|
Nieuwe Kerk (The Hague)
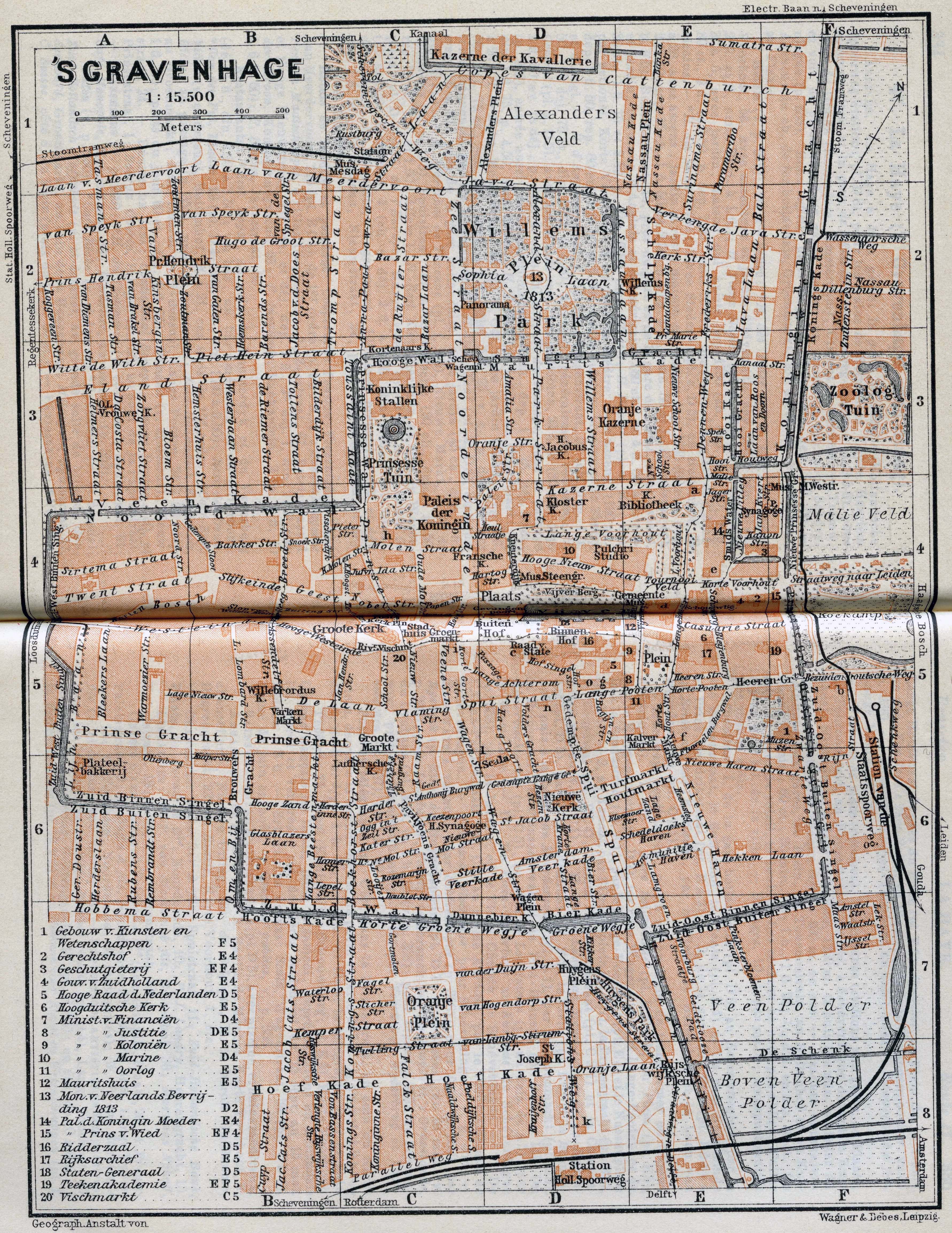
The Nieuwe Kerk (; en, New Church) is a Dutch Baroque Protestant church in The Hague, located across from the modern city hall on the Spui. It was built in 1649 after the Great Church had become too small. Construction was completed in 1656. History The church was designed by the architect Peter Noorwits, Rijksmonument report who was assisted by the painter and architect Bartholomeus van Bassen. The church is considered a highlight of the early Protestant church architecture in the Netherlands. Like many churches of that time was the New Church, a central building. Unlike other central building, the church is no simple circular or multifaceted plan but there is a space of two octagonal sections which are connected by a slightly smaller proportion in which the pulpit was prepared. The Dutch Baroque architecture of the church shows elements of both Renaissance and Classicism. Two church bells by Coenraat Wegewaert in 1656 hang in their original bell-chairs, 100,2 cm and 81, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nieuwe Kerk, The Hague (DSCF1312)
The Nieuwe Kerk (; en, New Church) is a Dutch Baroque architecture, Dutch Baroque Protestantism in the Netherlands, Protestant Church (building), church in The Hague, located across from the The Hague City Hall, modern city hall on the Spui (The Hague), Spui. It was built in 1649 after the Grote of Sint-Jacobskerk (The Hague), Great Church had become too small. Construction was completed in 1656. History The church was designed by the architect Peter Noorwits,Rijksmonument report who was assisted by the painter and architect Bartholomeus van Bassen. The church is considered a highlight of the early Protestant church architecture in the Netherlands. Like many churches of that time was the New Church, a central building. Unlike other central building, the church is no simple circular or multifaceted plan but there is a space of two octagonal sections which are connected by a slightly smaller proportion in which the pulpit was prepared. The Dutch Baroque architecture of the church ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Duyschot
Johannes is a Medieval Latin form of the personal name that usually appears as "John" in English language contexts. It is a variant of the Greek and Classical Latin variants (Ιωάννης, ''Ioannes''), itself derived from the Hebrew name '' Yehochanan'', meaning "Yahweh is gracious". The name became popular in Northern Europe, especially in Germany because of Christianity. Common German variants for Johannes are ''Johann'', ''Hannes'', '' Hans'' (diminutized to ''Hänschen'' or ''Hänsel'', as known from "''Hansel and Gretel''", a fairy tale by the Grimm brothers), '' Jens'' (from Danish) and ''Jan'' (from Dutch, and found in many countries). In the Netherlands, Johannes was without interruption the most common masculine birth name until 1989. The English equivalent for Johannes is John. In other languages *Joan, Jan, Gjon, Gjin and Gjovalin in Albanian *'' Yoe'' or '' Yohe'', uncommon American form''Dictionary of American Family Names'', Oxford University Press, 2013. *Yaḥy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestant Churches In The Netherlands
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to be growing errors, abuses, and discrepancies within it. Protestantism emphasizes the Christian believer's justification by God in faith alone (') rather than by a combination of faith with good works as in Catholicism; the teaching that salvation comes by divine grace or "unmerited favor" only ('); the priesthood of all faithful believers in the Church; and the ''sola scriptura'' ("scripture alone") that posits the Bible as the sole infallible source of authority for Christian faith and practice. Most Protestants, with the exception of Anglo-Papalism, reject the Catholic doctrine of papal supremacy, but disagree among themselves regarding the number of sacraments, the real presence of Christ in the Eucharist, and matters of ecclesiastical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octagonal Churches
In geometry, an octagon (from the Greek ὀκτάγωνον ''oktágōnon'', "eight angles") is an eight-sided polygon or 8-gon. A '' regular octagon'' has Schläfli symbol and can also be constructed as a quasiregular truncated square, t, which alternates two types of edges. A truncated octagon, t is a hexadecagon, . A 3D analog of the octagon can be the rhombicuboctahedron with the triangular faces on it like the replaced edges, if one considers the octagon to be a truncated square. Properties of the general octagon The sum of all the internal angles of any octagon is 1080°. As with all polygons, the external angles total 360°. If squares are constructed all internally or all externally on the sides of an octagon, then the midpoints of the segments connecting the centers of opposite squares form a quadrilateral that is both equidiagonal and orthodiagonal (that is, whose diagonals are equal in length and at right angles to each other).Dao Thanh Oai (2015), "Equilater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherlandish Baroque Art
The Low Countries comprise the coastal Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta region in Western Europe, whose definition usually includes the modern countries of Luxembourg, Belgium and the Netherlands. Both Belgium and the Netherlands derived their names from earlier names for the region, due to ''nether'' meaning "low" and ''Belgica'' being the Latinized name for all the Low Countries, a nomenclature that became obsolete after Belgium's secession in 1830. The Low Countries—and the Netherlands and Belgium—had in their history exceptionally many and widely varying names, resulting in equally varying names in different languages. There is diversity even within languages: the use of one word for the country and another for the adjective form is common. This holds for English, where ''Dutch'' is the adjective form for the country "the Netherlands". Moreover, many languages have the same word for both the country of the Netherlands and the region of the Low Countries, e.g., French (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churches In The Hague
Church may refer to: Religion * Church (building), a building for Christian religious activities * Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination * Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship * Christian denomination, a Christian organization with distinct doctrine and practice * Christian Church, either the collective body of all Christian believers, or early Christianity Places United Kingdom * Church (Liverpool ward), a Liverpool City Council ward * Church (Reading ward), a Reading Borough Council ward * Church (Sefton ward), a Metropolitan Borough of Sefton ward * Church, Lancashire, England United States * Church, Iowa, an unincorporated community * Church Lake, a lake in Minnesota Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Church magazine'', a pastoral theology magazine published by the National Pastoral Life Center Fictional entities * Church (Red vs. Blue), Church (''Red vs. Blue''), a fictional character in the video web series '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings Of The Dutch Golden Age
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque Church Buildings
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including the Iberian Peninsula it continued, together with new styles, until the first decade of the 19th century. It followed Renaissance art and Mannerism and preceded the Rococo (in the past often referred to as "late Baroque") and Neoclassical styles. It was encouraged by the Catholic Church as a means to counter the simplicity and austerity of Protestant architecture, art, and music, though Lutheran Baroque art developed in parts of Europe as well. The Baroque style used contrast, movement, exuberant detail, deep colour, grandeur, and surprise to achieve a sense of awe. The style began at the start of the 17th century in Rome, then spread rapidly to France, northern Italy, Spain, and Portugal, then to Austria, southern Germany, and Russia. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque Architecture In The Netherlands
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including the Iberian Peninsula it continued, together with new styles, until the first decade of the 19th century. It followed Renaissance art and Mannerism and preceded the Rococo (in the past often referred to as "late Baroque") and Neoclassical styles. It was encouraged by the Catholic Church as a means to counter the simplicity and austerity of Protestant architecture, art, and music, though Lutheran Baroque art developed in parts of Europe as well. The Baroque style used contrast, movement, exuberant detail, deep colour, grandeur, and surprise to achieve a sense of awe. The style began at the start of the 17th century in Rome, then spread rapidly to France, northern Italy, Spain, and Portugal, then to Austria, southern Germany, and Russia. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |