|
ORFeome
In molecular genetics, an ORFeome refers to the complete set of open reading frames (ORFs) in a genome. The term may also be used to describe a set of cloned ORFs. ORFs correspond to the protein coding sequences (CDS) of genes. ORFs can be found in genome sequences by computer programs such as GENSCAN and then amplified by PCR. While this is relatively trivial in bacteria the problem is non-trivial in eukaryotic genomes because of the presence of introns and exons as well as splice variants. Use in research The usage of complete ORFeomes reflects a new trend in biology that can be succinctly summarized as omics. ORFeomes are used for the study of protein-protein interactions, protein microarrays, the study of antigens, and other fields of study. Cloned ORFeomes Complete ORF sets have been cloned for a number of organisms including '' Brucella melitensis'', ''Chlamydia pneumoniae'', ''Escherichia coli'', ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', ''Schizosaccharomyce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Reading Frames
In molecular biology, reading frames are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible reading frames will be "open" (the "reading", however, refers to the RNA produced by transcription of the DNA and its subsequent interaction with the ribosome in translation). Such an open reading frame (ORF) may contain a start codon (usually AUG in terms of RNA) and by definition cannot extend beyond a stop codon (usually UAA, UAG or UGA in RNA). That start codon (not necessarily the first) indicates where translation may start. The transcription termination site is located after the ORF, beyond the translation stop codon. If transcription were to cease before the stop codon, an incomplete protein would be made during translation. In eukaryotic genes with multiple exons, introns are removed and exons are then joined together after transcription to yield ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Genetics
Molecular genetics is a branch of biology that addresses how differences in the structures or expression of DNA molecules manifests as variation among organisms. Molecular genetics often applies an "investigative approach" to determine the structure and/or function of genes in an organism's genome using genetic screens. The field of study is based on the merging of several sub-fields in biology: classical Mendelian inheritance, cellular biology, molecular biology, biochemistry, and biotechnology. It integrates these disciplines to explore things like genetic inheritance, gene regulation and expression, and the molecular mechanism behind various life processes. A key goal of molecular genetics is to identify and study genetic mutations. Researchers search for mutations in a gene or induce mutations in a gene to link a gene sequence to a specific phenotype. Therefore molecular genetics is a powerful methodology for linking mutations to genetic conditions that may aid th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herpesviridae
''Orthoherpesviridae'', previously named and more widely known as ''Herpesviridae'', is a large family of DNA viruses that cause infections and certain diseases in animals, including humans. The members of this family are commonly known as herpesviruses. The family name is derived from the Greek word ἕρπειν ( 'to creep'), referring to spreading cutaneous lesions, usually involving blisters, seen in flares of herpes simplex 1, herpes simplex 2 and herpes zoster ( shingles). In 1971, the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) established ''Herpesvirus'' as a genus with 23 viruses among four groups. Since then, the number of identified herpesviruses has grown to more than 100. Herpesviruses can cause both latent and lytic infections. Nine herpesvirus types are known to primarily infect humans, at least five of which are extremely widespread among most human populations, and which cause common diseases: herpes simplex 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2, also know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe, meaning that it can grow without oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
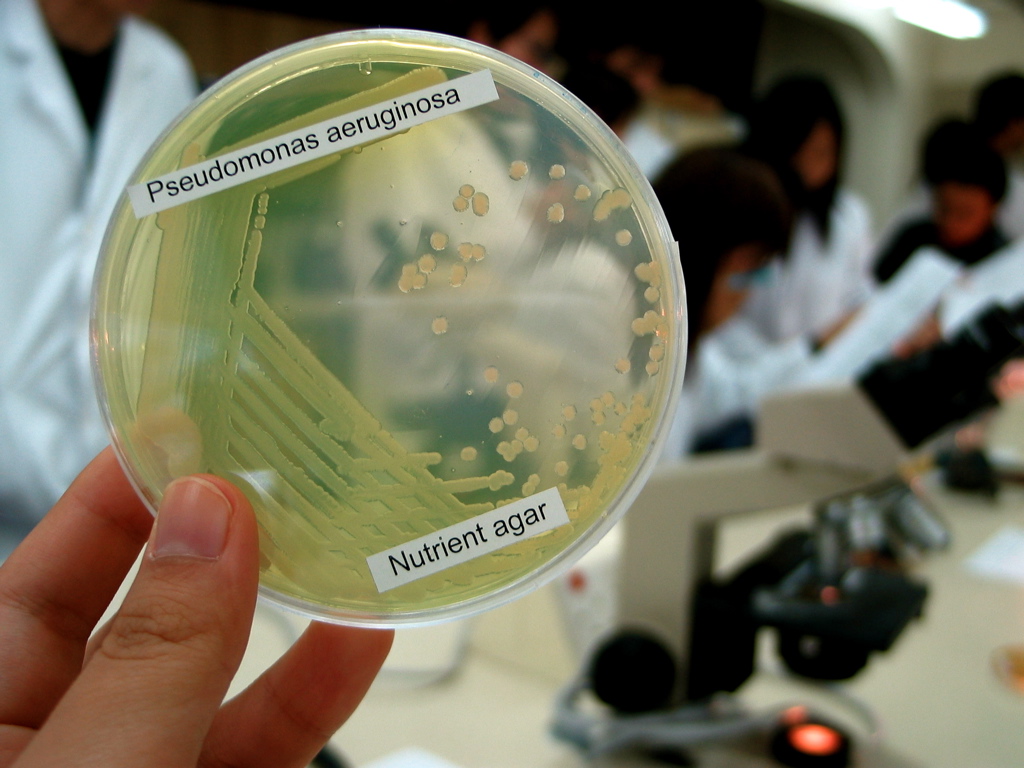
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common Bacterial capsule, encapsulated, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Aerobic organism, aerobic–facultative anaerobe, facultatively anaerobic, Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped bacteria, bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aeruginosa'' is a multiple drug resistance, multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes. ''P. aeruginosa'' is able to selectively inhibit various antibiotics from penetrating its outer membrane'' ''– and has high resistance to several antibiotics. According to the World Health Organization ''P. aeruginosa'' poses one of the greatest threats to humans in terms of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neisseria Gonorrhoeae
''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', also known as ''gonococcus'' (singular) or ''gonococci'' (plural), is a species of Gram-negative diplococci bacteria first isolated by Albert Ludwig Sigesmund Neisser, Albert Neisser in 1879. An obligate human pathogen, it primarily colonizes the mucosal lining of the urogenital tract; however, it is also capable of adhering to the mucosa of the nose, pharynx, rectum, and conjunctiva. It causes the sexually transmitted infection, sexually transmitted genitourinary infection gonorrhea as well as other forms of gonococcal disease including disseminated gonococcemia, septic arthritis, and gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum. ''N. gonorrhoeae'' is Oxidase test, oxidase positive and a microaerophile that is capable of surviving Phagocyte, phagocytosis and growing inside neutrophils. Microbiological culture, Culturing it requires carbon dioxide supplementation and enriched agar (chocolate agar) with various antibiotics (Thayer–Martin agar, Thayer–Martin). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut, where they constitute about 0.1%, along with other facultative anaerobes. These bacteria are mostly harmless or even beneficial to humans. For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by harmful pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. coli'' and humans are a type of mutualistic biological relationship—where both the humans and the ''E. coli'' are benefitting each other. ''E. coli'' is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydophila Pneumoniae
''Chlamydia'' is a genus of pathogenic Gram-negative bacteria that are obligate intracellular parasites. ''Chlamydia'' infections are the most common bacterial sexually transmitted diseases in humans and are the leading cause of infectious blindness worldwide. Humans mainly contract '' C. trachomatis'', '' C. pneumoniae'', ''C. abortus'', and '' C. psittaci''. Classification Because of ''Chlamydia''s unique developmental cycle, it was taxonomically classified in a separate order. ''Chlamydia'' is part of the order Chlamydiales, family Chlamydiaceae. ' (1999–2009) Earlier criteria for differentiation of chlamydial species did not always work well. For example, at that time '' C. psittaci'' was distinguished from '' C. trachomatis'' by sulfadiazine resistance, although not all strains identified as ''C. psittaci'' at the time were resistant, and '' C. pneumoniae'' was classified by its appearance under electron microscopy (EM) and its ability to infect humans, although the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brucella Melitensis
''Brucella melitensis'' is a Gram-negative coccobacillus bacterium from the Brucellaceae family. The bacterium causes ovine brucellosis, along with '' Brucella ovis''. Humans can become infected if they have contact with an infected animal or its byproducts. Animals acquire ''B. melitensis'' by venereal transmission. The organism is found in blood, urine, milk, and semen. It is zoonotic, unlike ''B. ovis'', causing Malta fever or localized brucellosis in humans. Clinical manifestation The bacterium causes severe inflammation of the epididymis, with formation of spermatoceles and fibrinous adhesions. This disease is known as ovine brucellosis, and is a reportable disease in the USA. In goats and sheep, ''B. melitensis'' can cause abortion, stillbirth, and weak offspring for the first gestation after the animal is infected. Mastitis can happen, but is uncommon. The infection can also reduce milk yield by at least 10%. The placenta might also be retained, and the animal can suff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Microarray
A protein microarray (or protein chip) is a high-throughput method used to track the interactions and activities of proteins, and to determine their function, and determining function on a large scale. Its main advantage lies in the fact that large numbers of proteins can be tracked in parallel. The chip consists of a support surface such as a glass slide, nitrocellulose membrane, bead, or microtitre plate, to which an array of capture proteins is bound. Probe molecules, typically labeled with a fluorescent dye, are added to the array. Any reaction between the probe and the immobilised protein emits a fluorescent signal that is read by a laser scanner. Protein microarrays are rapid, automated, economical, and highly sensitive, consuming small quantities of samples and reagents. The concept and methodology of protein microarrays was first introduced and illustrated in antibody microarrays (also referred to as antibody matrix) in 1983 in a scientific publication and a series of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omics
Omics is the collective characterization and quantification of entire sets of biological molecules and the investigation of how they translate into the structure, function, and dynamics of an organism or group of organisms. The branches of science known informally as ''omics'' are various disciplines in biology whose names end in the suffix ''wikt:-omics, -omics'', such as genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, metagenomics, phenomics and transcriptomics. The related suffix -ome is used to address the objects of study of such fields, such as the genome, proteome or metabolome respectively. The suffix ''-ome'' as used in molecular biology refers to a ''totality'' of some sort; it is an example of a "neo-suffix" formed by abstraction from various Greek terms in , a sequence that does not form an identifiable suffix in Greek. Functional genomics aims at identifying the functions of as many genes as possible of a given organism. It combines different -omics techniques such as transcr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Splicing
Alternative splicing, alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative RNA splicing, splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to produce different splice variants. For example, some exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final RNA product of the gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different splice variants. In the case of protein-coding genes, the proteins translated from these splice variants may contain differences in their amino acid sequence and in their biological functions (see Figure). Biologically relevant alternative splicing occurs as a normal phenomenon in eukaryotes, where it increases the number of proteins that can be encoded by the genome. In humans, it is widely believed that ~95% of multi-exonic genes are alternatively spliced to produce functional alternative products from the same gene but many scientists believe that most of the observed splice variants ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |