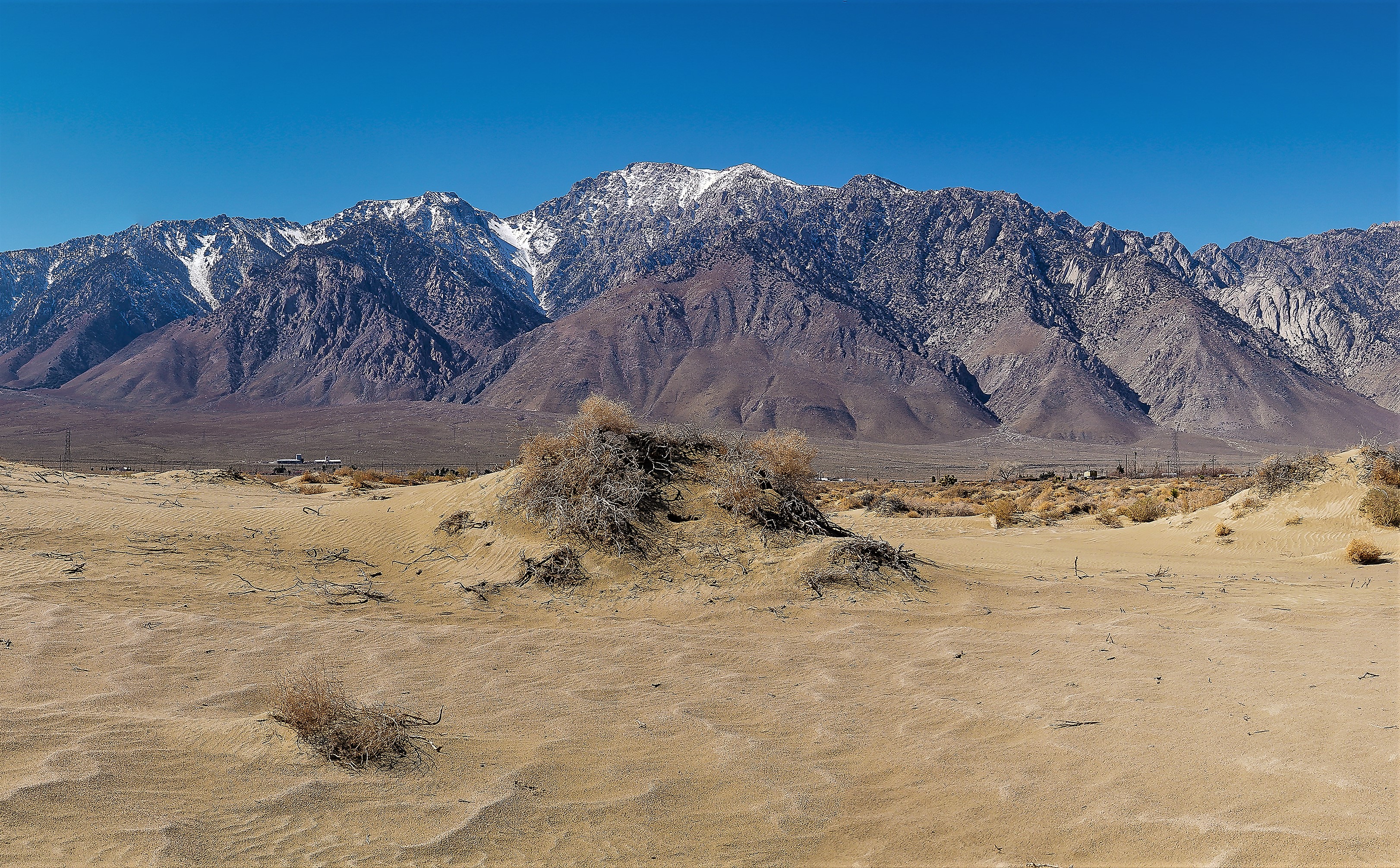
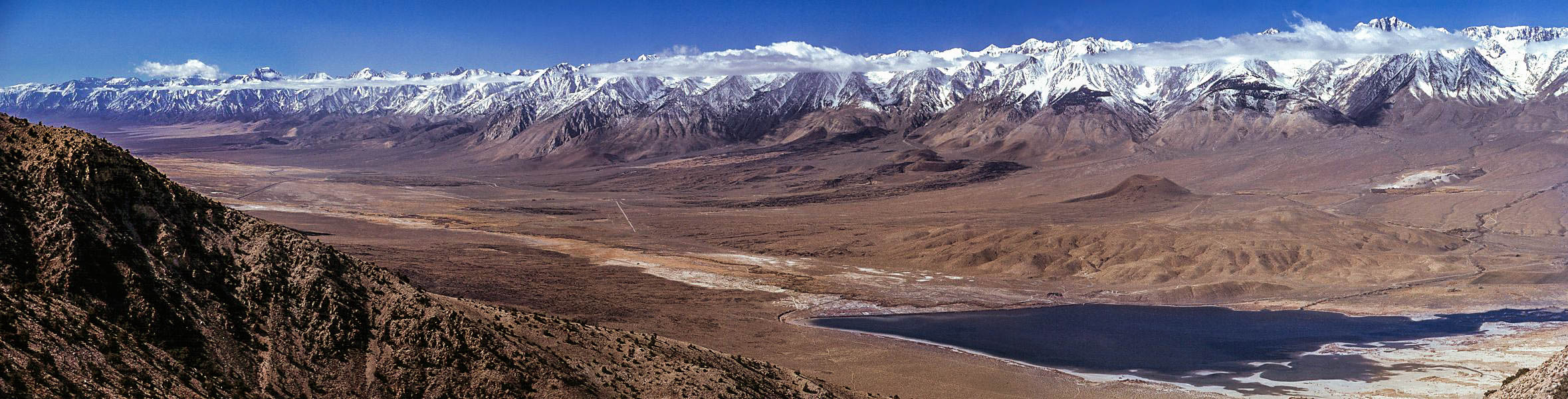
Olancha (Timbisha: ''Pakwa' si'') is a census-designated place in Inyo County, California, United States. Olancha is located on U.S. Route 395 in California, south-southeast of Independence. As of the 2010 census, the population was 192, up from 134 at the 2000 census. Located in the Owens Valley next to the now mostly dry Owens Lake, the arid settlement is home to a major bottled water plant for Crystal Geyser Natural Alpine Spring Water. Geography Olancha is an unincorporated community located in the Owens Valley on the eastern slope of the Sierra Nevada mountain range at the elevation of , in Inyo County, California. It is on US Highway 395 near the junction of State Route 190, approximately due north of Los Angeles. Owens Lake - a dry saline lakebed - lies to the northeast of Olancha. Olancha Creek flows from the slopes of nearby Olancha Peak (12,123 ft), passing near the town of Olancha, and finally towards Owens Lake. To the east of town lie some sand dunes, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unincorporated Community
An unincorporated area is a parcel of land that is not governed by a local general-purpose municipal corporation. (At p. 178.) They may be governed or serviced by an encompassing unit (such as a county) or another branch of the state (such as the military). There are many unincorporated communities and areas in the United States and Canada, but many countries do not use the concept of an unincorporated area. By country Argentina In Argentina, the provinces of Chubut Province, Chubut, Córdoba Province (Argentina), Córdoba, Entre Ríos Province, Entre Ríos, Formosa Province, Formosa, Neuquén Province, Neuquén, Río Negro Province, Río Negro, San Luis Province, San Luis, Santa Cruz Province, Argentina, Santa Cruz, Santiago del Estero Province, Santiago del Estero, Tierra del Fuego Province, Argentina, Tierra del Fuego, and Tucumán Province, Tucumán have areas that are outside any municipality or commune. Australia Unlike many other countries, Australia has only local go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamp Mill
A stamp mill (or stamp battery or stamping mill) is a type of Mill (grinding), mill machine that crushes material by pounding rather than Mill (grinding), grinding, either for further processing or for extraction of metallic ores. Breaking material down is a type of unit operation. Description A stamp mill consists of a set of heavy steel (iron-shod wood in some cases) stamps, loosely held vertically in a frame, in which the stamps can slide up and down. They are lifted by Cam (mechanism), cams on a horizontal rotating camshaft, shaft. As the cam moves from under the stamp, the stamp falls onto the ore below, crushing the rock, and the lifting process is repeated at the next pass of the cam. Each one frame and stamp set is sometimes called a "battery" or, confusingly, a "stamp" and mills are sometimes categorised by how many stamps they have, i.e. a "10 stamp mill" has 10 sets. They usually are arranged linearly, but when a mill is enlarged, a new line of them may be construct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coso Range
The Coso Range of eastern California is located immediately south of Owens Lake, east of the Sierra Nevada, and west of the Argus Range. The southern part of the range lies in the restricted Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake and the northern part of the range is designated as the Coso Range Wilderness. The mountains include Coso Peak, at above sea level, as well as Silver Peak and Silver Mountain, both more than in height. The range is underlain principally by Mesozoic granitic rocks that are partly veneered by upper Cenozoic volcanic rocks of the Coso Volcanic Field. The volcanic units (in apparent decreasing age) include (1) widespread basaltic flows, (2) dacitic flows and tuff, and (3) rhyolitic domes and flows and basaltic cones and flows. These volcanic rocks are encompassed by an oval-shaped zone of late Cenozoic ring faulting that measures about east to west and north to south and that defines a structural basin. Most of the Coso Range and a slice of the adjacent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
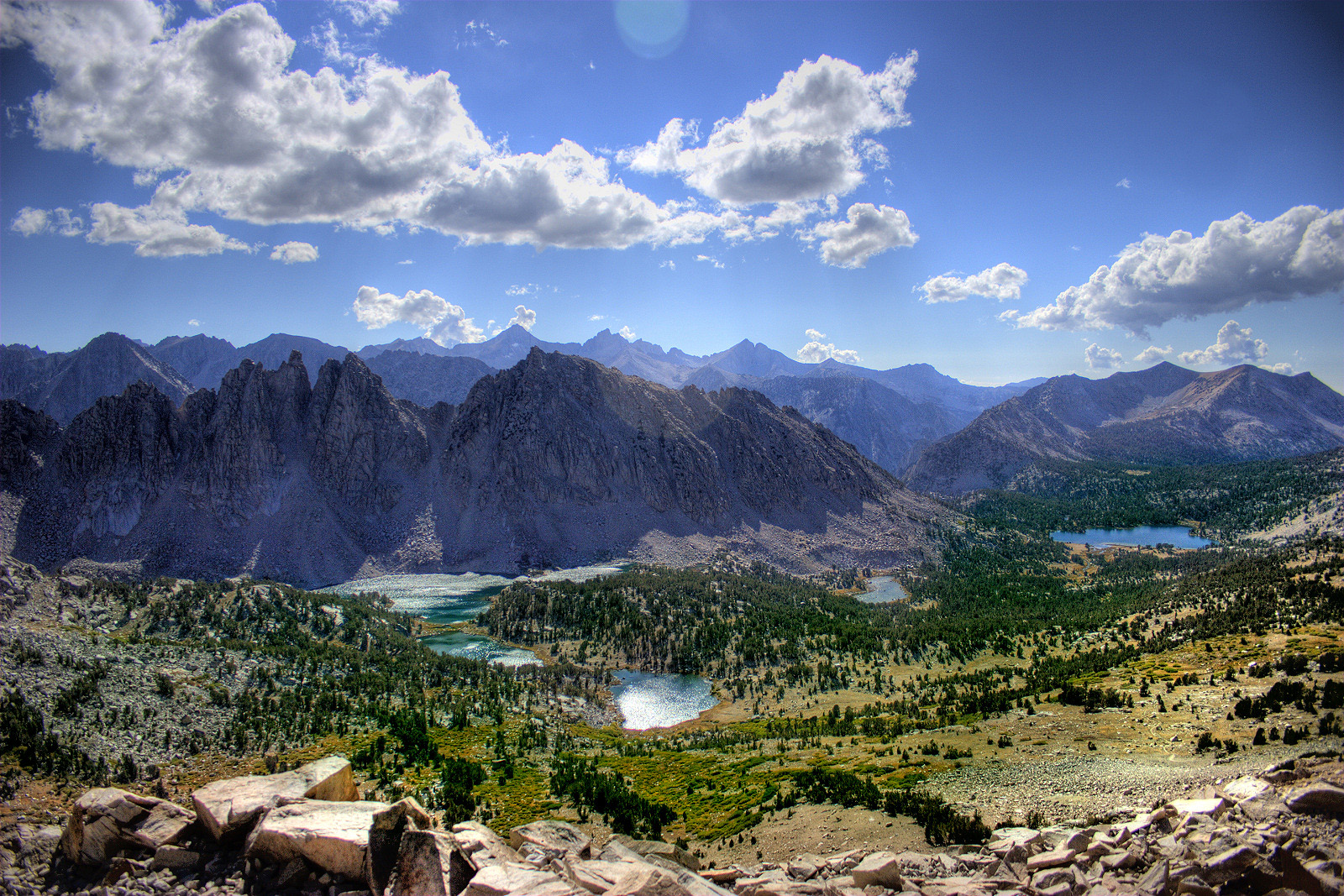
Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada ( ) is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primarily in Nevada. The Sierra Nevada is part of the American Cordillera, an almost continuous chain of mountain ranges that forms the western "backbone" of the Americas. The Sierra runs north-south, and its width ranges from to across east–west. Notable features include the General Sherman Tree, the largest tree in the world by volume; Lake Tahoe, the largest alpine lake in North America; Mount Whitney at , the highest point in the contiguous United States; and Yosemite Valley sculpted by glaciers from one-hundred-million-year-old granite, containing high waterfalls. The Sierra is home to three national parks, twenty-six wilderness areas, ten national forests, and two national monuments. These areas include Yosemite, Sequoia, and Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
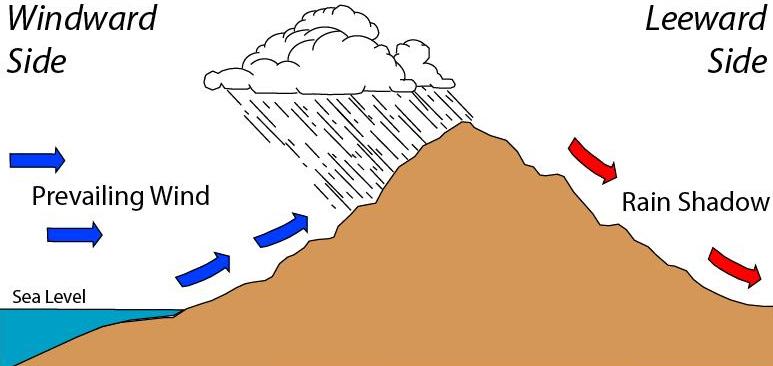
Rainshadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side. Evaporated moisture from bodies of water (such as oceans and large lakes) is carried by the prevailing onshore breezes towards the drier and hotter inland areas. When encountering elevated landforms, the moist air is driven upslope towards the peak, where it expands, cools, and its moisture condenses and starts to precipitate. If the landforms are tall and wide enough, most of the humidity will be lost to precipitation over the windward side (also known as the ''rainward'' side) before ever making it past the top. As the air descends the leeward side of the landforms, it is compressed and heated, producing Foehn winds that ''absorb'' moisture downslope and cast a broad "shadow" of dry climate region behind the mountain crests. This climate typically takes the form of shrub–steppe, xeric shrublands, or deserts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-arid Climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-arid climates, depending on variables such as temperature, and they give rise to different biomes. Defining attributes of semi-arid climates A more precise definition is given by the Köppen climate classification, which treats steppe climates (''BSh'' and ''BSk'') as intermediates between desert climates (BW) and humid climates (A, C, D) in ecological characteristics and agricultural potential. Semi-arid climates tend to support short, thorny or scrubby vegetation and are usually dominated by either grasses or shrubs as they usually cannot support forests. To determine if a location has a semi-arid climate, the precipitation threshold must first be determined. The method used to find the precipitation threshold (in millimeters): * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the ''A'' group, indicated by the third letter for climates in ''B'', ''C'', ''D'', and the second letter for climates in ''E''. Other examples include: ''Cfb'' indicating an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending ''b.'', while ''Dwb'' indicates a semi-Monsoon continental climate, monsoonal continental climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olancha Peak
Olancha Peak is a mountain in the Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada of California. It rises to an elevation of on the Tulare-Inyo county line in the South Sierra Wilderness. It takes its name from the nearby town of Olancha, California, Olancha. The mountain is also known as "Indianhead" and "the Sleeping Maiden", as some think that parts of the ridgeline of the southern slope of the mountain, when viewed from certain angles, resembles either the face of a man or the figure of a woman lying on her back. The peak is one of the highest in the Sierra Nevada south of Mount Whitney. It is the southernmost peak that is significantly above treeline on the Sierra Nevada escarpment. Due to the high elevation, most of the precipitation the mountain receives consists of snow. References External links * * {{Authority control Mountains of the Sierra Nevada (United States) Mountains of Inyo County, California Mountains of Tulare County, California Inyo National Forest Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olancha Creek
Olancha (Timbisha: ''Pakwa' si'') is a census-designated place in Inyo County, California, United States. Olancha is located on U.S. Route 395 in California, south-southeast of Independence. As of the 2010 census, the population was 192, up from 134 at the 2000 census. Located in the Owens Valley next to the now mostly dry Owens Lake, the arid settlement is home to a major bottled water plant for Crystal Geyser Natural Alpine Spring Water. Geography Olancha is an unincorporated community located in the Owens Valley on the eastern slope of the Sierra Nevada mountain range at the elevation of , in Inyo County, California. It is on US Highway 395 near the junction of State Route 190, approximately due north of Los Angeles. Owens Lake - a dry saline lakebed - lies to the northeast of Olancha. Olancha Creek flows from the slopes of nearby Olancha Peak (12,123 ft), passing near the town of Olancha, and finally towards Owens Lake. To the east of town lie some sand dunes, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highway 395
Route 395 or Highway 395 may refer to: Canada * British Columbia Highway 395 * Manitoba Provincial Road 395 * New Brunswick Route 395 Route 395 is a long mostly North–South secondary highway in the northwest portion of New Brunswick, Canada. The route's North-Eastern terminus starts at an intersection in the community of Hazeldean. The road travels south-east to the commun ... * Nova Scotia Route 395 * Quebec Route 395 Great Britain * A395 road Japan * Japan National Route 395 United States * Interstate 395 * U.S. Route 395 * Arkansas Highway 395 * California State Route 395 (former) * Florida State Road 395 (former) * Kentucky Route 395 * Massachusetts Route 395 (former) * Nevada State Route 395 (former) * New Mexico State Road 395 * New York State Route 395 * Oregon Route 395 (former) * Washington State Route 395 (former) {{Road index, 395 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inyo County
Inyo County () is a county in the eastern central part of the U.S. state of California, located between the Sierra Nevada and the state of Nevada. In the 2020 census, the population was 19,016. The county seat is Independence. Inyo County is on the east side of the Sierra Nevada and southeast of Yosemite National Park in Central California. It contains the Owens River Valley; it is flanked to the west by the Sierra Nevada and to the east by the White Mountains and the Inyo Mountains. Mono County is to the north. With an area of , Inyo is the second-largest county by area in California, after San Bernardino County which is directly south of Inyo County. Almost half of Inyo County's area is within Death Valley National Park. However, with a population density of 1.8 people per square mile, it also has the second-lowest population density in California, after Alpine County. History Present-day Inyo county has been the historic homeland for thousands of years of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |