|
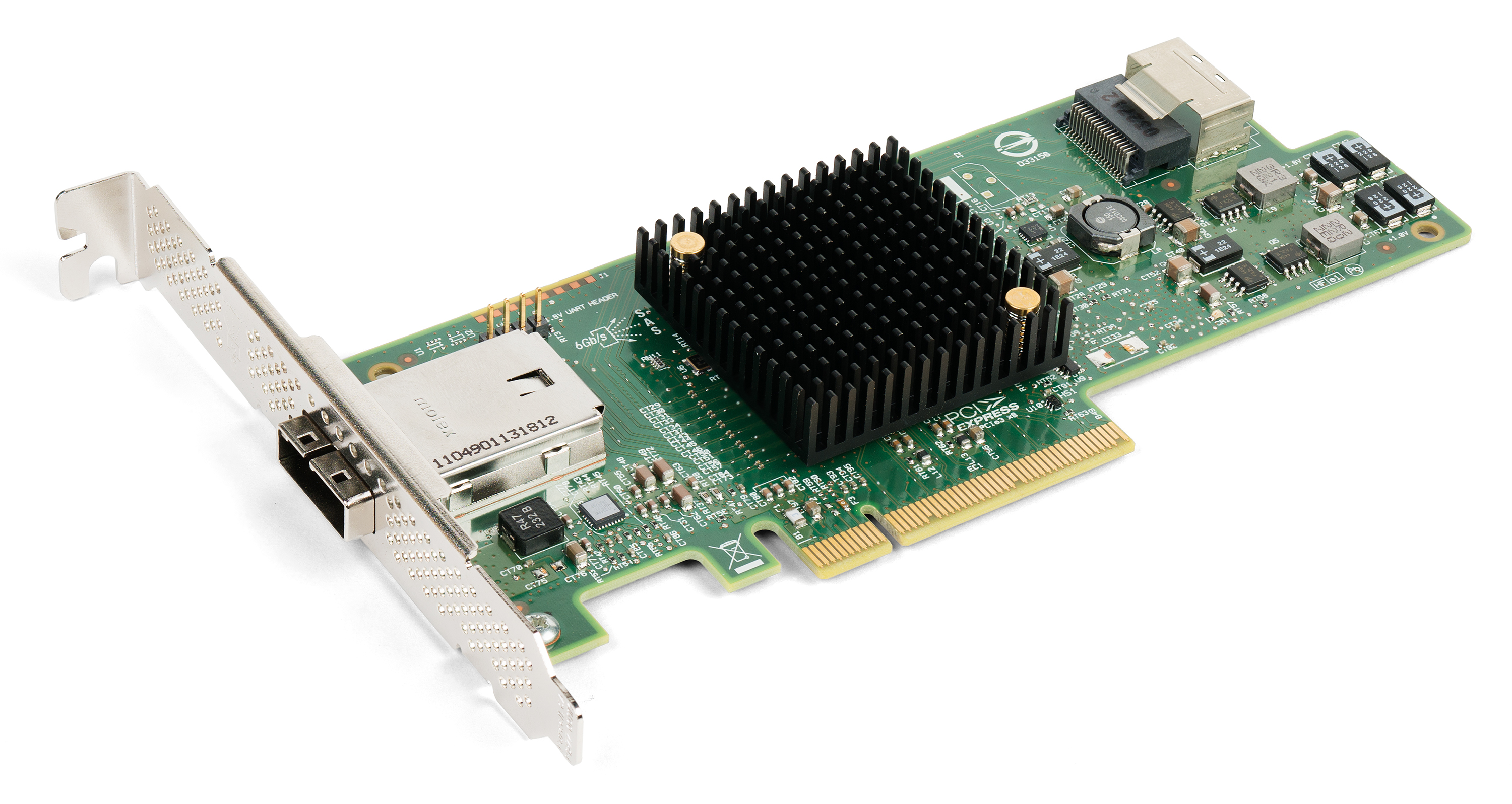
Nvidia BlueField
Nvidia BlueField is a line of data processing units (DPUs) designed and produced by Nvidia. Initially developed by Mellanox Technologies, the BlueField IP was acquired by Nvidia in March 2019, when Nvidia acquired Mellanox Technologies for US$6.9 billion. The first Nvidia produced BlueField cards, named BlueField-2, were shipped for review shortly after their announcement at VMworld 2019, and were officially launched at GTC 2020. Also launched at GTC 2020 was the Nvidia BlueField-2X, an Nvidia BlueField card with an Ampere generation graphics processing unit (GPU) integrated onto the same card. BlueField-3 and BlueField-4 DPUs were first announced at GTC 2021, with the tentative launch dates for these cards being 2022 and 2024 respectively. Nvidia BlueField cards are targeted for use in datacenters and high performance computing, where latency and bandwidth are important for efficient computation. BlueField cards differ from network interface controllers in their offloading o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Data Processing Unit
A data processing unit (DPU) is a programmable Processor (computing), computer processor that tightly integrates a general-purpose CPU with Network interface controller, network interface hardware. Sometimes they are called "IPUs" (for "infrastructure processing unit") or "SmartNICs". They can be used in place of traditional Network interface controller, NICs to relieve the main CPU of complex networking responsibilities and other "infrastructural" duties; although their features vary, they may be used to perform Encryption, encryption/decryption, serve as a firewall (computing), firewall, handle TCP/IP, process HTTP requests, or even function as a hypervisor or Disk array controller, storage controller. These devices can be attractive to cloud computing providers whose servers might otherwise spend a significant amount of CPU time on these tasks, cutting into the cycles they can provide to guests. AI Factory, AI factories are an emerging use case for DPUs. In these environments, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
ARM Architecture Family
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of RISC instruction set architectures (ISAs) for computer processors. Arm Holdings develops the ISAs and licenses them to other companies, who build the physical devices that use the instruction set. It also designs and licenses cores that implement these ISAs. Due to their low costs, low power consumption, and low heat generation, ARM processors are useful for light, portable, battery-powered devices, including smartphones, laptops, and tablet computers, as well as embedded systems. However, ARM processors are also used for desktops and servers, including Fugaku, the world's fastest supercomputer from 2020 to 2022. With over 230 billion ARM chips produced, , ARM is the most widely used family of instruction set architectures. There have been several generations of the ARM design. The original ARM1 used a 32-bit internal structure but h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
System On A Chip
A system on a chip (SoC) is an integrated circuit that combines most or all key components of a computer or Electronics, electronic system onto a single microchip. Typically, an SoC includes a central processing unit (CPU) with computer memory, memory, input/output, and computer data storage#Secondary storage, data storage control functions, along with optional features like a graphics processing unit (GPU), Wi-Fi connectivity, and radio frequency processing. This high level of integration minimizes the need for separate, discrete components, thereby enhancing Performance per watt, power efficiency and simplifying device design. High-performance SoCs are often paired with dedicated memory, such as LPDDR, and flash storage chips, such as Universal Flash Storage, eUFS or eMMC, which may be stacked directly on top of the SoC in a Package on a package, package-on-package (PoP) configuration or placed nearby on the motherboard. Some SoCs also operate alongside specialized chips, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
SPECint
SPEC INT is a computer benchmark specification for CPU integer processing power. It is maintained by the Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation (SPEC). SPEC INT is the integer performance testing component of the SPEC test suite. The first SPEC test suite, CPU92, was announced in 1992. It was followed by CPU95, CPU2000, and CPU2006. The latest standard is SPEC CPU 2017 and consists of SPEC speed and SPEC rate (aka SPECCPU_2017). SPEC INT 2006 CPU2006 is a set of benchmarks designed to test the CPU performance of a modern server computer system. It is split into two components, the first being CINT2006, the other being CFP2006 ( SPECfp), for floating point testing. SPEC defines a base runtime for each of the 12 benchmark programs. For SPECint2006, that number ranges from 1000 to 3000 seconds. The timed test is run on the system, and the time of the test system is compared to the reference time, and a ratio is computed. That ratio becomes the SPEC INT score for that tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nvidia Tesla
Nvidia Tesla is the former name for a line of products developed by Nvidia targeted at stream processing or GPGPU, general-purpose graphics processing units (GPGPU), named after pioneering electrical engineer Nikola Tesla. Its products began using GPUs from the GeForce 8 series, G80 series, and have continued to accompany the release of new chips. They are programmable using the CUDA or OpenCL application programming interface, APIs. The Nvidia Tesla product line competed with AMD's Radeon Instinct and Intel Xeon Phi lines of deep learning and GPU cards. Nvidia retired the Tesla brand in May 2020, reportedly because of potential confusion with the Tesla, Inc., brand of cars. Its new GPUs are branded Nvidia Data Center GPUs as in the Ampere (microarchitecture), Ampere-based A100 GPU. Nvidia DGX servers feature Nvidia GPGPUs. Overview Offering computational power much greater than traditional Central processing units, microprocessors, the Tesla products targeted the high-perfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a high-speed standard used to connect hardware components inside computers. It is designed to replace older expansion bus standards such as Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI, PCI-X and Accelerated Graphics Port, AGP. Developed and maintained by the PCI-SIG (PCI Special Interest Group), PCIe is commonly used to connect graphics cards, sound cards, Wi-Fi and Ethernet adapters, and storage devices such as solid-state drives and hard disk drives. Compared to earlier standards, PCIe supports faster data transfer, uses fewer pins, takes up less space, and allows devices to be added or removed while the computer is running (hot swapping). It also includes better error detection and supports newer features like I/O virtualization for advanced computing needs. PCIe connections are made through "lanes," which are pairs of wires that send and receive data. Devices can use one or more lanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Remote Management
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) is the process of supervising and controlling IT systems (such as network devices, desktops, servers and mobile devices) by means of locally installed agents that can be accessed by a management service provider. Functions include the ability to: * install new or updated software remotely (including patches, updates and configuration changes) * detect new devices and automatically install the RMM agent and configure the device * observe the behavior of the managed device and software for performance and diagnostic tasks * perform alerting and provide reports and dashboards Traditionally this function has been done on site at a company but many MSPs are performing this function remotely using integrated Software as a Service (SaaS) platforms. See also * Network management * Network monitoring * Application service management * Application performance management * Managed services * Information technology outsourcing Outsourcing is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of Scheduling (computing), processor time, mass storage, peripherals, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computerfrom cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. , Android (operating system), Android is the most popular operating system with a 46% market share, followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
DDR5 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 5 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR5 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory. Compared to its predecessor DDR4 SDRAM, DDR5 was planned to reduce power consumption, while doubling bandwidth. The standard, originally targeted for 2018, was released on July 14, 2020. A new feature called Decision Feedback Equalization (DFE) enables input/output (I/O) speed scalability for higher bandwidth and performance improvement. DDR5 has about the same latency as DDR4 and DDR3. DDR5 octuples the maximum DIMM capacity from 64 GB to 512 GB. DDR5 also has higher frequencies than DDR4, up to 9600 MT/s is currently possible, 8200 MT/s translates into around 66 GB/s of bandwidth. Using liquid nitrogen 13000 MT/s speeds were achieved. Rambus announced a working DDR5 dual in-line memory module (DIMM) in September 2017. On November 15, 2018, SK Hynix announced completion of its first DDR5 RAM chip; running at 5.2 GT/s at 1.1 V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
High Bandwidth Memory
High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) is a computer memory interface for 3D-stacked synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) initially from Samsung, AMD and SK Hynix. It is used in conjunction with high-performance graphics accelerators, network devices, high-performance datacenter AI ASICs, as on-package cache in CPUs and on-package RAM in upcoming CPUs, and FPGAs and in some supercomputers (such as the NEC SX-Aurora TSUBASA and Fujitsu A64FX). The first HBM memory chip was produced by SK Hynix in 2013, and the first devices to use HBM were the AMD Fiji GPUs in 2015. HBM was adopted by JEDEC as an industry standard in October 2013.High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) DRAM (JESD235) JEDEC, October 2013 The second generation, HBM2, was accepted by JEDEC in January 2016. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
DDR4 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 4 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR4 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory with a high bandwidth (" double data rate") interface. Released to the market in 2014, it is a variant of dynamic random-access memory (DRAM), some of which have been in use since the early 1970s, and a higher-speed successor to the DDR2 and DDR3 technologies. DDR4 is not compatible with any earlier type of random-access memory (RAM) due to different signaling voltage and physical interface, besides other factors. DDR4 SDRAM was released to the public market in Q2 2014, focusing on ECC memory, while the non-ECC DDR4 modules became available in Q3 2014, accompanying the launch of Haswell-E processors that require DDR4 memory. Features The primary advantages of DDR4 over its predecessor, DDR3, include higher module density and lower voltage requirements, coupled with higher data rate transfer speeds. The DDR4 standard allows for DIMMs of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
MIPS Architecture
MIPS (Microprocessor without Interlocked Pipelined Stages) is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures (ISA)Price, Charles (September 1995). ''MIPS IV Instruction Set'' (Revision 3.2), MIPS Technologies, Inc. developed by MIPS Computer Systems, now MIPS Technologies, based in the United States. There are multiple versions of MIPS, including MIPS I, II, III, IV, and V, as well as five releases of MIPS32/64 (for 32- and 64-bit implementations, respectively). The early MIPS architectures were 32-bit; 64-bit versions were developed later. As of April 2017, the current version of MIPS is MIPS32/64 Release 6. MIPS32/64 primarily differs from MIPS I–V by defining the privileged kernel mode System Control Coprocessor in addition to the user mode architecture. The MIPS architecture has several optional extensions: MIPS-3D, a simple set of floating-point SIMD instructions dedicated to 3D computer graphics; MDMX (MaDMaX), a more extensive i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |