|
Non-fermenter
Non-fermenters (also non-fermenting bacteria) are a taxonomically heterogeneous group of bacteria of the phylum Pseudomonadota that cannot Catabolism, catabolize glucose, and are thus unable to fermentation (biochemistry), ferment. This does not necessarily exclude that species can catabolize other sugars or have anaerobiosis like fermenting bacteria. The coccoid or bacillary bacteria can be found in soil or wet areas. They are non-spore, sporulating bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative. Some species are also pathogenic for humans, so their detection (e.g. with analytical profile index 20 NE) has great relevance in the diagnosis of bacterial infections. List of non-fermenters * ''Acinetobacter'' * ''Alcaligenes'' * ''Bordetella'' * ''Burkholderia'' * ''Legionella'' * ''Moraxella'' * ''Pseudomonas'' *''Shewanella'' * ''Stenotrophomonas'' Also, pathogenic species include ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' and ''Moraxella catarrhalis''. References *Kayser et al. (2005): ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcaligenes
''Alcaligenes'' is a genus of Gram-negative, Aerobic organism, aerobic, Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped bacteria. The species are motile with amphitrichous flagella and rarely nonmotile. It is a genus of Non-fermenter, non-fermenting bacteria (in the family Alcaligenaceae). Additionally, some strains of ''Alcaligenes'' are capable of anaerobic respiration, but they must be in the presence of nitrate or nitrite; otherwise, their metabolism is respiratory and never fermentative; The genus does not use Carbohydrate, carbohydrates. Strains of ''Alcaligene''s (such as ''A. faecalis'') are found mostly in the Gastrointestinal tract, intestinal tracts of Vertebrate, vertebrates, decaying materials, dairy products, water, and soil; they can be isolated from human respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts and wounds in hospitalized patients with compromised immune systems. They are occasionally the cause of opportunistic infections, including Sepsis, nosocomial sepsis. ''Alcaligenes faecalis'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermentation (biochemistry)
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food production, it may more broadly refer to any process in which the activity of microorganisms brings about a desirable change to a foodstuff or beverage. The science of fermentation is known as zymology. In microorganisms, fermentation is the primary means of producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the degradation of organic nutrients anaerobically. Humans have used fermentation to produce foodstuffs and beverages since the Neolithic age. For example, fermentation is used for preservation in a process that produces lactic acid found in such sour foods as pickled cucumbers, kombucha, kimchi, and yogurt, as well as for producing alcoholic beverages such as wine and beer. Fermentation also occurs within the gastrointestinal tracts of all an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burkholderia
''Burkholderia'' is a genus of Pseudomonadota whose pathogenic members include the ''Burkholderia cepacia'' complex, which attacks humans and ''Burkholderia mallei'', responsible for glanders, a disease that occurs mostly in horses and related animals; ''Burkholderia pseudomallei'', causative agent of melioidosis; and '' Burkholderia cepacia'', an important pathogen of pulmonary infections in people with cystic fibrosis (CF). ''Burkholderia'' species is also found marine environment. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and characterized ''Burkholderia cepacia'' from marine sponges of the Saint Martin's Island of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh. The ''Burkholderia'' (previously part of ''Pseudomonas'') genus name refers to a group of virtually ubiquitous Gram-negative, obligately aerobic, rod-shaped bacteria that are motile by means of single or multiple polar flagella, with the exception of ''Burkholderia mallei'', which is nonmotile. Members belonging to the genus do not produce s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
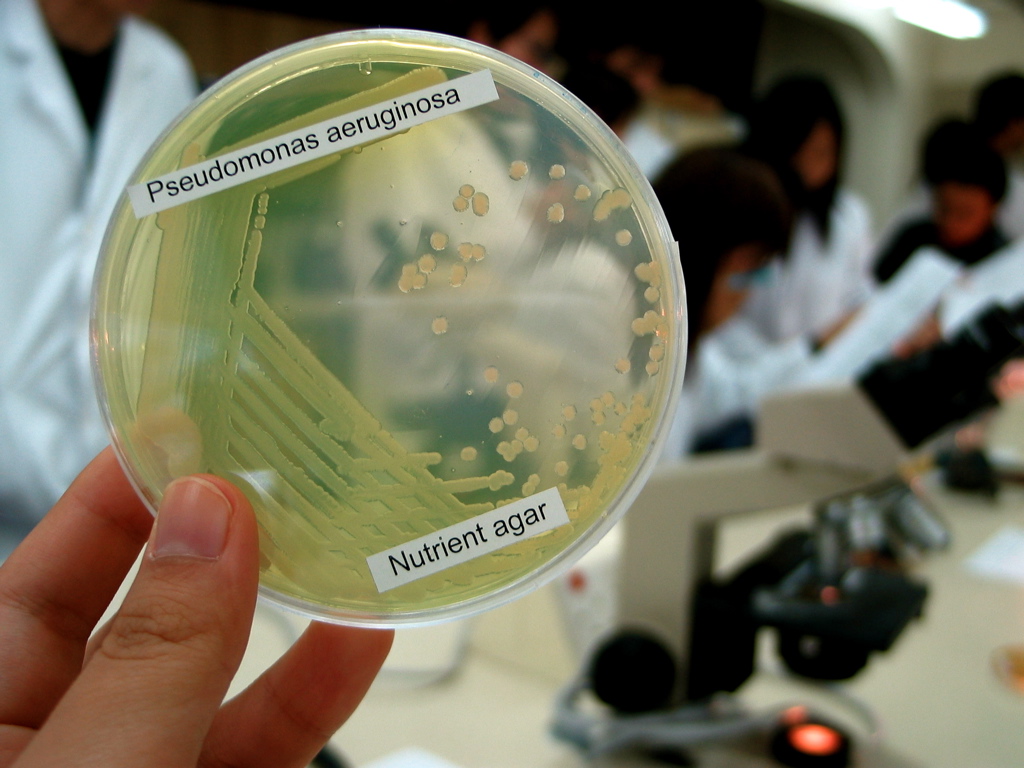
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic–facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aeruginosa'' is a multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes. The organism is considered opportunistic insofar as serious infection often occurs during existing diseases or conditions – most notably cystic fibrosis and traumatic burns. It generally affects the immunocompromised but can also infect the immunocompetent as in hot tub folliculitis. Treatment of ''P. aeruginosa'' infections can be difficult due to its natural resistance to antibiotics. When more advanced antibiotic drug regimens are needed adverse effects may re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stenotrophomonas
''Stenotrophomonas'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, comprising at least ten species. The main reservoirs of Stenotrophomonas are soil and plants. ''Stenotrophomonas'' species range from common soil organisms (''S. nitritireducens'') to opportunistic human pathogens ('' S. maltophilia''); the molecular taxonomy of the genus is still somewhat unclear. Importance The most common species, ''S. maltophilia'' is very versatile and can be beneficial for plant growth and health, can be used in agriculture, biocontrol, bioremediation and phytoremediation strategies as well as the production of biomolecules of economic value. On the other hand, some of '' S. maltophilia'' strains are pathogenic to humans with multidrug resistant profile. ''S. indologenes'' can also cause or be part of polymicrobial infections in humans, especially small children. ''Stenotrophomonas'' can also be phytopathogenic unlike closely related genera '' Xylella'' and ''Xanthomonas''. Members of the genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shewanella
''Shewanella'' is the sole genus included in the marine bacteria family Shewanellaceae. Some species within it were formerly classed as ''Alteromonas''. ''Shewanella'' consists of facultatively anaerobic Gram-negative rods, most of which are found in extreme aquatic habitats where the temperature is very low and the pressure is very high. ''Shewanella'' bacteria are a normal component of the surface flora of fish and are implicated in fish spoilage. ''Shewanella chilikensis'', a species of the genus ''Shewanella'' commonly found in the marine sponges of Saint Martin's Island of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh. ''Shewanella oneidensis'' MR-1 is a widely used laboratory model to study anaerobic respiration of metals and other anaerobic extracellular electron acceptors, and for teaching about microbial electrogenesis and microbial fuel cells. Biochemical characteristics of ''Shewanella'' species Colony, morphological, physiological, and biochemical characteristics of ''Shewanell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonas
''Pseudomonas'' is a genus of Gram-negative, Gammaproteobacteria, belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae and containing 191 described species. The members of the genus demonstrate a great deal of metabolic diversity and consequently are able to colonize a wide range of niches. Their ease of culture ''in vitro'' and availability of an increasing number of ''Pseudomonas'' strain genome sequences has made the genus an excellent focus for scientific research; the best studied species include ''P. aeruginosa'' in its role as an opportunistic human pathogen, the plant pathogen '' P. syringae'', the soil bacterium '' P. putida'', and the plant growth-promoting ''P. fluorescens, P. lini, P. migulae'', and ''P. graminis''. Because of their widespread occurrence in water and plant seeds such as dicots, the pseudomonads were observed early in the history of microbiology. The generic name ''Pseudomonas'' created for these organisms was defined in rather vague terms by Walter Migula i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moraxella
''Moraxella'' is a genus of gram-negative bacteria in the family Moraxellaceae. It is named after the Swiss ophthalmologist Victor Morax. The organisms are short rods, coccobacilli, or as in the case of ''Moraxella catarrhalis'', diplococci in morphology, with asaccharolytic, oxidase-positive, and catalase-positive properties.Ala'Aldeen, D. A. A. (2007). "Neisseria and moraxella". In Greenwood, David; Slack, Richard; Peitherer, John; & Barer, Mike (Eds.), ''Medical Microbiology'' (17th ed.), p. 258. Elsevier. . ''M. catarrhalis'' is the clinically most important species under this genus. Roles in disease The organisms are commensals of mucosal surfaces and sometimes give rise to opportunistic infection. * ''M. catarrhalis'' usually resides in respiratory tract, but can gain access to the lower respiratory tract in patients with chronic chest disease or compromised host defenses, thus causing tracheobronchitis and pneumonia. For example, it causes a significant proportion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legionella
''Legionella'' is a genus of pathogenic gram-negative bacteria that includes the species '' L. pneumophila'', causing legionellosis (all illnesses caused by ''Legionella'') including a pneumonia-type illness called Legionnaires' disease and a mild flu-like illness called Pontiac fever. ''Legionella'' may be visualized with a silver stain or cultured in cysteine-containing media such as buffered charcoal yeast extract agar. It is common in many environments, including soil and aquatic systems, with at least 50 species and 70 serogroups identified. These bacteria, however, are not transmissible from person to person; furthermore, most people exposed to the bacteria do not become ill. Most outbreaks are traced to poorly maintained cooling towers. The side chains of the cell wall carry the bases responsible for the somatic antigen specificity of these organisms. The chemical composition of these side chains both with respect to components and arrangement of the different sugars de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bordetella
''Bordetella'' () is a genus of small (0.2 – 0.7 µm), gram-negative coccobacilli of the phylum Pseudomonadota. ''Bordetella'' species, with the exception of '' B. petrii'', are obligate aerobes, as well as highly fastidious, or difficult to culture. All species can infect humans. The first three species to be described ('' B. pertussis'', '' B. parapertussis'', '' B. bronchiseptica''); are sometimes referred to as the 'classical species'. Two of these (''B. bronchiseptica'' and ''B. pertussis'') are also motile. ''B. pertussis'' and occasionally ''B. parapertussis'' cause pertussis or whooping cough in humans, and some ''B. parapertussis'' strains can colonise sheep. ''B. bronchiseptica'' rarely infects healthy humans, though disease in immunocompromised patients has been reported. ''B. bronchiseptica'' causes several diseases in other mammals, including kennel cough and atrophic rhinitis in dogs and pigs, respectively. Other members of the genus cause similar diseases in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonadota
Pseudomonadota (synonym Proteobacteria) is a major phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. The renaming of phyla in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier names of long standing in the literature. The phylum Proteobacteria includes a wide variety of pathogenic genera, such as ''Escherichia'', '' Salmonella'', ''Vibrio'', ''Yersinia'', ''Legionella'', and many others.Slonczewski JL, Foster JW, Foster E. Microbiology: An Evolving Science 5th Ed. WW Norton & Company; 2020. Others are free-living (nonparasitic) and include many of the bacteria responsible for nitrogen fixation. Carl Woese established this grouping in 1987, calling it informally the "purple bacteria and their relatives". Because of the great diversity of forms found in this group, it was later informally named Proteobacteria, after Proteus, a Greek god of the sea capable of assuming many different shapes (not after the Proteobacteria genus ''Proteus''). In 2021 the Internat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |