|
Nuño Sánchez
Nuño Sánchez (, ''Nunyó'', or'' Nunyo Sanç'', ) ( 1185 – 1242) was a nobleman and statesman in the Crown of Aragon. Nuño was the son of Sancho, Count of Provence, Sancho, Count of Provence, County of Roussillon, Roussillon, and County of Cerdanya, Cerdagne, and Sancha Núñez of the House of Lara. His father was dispossessed of Provence in 1185 but maintained Roussillon and Cerdagne until his death in 1223, handing control of them over to his son as early as 1212. He was formally invested with them by Peter II of Aragon later that year. His full Latin title was ''Nunus Sancii, Dei gratia dominus de Rossillionis, Vallis de Asperii, Conflent et Cerritane'' ("Nuño Sánchez, by the grace of God lord of Roussillon, Vallespir, County of Conflent, Conflent and Cerdagne"). His investment was of little help to Peter, for Nuño arrived too late to be of any service at the Battle of Muret (1213), where Peter died. Subsequently, he and his father served as regents for Peter's minor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pintura Mural Del Sal%C3%B3 Del Tinell - Nun%C3%B3 San%C3%A7 A La Conquesta De Mallorca
Pintura or Pinturas may refer to: * Pintura, Utah, an unincorporated community in Washington County, Utah * Pinturas River, a river in Patagonia Argentina * Pinturas River Canyon or ''Cañadón Río Pinturas'', a town of Perito Moreno in Santa Cruz, Argentina * Pintura á pó, type of coating that is applied as a free-flowing, dry powder * Pintura (Philippine comics), a superhero in the Filipino comic book ''Bayan Knights'' {{Disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard IV Of Bigorre
Bernard ('' Bernhard'') is a French and West Germanic masculine given name. It has West Germanic origin and is also a surname. The name is attested from at least the 9th century. West Germanic ''Bernhard'' is composed from the two elements ''bern'' "bear" and ''hard'' "brave, hardy". Its native Old English cognate was ''Beornheard'', which was replaced or merged with the French form ''Bernard'' that was brought to England after the Norman Conquest. The name ''Bernhard'' was notably popular among Old Frisian speakers. Its wider use was popularized due to Saint Bernhard of Clairvaux (canonized in 1174). In Ireland, the name was an anglicized form of Brian. Geographical distribution Bernard is the second most common surname in France. As of 2014, 42.2% of all known bearers of the surname ''Bernard'' were residents of France (frequency 1:392), 12.5% of the United States (1:7,203), 7.0% of Haiti (1:382), 6.6% of Tanzania (1:1,961), 4.8% of Canada (1:1,896), 3.6% of Nigeria (1:12,221 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navarre
Navarre ( ; ; ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre, is a landlocked foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, bordering the Basque Autonomous Community, La Rioja, and Aragon in Spain and New Aquitaine in France. The capital city is Pamplona (). The present-day province makes up the majority of the territory of the medieval Kingdom of Navarre, a long-standing Pyrenean kingdom that occupied lands on both sides of the western Pyrenees, with its northernmost part, Lower Navarre, located in the southwest corner of France. Navarre is in the transition zone between the green Cantabrian Coast and semi-arid interior areas and thus its landscapes vary widely across the region. Being in a transition zone also produces a highly variable climate, with summers that are a mix of cooler spells and heat waves, and winters that are mild for the latitude. Navarre is one of the historic Basque provinces: its Basque features are conspicuous in the north, but vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
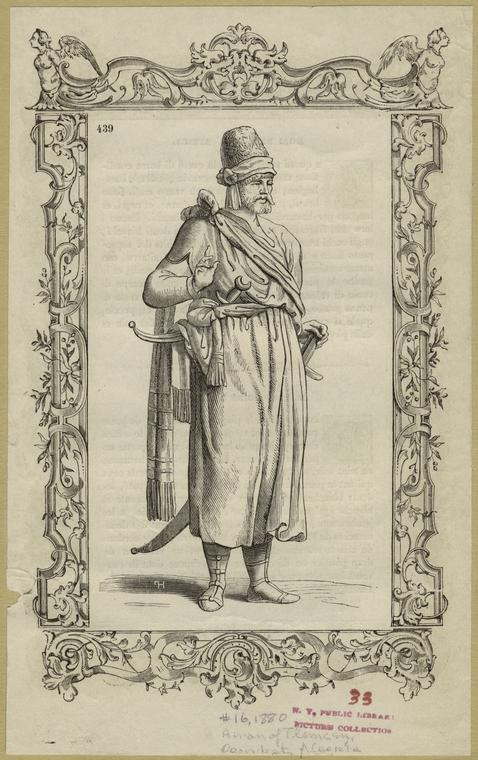
Zayyanid Dynasty
The Zayyanid dynasty or Ziyanids (, ''Ziyāniyyūn'') or Abd al-Wadids (, ''Bānu ʿAbd āl-Wād'') was a Berber Zenata dynasty that ruled the Kingdom of Tlemcen, mainly in modern Algeria centered on the town of Tlemcen in northwest Algeria. The Zayyanid dynasty's rule lasted from 1235 to 1557. History On the collapse of the Almohad Caliphate's rule around 1236, the Kingdom of Tlemcen became independent under the rule of the Zayyanids, and Yaghmurasen Ibn Zyan. Ibn Zyan was able to maintain control over the rival Berber groups, and when faced with the outside threat of the Marinids, he formed an alliance with the Sultan of Granada and the King of Castile, Alfonso X. After an eight-year siege of Tlemcen by the Marinids that ended in 1307, the reigns of Abu Hammu I (r. 1308–1318) and Abu Tashufin I (r. 1318–1337) marked a second political apogee of the Zayyanids with a consolidated hold over the central Maghreb. This period of strength was followed by a Marinid oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Tlemcen
The Kingdom of Tlemcen or Zayyanid Kingdom of Tlemcen () was a kingdom ruled by the Berber Zayyanid dynasty in what is now the northwest of Algeria. Its territory stretched from Tlemcen to the Chelif bend and Algiers, and at its zenith reached Sijilmasa and the Moulouya River in the west, Tuat to the south and the Soummam in the east.الدولة الزيانية في عهد يغمراسن: دراسة تاريخية وحضارية 633 هـ - 681 هـ / 1235 م - 1282 مخالد بلع ربي Al Manhal [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlemcen
Tlemcen (; ) is the second-largest city in northwestern Algeria after Oran and is the capital of Tlemcen Province. The city has developed leather, carpet, and textile industries, which it exports through the port of Rachgoun. It had a population of 140,158, as of the 2008 census. A major centre of the Medieval Muslim Algeria, Central Maghreb, the city is a mix of Arabs, Arab, Berbers, Berber, al-Andalus, 'Āndalusī, Ottoman Empire, Ottoman, and Western influence on Africa, Western influences. From this mosaic of influences, the city derives the title of capital of Andalusian art in Algeria. Various titles are attributed to the city including "the Pearl of the Maghreb", "the African Granada" and "the Medina of the West". Etymology The name Tlemcen (''Tilimsān'') was given by the Zayyanid King Yaghmurasen Ibn Zyan. One possible etymology is that it comes from a Berber languages, Berber word ''tilmas'' 'spring, water-hole', or from the combination of the Berber words ''tala'' 'fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almoravids
The Almoravid dynasty () was a Berber Muslim dynasty centered in the territory of present-day Morocco. It established an empire that stretched over the western Maghreb and Al-Andalus, starting in the 1050s and lasting until its fall to the Almohads in 1147. The Almoravids emerged from a coalition of the Lamtuna, Gudala, and Massufa, nomadic Berber tribes living in what is now Mauritania and the Western Sahara, traversing the territory between the Draa, the Niger, and the Senegal rivers. During their expansion into the Maghreb, they founded the city of Marrakesh as a capital, . Shortly after this, the empire was divided into two branches: a northern one centered in the Maghreb, led by Yusuf ibn Tashfin and his descendants, and a southern one based in the Sahara, led by Abu Bakr ibn Umar and his descendants. The Almoravids expanded their control to al-Andalus (the Muslim territories in Iberia) and were crucial in temporarily halting the advance of the Christian kingdoms in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conquest Of Majorca
The conquest of the Majorca, island of Majorca on behalf of the Roman Catholic kingdoms was carried out by King James I of Aragon between 1229 and 1231. The pact to carry out the invasion, concluded between James I and the ecclesiastical and secular leaders, was ratified in Tarragona on 28 August 1229. It was open and promised conditions of parity for all who wished to participate. James I reached an agreement regarding the arrival of the Catholic troops with a local chief in the Port de Pollença, but the strong mistral winds forced the king to divert to the southern part of the island. He landed at midnight on 10 September 1229, on the coast where there is now the tourist resort of Santa Ponsa, the population centre of the Calviá municipality. Although the city of Madina Mayurqa (now Palma de Mallorca) fell within the first year of the conquest, the Muslim resistance in the mountains lasted for three years. After the conquest, James I divided the land among the nobles who a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Majorca
Mallorca, or Majorca, is the largest of the Balearic Islands, which are part of Spain, and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, seventh largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. The capital of the island, Palma, Majorca, Palma, is also the capital of the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of the Balearic Islands. The Balearic Islands have been an autonomous region of Spain since 1983. There are two small islands off the coast of Mallorca: Cabrera, Balearic Islands, Cabrera (southeast of Palma) and Dragonera (west of Palma). The anthem of Mallorca is "La Balanguera". Like the other Balearic Islands of Menorca, Ibiza, and Formentera, the island is a highly popular holiday destination, particularly for tourists from the Netherlands, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, Germany, and the United Kingdom. The international airport, Palma de Mallorca Airport, is one of the busiest in Spain; it was used by 28 million passengers in 2017, with use increasing ever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homage (feudal)
Homage (/ˈhɒmɪdʒ/ or ) (from Medieval Latin , lit. "pertaining to a man") in the Middle Ages was the ceremony in which a feudal tenant or vassal pledged reverence and submission to his feudal lord, receiving in exchange the symbolic title to his new position ( investiture). It was a symbolic acknowledgement to the lord that the vassal was, literally, his man (''homme''). The oath known as "fealty" implied lesser obligations than did "homage". Further, one could swear "fealty" to many different overlords with respect to different land holdings, but "homage" could only be performed to a single liege, as one could not be "his man" (i.e., committed to military service) to more than one "liege lord". The ceremony of homage was used in many regions of Europe to symbolically bind two men together. The vassal to-be would go down on their knee and place their palms together as if praying. The lord to-be would place his hands over the hands of the vassal, while the vassal made a short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis VIII Of France
Louis VIII (5 September 1187 8 November 1226), nicknamed The Lion (), was King of France from 1223 to 1226. As a prince, he invaded Kingdom of England, England on 21 May 1216 and was Excommunication in the Catholic Church, excommunicated by a papal legate on 29 May 1216. On 2 June 1216, Louis was proclaimed "King of England" by rebellious barons in London, though never crowned. With the assistance of allies in England and Scotland he gained control of approximately one third of the English kingdom and part of Southern Wales. He was eventually defeated by English loyalists and those barons who swapped sides following the death of King John of England, King John. After the Treaty of Lambeth, he was paid 10,000 mark (currency), marks, pledged never to invade England again, and was absolved of his excommunication. As prince and fulfilling his father's crusading vow, Louis led forces during the Albigensian Crusade in support of Simon de Montfort, 5th Earl of Leicester, Simon de Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peyrepertuse
Peyrepertuse (; Languedocien: ''Castèl de Pèirapertusa'') is a ruined fortress and one of the so-called Cathar castles located high in the French Pyrénées in the commune of Duilhac-sous-Peyrepertuse, in the Aude ''département'', and has been associated with the Counts of Narbonne and Barcelona. It was the former seigneury of the Peyrepertusès (in Occitan Pèirapertusés) which means "pierced stone." Geography It is located on a limestone ridge at about an altitude of 800 m, on top of a hill which separates Duilhac from the town of Rouffiac-des-Corbières, towering over scrubland and vineyards. A strategic position which enables one at the same time to see far into the valleys that circle it, to control the mountain passes, or to send communication signals to the château de Quéribus a little further south. The view of the castle from Duilhac (to the south) is impressive thanks to the 30 to 40 meter cliff on which the Castle is perched. The main entrance is located o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |