|
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate is a hindered phenolic antioxidant commonly used as a polymer stabiliser. Synthesis Base catalysed Michael addition of methyl acrylate to 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol forms the intermediate butyl- phloretic ester. High temperature transesterification of this with stearyl alcohol gives the final product. Applications Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate is significantly less volatile than simpler phenolic antioxidants such as butylhydroxytoluene (BHT). This makes it more suitable to stabilising plastics, as it is not driven out by the high temperatures experienced during plastic extrusion and moulding, when they are heated to 150-320 °C (300–600 °F). It is widely used in the commodity plastics, particularly in polyethylenes and polypropylene. It has approval for use in food contact materials, such as plastic food packaging in the EU and US, amongst others. It is one of the most common p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antioxidant
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals. This can lead to polymerization and other chain reactions. They are frequently added to industrial products, such as fuels and lubricants, to prevent oxidation, and to foods to prevent spoilage, in particular the rancidification of oils and fats. In cells, antioxidants such as glutathione, mycothiol or bacillithiol, and enzyme systems like superoxide dismutase, can prevent damage from oxidative stress. The only dietary antioxidants are vitamins A, C, and E, but the term ''antioxidant'' has also been applied to numerous other dietary compounds that only have antioxidant properties in vitro, with little evidence for antioxidant properties in vivo. Dietary supplements marketed as antioxidants have not been shown to maintain health or prevent disease in humans. History As part of their adaptation from marine life, terrestrial plants began producing non-marine anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer Stabiliser
Polymer stabilizers (British English: polymer stabilisers) are chemical additives which may be added to polymeric materials to inhibit or retard their degradation. Mainly they protect plastic and rubber products against heat, oxidation, and UV light. The biggest quantity of stabilizers is used for polyvinyl chloride (PVC), as the production and processing of this type of plastic would not be possible without stabilizing chemicals. Common polymer degradation processes include oxidation, UV-damage, thermal degradation, ozonolysis, combinations thereof such as photo-oxidation, as well as reactions with catalyst residues, dyes, or impurities. All of these degrade the polymer at a chemical level, via chain scission, uncontrolled recombination and cross-linking, which adversely affects many key properties such as strength, malleability, appearance and colour. Stabilizers are used at all stages of the polymer life-cycle. They allow plastic items to be produced faster and with fewer de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Addition
In organic chemistry, the Michael reaction or Michael addition is a reaction between a Michael donor (an enolate or other nucleophile) and a Michael acceptor (usually an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl) to produce a Michael adduct by creating a carbon-carbon bond at the acceptor's β-carbon. It belongs to the larger class of conjugate additions and is widely used for the mild formation of carbon-carbon bonds. The Michael addition is an important atom-economical method for diastereoselective and enantioselective C–C bond formation, and many asymmetric variants exist : In this general Michael addition scheme, either or both of R and R' on the nucleophile (the Michael donor) represent electron-withdrawing substituents such as acyl, cyano, nitro, or sulfone groups, which make the adjacent methylene hydrogen acidic enough to form a carbanion when reacted with the base, ''B:''. For the alkene (the Michael acceptor), the R" substituent is usually a carbonyl, which makes the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Acrylate
Methyl acrylate is an organic compound, more accurately the methyl ester of acrylic acid. It is a colourless liquid with a characteristic acrid odor. It is mainly produced to make acrylate fiber, which is used to weave synthetic carpets. It is also a reagent in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical intermediates. Production The standard industrial reaction for producing methyl acrylate is esterification with methanol under acid catalysis (sulfuric acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid or acidic ion exchangers.). The transesterification is facilitated because methanol and methyl acrylate form a low boiling azeotrope (boiling point 62–63 °C). The patent literature describes a one-pot route involving vapor-phase oxidation of propene or 2-propenal with oxygen in the presence of methanol. Other methods Methyl acrylate can be prepared by debromination of methyl 2,3-dibromopropanoate with zinc.F. Beilstein: ''Handbuch der organischen Chemie'', 3. Auflage, 1. Band. Verlag Leopold Voss, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2,6-di-tert-butylphenol
2,6-Di-''tert''-butylphenol is an organic compound with the structural formula 2,6-((CH3)3C)2C6H3OH. This colorless solid alkylated phenol and its derivatives are used industrially as UV stabilizers and antioxidants for hydrocarbon-based products ranging from petrochemicals to plastics. Illustrative of its usefulness, it prevents gumming in aviation fuels. Production 2,6-Di-''tert''-butylphenol is prepared industrially via the Friedel–Crafts alkylation of phenol with isobutene catalyzed by aluminium phenoxide: :C6H5OH + 2 CH2=C(CH3)2 → ((CH3)3C)2C6H3OH In this way, approximately 2.5M kg/y are produced. Applications Its dominant use is as an antioxidant. 2,6-di-''tert''-butylphenol is a precursor to more complex compounds used as antioxidants and light-protection agents for the stabilization for polymers. Of particular note is methyl-3-(3,5-di-''tert''-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)-propionate (CAS# 6386-38-5), which is formed by the Michael addition of methyl methacrylat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phloretic Acid
Phloretic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4(CH2)2CO2H. It is a white solid. The compound contains both phenol and carboxylic acid functional groups. It is sometimes called Desaminotyrosine (DAT) because it is identical to the common alpha amino acid tyrosine except for the absence of the amino functional group on the alpha carbon. Production and occurrence Phloretic acid is produced by reduction of the unsaturated side chain of p-coumaric acid. Together with phloroglucinol, it is produced by the action of the enzyme phloretin hydrolase on phloretin. It is found in olives. It is found in the rumen of sheep fed with dried grass. It is also an urinary metabolite of tyrosine in rats. Polyesters have been prepared from phloretic acid. It is one of the products of flavonoid Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word ''flavus'', meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transesterification
In organic chemistry, transesterification is the process of exchanging the organic group R″ of an ester with the organic group R' of an alcohol. These reactions are often catalyzed by the addition of an acid or base catalyst. The reaction can also be accomplished with the help of other enzymes, particularly lipases (one example is the lipase E.C.3.1.1.3). Strong acids catalyse the reaction by donating a proton to the carbonyl group, thus making it a more potent electrophile, whereas bases catalyse the reaction by removing a proton from the alcohol, thus making it more nucleophilic. If the alcohol produced by the reaction can be separated from the reactants by distillation this will drive the equilibrium toward the products, this means that esters with larger alkoxy groups can be made from methyl or ethyl esters in high purity by heating the mixture of ester, acid/base, and large alcohol. Mechanism In the transesterification mechanism, the carbonyl carbon of the starting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stearyl Alcohol
Stearyl alcohol, or 1-octadecanol, is an organic compound classified as a saturated fatty alcohol with the formula CH3(CH2)16CH2OH. It takes the form of white granules or flakes, which are insoluble in water. It has a wide range of uses as an ingredient in lubricants, resins, perfumes, and cosmetics. It is used as an emollient, emulsifier, and thickener in ointments, and is widely used as a hair coating in shampoos and hair conditioners. Stearyl heptanoate, the ester of stearyl alcohol and heptanoic acid (enanthic acid), is found in most cosmetic eyeliners. Stearyl alcohol has also found application as an evaporation suppressing monolayer when applied to the surface of water.Prime, E. L., Tran, D. N., Plazzer, M., Sunartio, D., Leung, A. H., Yiapanis, G., ... & Solomon, D. H. (2012). Rational design of monolayers for improved water evaporation mitigation. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 415, 47-58. Stearyl alcohol is prepared from steari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butylhydroxytoluene
Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), also known as dibutylhydroxytoluene, is a lipophilic organic compound, chemically a derivative of phenol, that is useful for its antioxidant properties. BHT is widely used to prevent free radical-mediated oxidation in fluids (e.g. fuels, oils) and other materials, and the regulations overseen by the U.S. F.D.A.—which considers BHT to be " generally recognized as safe"—allow small amounts to be added to foods. Despite this, and the earlier determination by the National Cancer Institute that BHT was noncarcinogenic in an animal model, societal concerns over its broad use have been expressed. BHT has also been postulated as an antiviral drug, but as of December 2022 , use of BHT as a drug is not supported by the scientific literature and it has not been approved by any drug regulatory agency for use as an antiviral. Natural occurrence Phytoplankton, including the green algae ''Botryococcus braunii'', as well as three different cyanobacteria (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
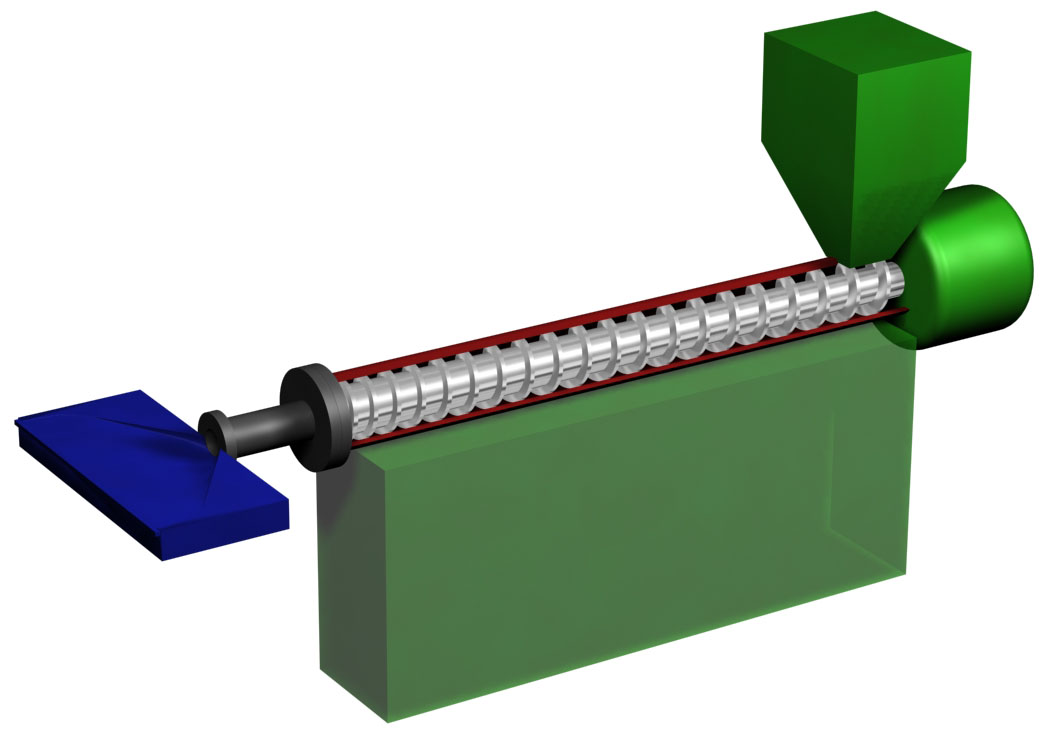
Plastic Extrusion
Plastics extrusion is a high-volume manufacturing process in which raw plastic is melted and formed into a continuous profile. Extrusion produces items such as pipe/tubing, weatherstripping, fencing, deck railings, window frames, plastic films and sheeting, thermoplastic coatings, and wire insulation. This process starts by feeding plastic material (pellets, granules, flakes or powders) from a hopper into the barrel of the extruder. The material is gradually melted by the mechanical energy generated by turning screws and by heaters arranged along the barrel. The molten polymer is then forced into a die, which shapes the polymer into a shape that hardens during cooling. History The first precursors to the modern extruder were developed in the early 19th century. In 1820, Thomas Hancock invented a rubber "masticator" designed to reclaim processed rubber scraps, and in 1836 Edwin Chaffee developed a two-roller machine to mix additives into rubber. The first thermoplastic extr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commodity Plastics
Commodity plastics or commodity polymers are plastics produced in high volumes for applications where exceptional material properties are not needed (such as packaging, food containers, and household products). In contrast to engineering plastics, commodity plastics tend to be inexpensive to produce and exhibit relatively weak mechanical properties. Some examples of commodity plastics are polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride, and poly(methyl methacrylate). Globally, the most widely used thermoplastic includes both Polypropylene and Polyethylene. Products made from commodity plastics include disposable plates, disposable cups, photographic and magnetic tape, clothing, reusable bags, medical trays, and seeding trays. Several investigations suggest that the kinetics of thermal degradation of commodity plastics is important to realize the complications it may bring because of the temperature that it goes through which includes production process or manufact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging (plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including bottles, etc.). , over 100 million tonnes of polyethylene resins are being produced annually, accounting for 34% of the total plastics market. Many kinds of polyethylene are known, with most having the chemical formula (C2H4)''n''. PE is usually a mixture of similar polymers of ethylene, with various values of ''n''. It can be ''low-density'' or ''high-density'': low-density polyethylene is extruded using high pressure () and high temperature (), while high-density polyethylene is extruded using low pressure () and low temperature (). Polyethylene is usually thermoplastic, but it can be modified to become thermosetting instead, for example, in cross-linked polyethylene. History Polyethylene was first synthesized by the German ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |