|
Niederhaslach Church
The Roman Catholic Parish church Saint John the Baptist (french: Église paroissiale Saint-Jean Baptiste), formerly Collegiate church Saint Florentius (''Collégiale Saint-Florent'') is the main church of the small city of Niederhaslach in Alsace. The building is widely considered one of the finest and most ornate examples of Gothic architecture and Gothic art in the Bas-Rhin departement of France.''HB Kunstführer Straßburg - Colmar - Elsaß'', 1986, History The church, which was originally dedicated to Florentius of Strasbourg, bishop of Strasbourg from 618–624, was built from 1274 on as a replacement for a building from the 7th century that had been the shrine since 810 (by order of bishop Ratho) of relics of the Saint. The new church was under construction until 1385: a fire on 4 June 1287 that destroyed everything but the choir as well as the accidental death of the architect Gerlach von Steinbach (the son of Erwin von Steinbach) in 1330 had slowed down its complet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niederhaslach
Niederhaslach is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. It is noteworthy for its Gothic 13th-15th century Niederhaslach Church. See also * Oberhaslach, a neighbouring commune * Communes of the Bas-Rhin department The following is a list of the 514 communes of the Bas-Rhin department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Communes of Bas-Rhin Bas-Rhin communes articles needing translation from French Wikipedia {{BasRhin-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relic
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains of a saint or the personal effects of the saint or venerated person preserved for purposes of veneration as a tangible memorial. Relics are an important aspect of some forms of Buddhism, Christianity, Islam, shamanism, and many other religions. ''Relic'' derives from the Latin ''reliquiae'', meaning "remains", and a form of the Latin verb ''relinquere'', to "leave behind, or abandon". A reliquary is a shrine that houses one or more religious relics. In classical antiquity In ancient Greece, a city or sanctuary might claim to possess, without necessarily displaying, the remains of a venerated hero as a part of a hero cult. Other venerable objects associated with the hero were more likely to be on display in sanctuaries, such as spears, shields, or other weaponry; chariots, ships or figureheads; furniture such as chairs or tripods; and clothing. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strasbourg Cathedral
Strasbourg Cathedral or the Cathedral of Our Lady of Strasbourg (french: Cathédrale Notre-Dame de Strasbourg, or ''Cathédrale de Strasbourg'', german: Liebfrauenmünster zu Straßburg or ''Straßburger Münster''), also known as Strasbourg Minster, is a Catholic cathedral in Strasbourg, Alsace, France. Although considerable parts of it are still in Romanesque architecture, it is widely consideredSusan Bernstein''Goethe's Architectonic Bildung and Buildings in Classical Weimar'' The Johns Hopkins University Press to be among the finest examples of Rayonnant Gothic architecture. Architect Erwin von Steinbach is credited for major contributions from 1277 to his death in 1318, and beyond through his son Johannes von Steinbach, and his grandson Gerlach von Steinbach, who succeeded him as chief architects. The Steinbachs's plans for the completion of the cathedral were not followed through by the chief architects who took over after them, and instead of the originally envisioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stained Glass
Stained glass is coloured glass as a material or works created from it. Throughout its thousand-year history, the term has been applied almost exclusively to the windows of churches and other significant religious buildings. Although traditionally made in flat panels and used as windows, the creations of modern stained glass artists also include three-dimensional structures and sculpture. Modern vernacular usage has often extended the term "stained glass" to include domestic lead light and '' objets d'art'' created from foil glasswork exemplified in the famous lamps of Louis Comfort Tiffany. As a material ''stained glass'' is glass that has been coloured by adding metallic salts during its manufacture, and usually then further decorating it in various ways. The coloured glass is crafted into ''stained glass windows'' in which small pieces of glass are arranged to form patterns or pictures, held together (traditionally) by strips of lead and supported by a rigid frame. Pai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Ministry Of Culture
The Ministry of Culture (french: Ministère de la Culture) is the ministry of the Government of France in charge of national museums and the . Its goal is to maintain the French identity through the promotion and protection of the arts (visual, plastic, theatrical, musical, dance, architectural, literary, televisual and cinematographic) on national soil and abroad. Its budget is mainly dedicated to the management of the (six national sites and hundred decentralised storage facilities) and the regional (culture centres). Its main office is in the in the 1st arrondissement of Paris on the . It is headed by the Minister of Culture, a cabinet member. The current officeholder has been since 20 May 2022. History Deriving from the Italian and Burgundian courts of the Renaissance, the notion that the state had a key role to play in the sponsoring of artistic production and that the arts were linked to national prestige was found in France from at least the 16th century on. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Les Dernières Nouvelles D'Alsace
''Les Dernières Nouvelles d'Alsace'', commonly known as ''DNA'', is a regional daily French newspaper covering the Alsace region. History and profile ''DNA'' was created in November 1877 as ''Neueste Nachrichten'' by German Heinrich Ludwig Kayser. It is part of East Burgundy group Rhone Alpes (EBRA), formerly France or East Media Group Est Républicain. Its principal owner is the press trust of the French bank Crédit Mutuel. Its headquarters is located at 17 rue de la Nuée-Bleue in Strasbourg since 13 July 1891. The ''DNA'' employs about 850 staff and 200 journalists in the Upper Rhine and Lower Rhine The Lower Rhine (german: Niederrhein; kilometres 660 to 1,033 of the river Rhine) flows from Bonn, Germany, to the North Sea at Hook of Holland, Netherlands (including the Nederrijn or "Nether Rhine" within the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta); al .... In 1995, it became the first French daily newspaper to have online presence. Its daily circulation in December 2009 was 180,0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Émile Boeswillwald
Émile Boeswillwald (2 February 1815 – 20 March 1896) was a French architect. He succeeded Prosper Mérimée as Inspector General of Historic Monuments and collaborated with Eugène Viollet-le-Duc. Life Emile Boeswillwald born in Strasbourg on 2 February 1815. He learned the trade of stonemason, continuing his apprenticeship in Munich in 1836. He then studied architecture in the workshop of Henri Labrouste and at the École des Beaux-Arts in 1837. Boeswillwald exhibited at the Salons of 1839, 1841, 1842, 1844 and 1855. In 1860 he was appointed inspector general of historical monuments. He thus became a member of the committee on historical monuments and the Council of Civil Buildings. In 1864 land was purchased beside the Villa Eugénie in Biarritz on which to erect a chapel designed by Boeswillwald. The chapel, dedicated to Our Lady of Guadeloupe, was consecrated in September 1865. It incorporated an eclectic mix of Roman and Byzantine art with Hispano-Moorish elements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chapter (religion)
A chapter ( la, capitulum or ') is one of several bodies of clergy in Roman Catholic, Old Catholic, Anglican, and Nordic Lutheran churches or their gatherings. Name The name derives from the habit of convening monks or canons for the reading of a chapter of the Bible or a heading of the order's rule. The 6th-century St Benedict directed that his monks begin their daily assemblies with such readings and over time expressions such as "coming together for the chapter" (') found their meaning transferred from the text to the meeting itself and then to the body gathering for it. The place of such meetings similarly became known as the "chapter house" or "room". Cathedral chapter A cathedral chapter is the body ("college") of advisors assisting the bishop of a diocese at the cathedral church. These were a development of the presbyteries (') made up of the priests and other church officials of cathedral cities in the early church. In the Catholic Church, they are n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ideas are considered fundamental principles of liberal democracy, while phrases like ''liberté, égalité, fraternité'' reappeared in other revolts, such as the 1917 Russian Revolution, and inspired campaigns for the abolitionism, abolition of slavery and universal suffrage. The values and institutions it created dominate French politics to this day. Its Causes of the French Revolution, causes are generally agreed to be a combination of social, political and economic factors, which the ''Ancien Régime'' proved unable to manage. In May 1789, widespread social distress led to the convocation of the Estates General of 1789, Estates General, which was converted into a National Assembly (French Revolution), National Assembly in June. Contin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slaughterhouse
A slaughterhouse, also called abattoir (), is a facility where animals are slaughtered to provide food. Slaughterhouses supply meat, which then becomes the responsibility of a packaging facility. Slaughterhouses that produce meat that is not intended for human consumption are sometimes referred to as ''knacker's yards'' or ''knackeries''. This is where animals are slaughtered that are not fit for human consumption or that can no longer work on a farm, such as retired work horses. Slaughtering animals on a large scale poses significant issues in terms of logistics, animal welfare, and the environment, and the process must meet public health requirements. Due to public aversion in different cultures, determining where to build slaughterhouses is also a matter of some consideration. Frequently, animal rights groups raise concerns about the methods of transport to and from slaughterhouses, preparation prior to slaughter, animal herding, and the killing itself. History Until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle, famine, and disease, while some areas of what is now modern Germany experienced population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. Until the 20th century, historians generally viewed it as a continuation of the religious struggle initiated by the 16th-century Reformation within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg attempted to resolve this by dividing the Empire into Lutheran and Catholic states, but over the next 50 years the expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries destabilised the settlement. While most modern commentators accept differences over religion and Imperial authority were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
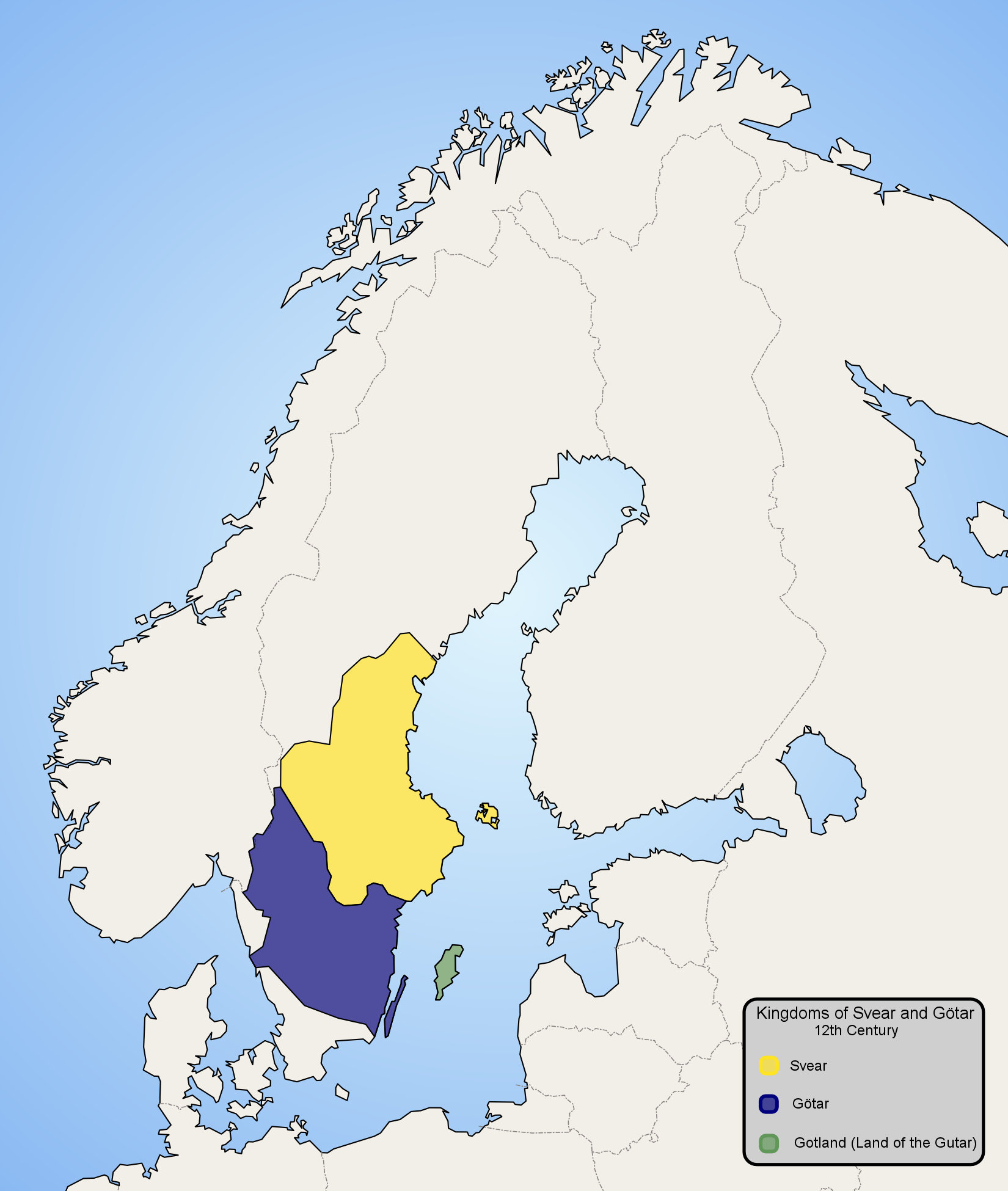
Swedes
Swedes ( sv, svenskar) are a North Germanic ethnic group native to the Nordic region, primarily their nation state of Sweden, who share a common ancestry, culture, history and language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countries, in particular Finland where they are an officially recognized minority, with a substantial diaspora in other countries, especially the United States. Etymology The English term "Swede" has been attested in English since the late 16th century and is of Middle Dutch or Middle Low German origin. In Swedish, the term is ''svensk'', which is from the name of '' svear'' (or Swedes), the people who inhabited Svealand in eastern central Sweden, and were listed as ''Suiones'' in Tacitus' history '' Germania'' from the first century AD. The term is believed to have been derived from the Proto-Indo-European reflexive pronominal root, , as the Latin ''suus''. The word must have meant "one's own (tribesmen)". The same root and original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)