|
Na H-Eileanan Siar
The Outer Hebrides () or Western Isles ( gd, Na h-Eileanan Siar or or ("islands of the strangers"); sco, Waster Isles), sometimes known as the Long Isle/Long Island ( gd, An t-Eilean Fada, links=no), is an island chain off the west coast of mainland Scotland. The islands are geographically coextensive with , one of the 32 unitary council areas of Scotland. They form part of the archipelago of the Hebrides, separated from the Scottish mainland and from the Inner Hebrides by the waters of the Minch, the Little Minch, and the Sea of the Hebrides. Scottish Gaelic is the predominant spoken language, although in a few areas English speakers form a majority. Most of the islands have a bedrock formed from ancient metamorphic rocks, and the climate is mild and oceanic. The 15 inhabited islands have a total population of and there are more than 50 substantial uninhabited islands. The distance from Barra Head to the Butt of Lewis is roughly . There are various important preh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clisham
, photo = View east south east from An Cliseam - geograph.org.uk - 1580282.jpg , photo_size = , photo_upright = , photo_alt = , photo_caption = , highest = , highest_location = , elevation = , elevation_ref = , prominence = , prominence_ref = , isolation = , isolation_ref = , listing = , coordinates = , coordinates_ref = , length = , length_ref = , etymology = , nickname = , native_name = , translation = Rocky cliff , pronunciation = , authority = Na h-Eileanan an Iar , location = Isle of Harris, Outer Hebrides , country = Scotland, United Kingdom , grid_ref_UK = NB154073 , first_ascent = , easiest_route = , normal_route ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome known as the Greco-Roman world. It is the period in which both Greek and Roman societies flourished and wielded huge influence throughout much of Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia. Conventionally, it is taken to begin with the earliest-recorded Epic Greek poetry of Homer (8th–7th-century BC), and continues through the emergence of Christianity (1st century AD) and the fall of the Western Roman Empire (5th-century AD). It ends with the decline of classical culture during late antiquity (250–750), a period overlapping with the Early Middle Ages (600–1000). Such a wide span of history and territory covers many disparate cultures and periods. ''Classical antiquity'' may also refer to an idealized vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
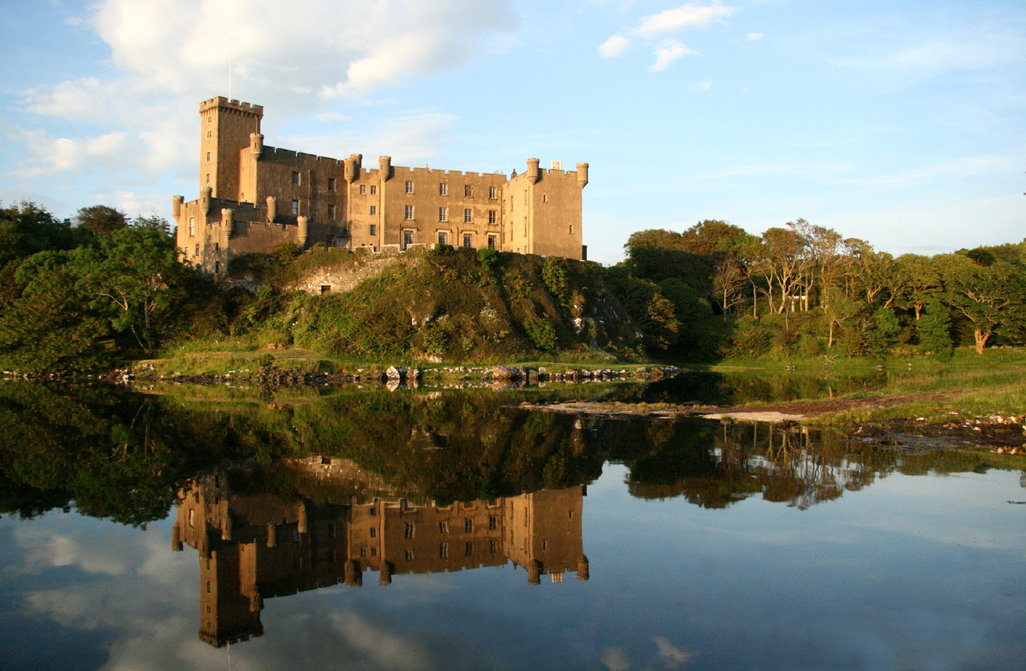
Lewis And Harris
Lewis and Harris ( gd, Leòdhas agus na Hearadh, sco, Lewis an Harris), or Lewis with Harris, is a single Scottish island in the Outer Hebrides, divided by mountains. It is the largest island in Scotland and the third largest in the British Isles, after Great Britain and the island of Ireland, with an area of , which is approximately 1% of the area of Great Britain. The northern two-thirds is called Lewis and the southern third Harris; each is frequently referred to as if it were a separate island. Etymology The island does not have a one-word name in either English or Scottish Gaelic, and is referred to as "Lewis and Harris", "Lewis with Harris", "Harris with Lewis" etc. Rarely used is the collective name of "the Long Island" ( gd, an t-Eilean Fada), although that epithet is sometimes applied to the entire archipelago of the Outer Hebrides, including the Uist group of islands and Barra. Geography Lewis–Harris boundary The boundary between Lewis and Harris runs fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Uist
South Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Deas, ; sco, Sooth Uist) is the second-largest island of the Outer Hebrides in Scotland. At the 2011 census, it had a usually resident population of 1,754: a decrease of 64 since 2001. The island, in common with the rest of the Hebrides, is one of the last remaining strongholds of the Gaelic language in Scotland. South Uist's inhabitants are known in Gaelic as ''Deasaich'' (Southerners). The population is about 90% Roman Catholic. The island is home to a nature reserve and a number of sites of archaeological interest, including the only location in the British Isles where prehistoric mummies have been found. In the northwest, there is a missile testing range. In 2006 South Uist, together with neighbouring Benbecula and Eriskay, was involved in Scotland's biggest-ever community land buyout by Stòras Uibhist. The group also owns the "biggest community wind farm in Scotland", Lochcarnan, on South Uist which opened in 2013. Geology In common with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Designation
A conservation designation is a name and/or acronym which explains the status of an area of land in terms of conservation or protection. Examples United Kingdom *Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) * Environmentally sensitive area * Local nature reserve (LNR) * Marine nature reserve (MNR) * National nature reserve (NNR) * National scenic area (NSA) *Nitrate vulnerable zone (NVZ) *Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) For a comprehensive list, see Conservation in the United Kingdom European Union *Special Area of Conservation *Special Protection Area United States Wildlands Project Multi-national *Under the Berne Convention ** Areas of Special Conservation Interest (ASCI) * Ramsar site A Ramsar site is a wetland site designated to be of international importance under the Ramsar Convention,8 ha (O) *** Permanent 8 ha (P) *** Seasonal Intermittent < 8 ha(Ts) ** |
Crofting
Crofting is a form of land tenure and small-scale food production particular to the Scottish Highlands, the islands of Scotland, and formerly on the Isle of Man. Within the 19th century townships, individual crofts were established on the better land, and a large area of poorer-quality hill ground was shared by all the crofters of the township for grazing of their livestock. Practice Crofting is a traditional social system in Scotland defined by small-scale food production. Crofting is characterised by its common working communities, or "townships". Individual crofts are typically established on of in-bye for better quality forage, arable and vegetable production. Each township manages poorer-quality hill ground as common grazing for cattle and sheep. Land use in the crofting counties is constrained by climate, soils, and topography. Since the late 20th century, the government has classified virtually all of the agricultural land in the Highlands and Islands as Severely Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland Clearances
The Highland Clearances ( gd, Fuadaichean nan Gàidheal , the "eviction of the Gaels") were the evictions of a significant number of tenants in the Scottish Highlands and Islands, mostly in two phases from 1750 to 1860. The first phase resulted from agricultural improvement, driven by the need for landlords to increase their income – many had substantial debts, with actual or potential bankruptcy being a large part of the story of the clearances. This involved the enclosure of the open fields managed on the run rig system and shared grazing. These were usually replaced with large-scale pastoral farms on which much higher rents were paid. The displaced tenants were expected to be employed in industries such as fishing, quarrying or the kelp industry. Their reduction in status from farmer to crofter was one of the causes of resentment. The second phase involved overcrowded crofting communities from the first phase that had lost the means to support themselves, through fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan MacNeil
Clan MacNeil, also known in Scotland as Clan Niall, is a highland Scottish clan of Irish origin. According to their early genealogies and some sources they're descended from Eógan mac Néill and Niall of the Nine Hostages. The clan is particularly associated with the Outer Hebridean island of Barra. The early history of Clan MacNeil is obscure, however despite this the clan claims to descend from the legendary Irish King Niall of the Nine Hostages, who is counted as the 1st Clan Chief, the current Clan Chief being the 47th. The clan itself takes its name from a ''Niall'' who lived in the 13th or early 14th century, and who belonged to the same dynastic family of Cowal and Knapdale as the ancestors of the Lamonts, MacEwens of Otter, Maclachlans, and the MacSweens. While the clan is centred in Barra in the Outer Hebrides, there is a branch of the clan in Argyll (McNeill/MacNeill) that some historians have speculated was more senior in line, or possibly even unrelated. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan Mackenzie
Clan Mackenzie ( gd, Clann Choinnich ) is a Scottish clan, traditionally associated with Kintail and lands in Ross-shire in the Scottish Highlands. Traditional genealogies trace the ancestors of the Mackenzie chiefs to the 12th century. However, the earliest Mackenzie chief recorded by contemporary evidence is Alexander Mackenzie of Kintail who died some time after 1471. Traditionally, during the Wars of Scottish Independence, the Mackenzies supported Robert the Bruce, but feuded with the Earls of Ross in the latter part of the 14th century. During the 15th and 16th-centuries the Mackenzies feuded with the neighboring clans of Munro and MacDonald. In the 17th century the Mackenzie chief was made Earl of Seaforth in the peerage of Scotland. During the Scottish Civil War of the 17th century the Mackenzies largely supported the Royalists. During the Jacobite rising of 1715 the chief and clan of Mackenzie supported the Jacobite cause. However, during the Jacobite rising of 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan Donald
Clan Donald, also known as Clan MacDonald ( gd, Clann Dòmhnaill; Mac Dòmhnaill ), is a Highland Scottish clan and one of the largest Scottish clans. The Lord Lyon King of Arms, the Scottish official with responsibility for regulating heraldry in that country, issuing new grants of coats of arms, and serving as the judge of the Court of the Lord Lyon, recognises under Scottish law the ''High Chief of Clan Donald''. Historically the chiefs of the Clan Donald held the title of Lord of the Isles until 1493 and two of those chiefs also held the title of Earl of Ross until 1476. There are also numerous branches to the Clan Donald and several of these have chiefs recognised by the Lord Lyon King of Arms; these are: Clan Macdonald of Sleat, Clan Macdonald of Clanranald, Clan MacDonell of Glengarry, Clan MacDonald of Keppoch, and Clan MacAlister. There are also notable historic branches of Clan Donald without chiefs so-recognised, these are: the Clan MacDonald of Dunnyveg, Clan Mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan MacLeod
Clan MacLeod (; gd, Clann Mac Leòid ) is a Highland Scottish clan associated with the Isle of Skye. There are two main branches of the clan: the MacLeods of Harris and Dunvegan, whose chief is MacLeod of MacLeod, are known in Gaelic as ' ("seed of Tormod"); the Clan MacLeod of Lewis and Raasay, whose chief is MacLeod of The Lewes ( gd, Mac Ghille Chaluim), are known in Gaelic as ' ("seed of Torcall"). Both branches claim descent from Leòd, who lived in the 13th century. Today, Clan MacLeod of The Lewes, Clan MacLeod of Raasay, and Clan MacLeod are represented by "Associated Clan MacLeod Societies", and the chiefs of the three clans. The association is made up of ten national societies across the world including: Australia, Canada, England, France, Germany, New Zealand, Scotland, South Africa, Switzerland, and the United States. History Origins The surname MacLeod means 'son of Leod'. The name Leod is an Anglicization of the Scottish Gaelic name Leòd, which is thought to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Clan
A Scottish clan (from Gaelic , literally 'children', more broadly 'kindred') is a kinship group among the Scottish people. Clans give a sense of shared identity and descent to members, and in modern times have an official structure recognised by the Court of the Lord Lyon, which regulates Scottish heraldry and coats of arms. Most clans have their own tartan patterns, usually dating from the 19th century, which members may incorporate into kilts or other clothing. The modern image of clans, each with their own tartan and specific land, was promulgated by the Scottish author Sir Walter Scott after influence by others. Historically, tartan designs were associated with Lowland and Highland districts whose weavers tended to produce cloth patterns favoured in those districts. By process of social evolution, it followed that the clans/families prominent in a particular district would wear the tartan of that district, and it was but a short step for that community to become identified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |