|
Nouvelles Annales De Mathématiques
The ''Nouvelles Annales de Mathématiques'' (subtitled ''Journal des candidats aux écoles polytechnique et normale'') was a French scientific journal in mathematics. It was established in 1842 by Olry Terquem and Camille-Christophe Gerono, and continued publication until 1927, with later editors including Charles-Ange Laisant and Raoul Bricard. , retrieved 2014-07-14. Initially published by Carilian-Goeury, it was taken over after several years by a different publisher, Bachelier. Although competing in subject matter with Joseph Lio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Journal
In academic publishing, a scientific journal is a periodical publication designed to further the progress of science by disseminating new research findings to the scientific community. These journals serve as a platform for researchers, scholars, and scientists to share their latest discoveries, insights, and methodologies across a multitude of scientific disciplines. Unlike professional or trade magazines, the articles are mostly written by scientists rather than staff writers employed by the journal. Scientific journals are characterized by their rigorous peer review process, which aims to ensure the validity, reliability, and quality of the published content. In peer review, submitted articles are reviewed by active scientists (peers) to ensure scientific rigor. With origins dating back to the 17th century, the publication of scientific journals has evolved significantly, advancing scientific knowledge, fostering academic discourse, and facilitating collaboration within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olry Terquem
Olry Terquem (16 June 1782 – 6 May 1862) was a French mathematician. He is known for his works in geometry and for founding two scientific journals, one of which was the first journal about the history of mathematics. He was also the pseudonymous author (as Tsarphati) of a sequence of letters advocating radical reform in Judaism.. He was French Jewish. Education and career Terquem grew up speaking Yiddish, and studying only the Hebrew language and the Talmud.. Biographical appendix, pp. 385–386. However, after the French Revolution his family came into contact with a wider society, and his studies broadened. Despite his poor French he was admitted to study mathematics at the École Polytechnique in Paris, beginning in 1801, as only the second Jew to study there.. See in particulapp. 60–61 He became an assistant there in 1803, and earned his doctorate in 1804. After finishing his studies he moved to Mainz (at that time known as Mayence and part of imperial France), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camille-Christophe Gerono
Camille-Christophe Gerono (1799 in Paris, France – 1891 in Paris) was a French mathematician. He concerned himself above all with geometry. The Lemniscate of Gerono or ''figure-eight curve'' was named after him. With Olry Terquem, he was founding co-editor in 1842 of the scientific journal ''Nouvelles Annales de Mathématiques The ''Nouvelles Annales de Mathématiques'' (subtitled ''Journal des candidats aux écoles polytechnique et normale'') was a French scientific journal in mathematics. It was established in 1842 by Olry Terquem and Camille-Christophe Gerono, and c ...''.. References 1799 births 1891 deaths 19th-century French mathematicians {{France-mathematician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles-Ange Laisant
Charles-Ange Laisant (1 November 1841 – 5 May 1920), French politician and mathematician, was born at Indre, near Nantes on 1 November 1841, and was educated at the École Polytechnique as a military engineer. He was a Freemason and a libertarian socialist. Politics He defended the fort of Issy at the Siege of Paris, and served in Corsica and in Algeria in 1873. In 1876 he resigned his commission to enter the Chamber as deputy for Nantes in the republican interest, and in 1879 he became director of the ''Le Petit Parisien''. For alleged libel on General Courtot de Cissey in this paper he was heavily fined. The Encyclopaedia Britannica article has the erroroneous "Anne" for the correct "Ange". In the Chamber he spoke chiefly on army questions; and was chairman of a commission appointed to consider army legislation, resigning in 1887 on the refusal of the Chamber to sanction the abolition of exemptions of any kind. He then became an adherent of the revisionist policy of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
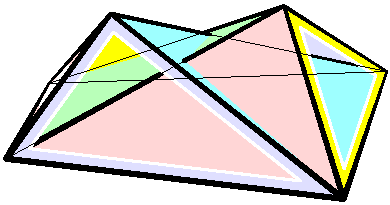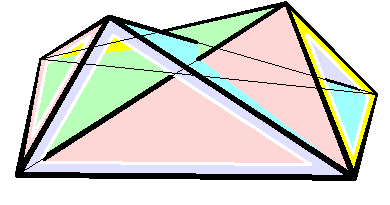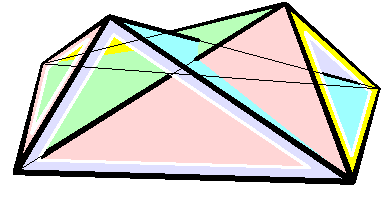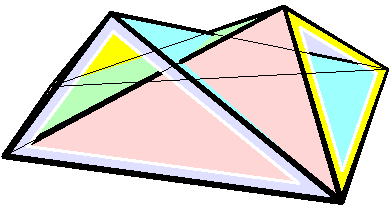
Raoul Bricard
Raoul Bricard (23 March 1870 – 26 November 1943) was a French engineer and a mathematician. He is best known for his work in geometry, especially descriptive geometry and scissors congruence, and kinematics, especially mechanical linkages. Biography Bricard taught geometry at Ecole Centrale des Arts et Manufactures. In 1908 he became a professor of applied geometry at the National Conservatory of Arts and Crafts in Paris. In 1932 he received the Poncelet Prize in mathematics from the Paris Academy of Sciences for his work in geometry. Work In 1896 Bricard published a paper on Hilbert's third problem, even before the problem was stated by Hilbert. In it he proved that mirror symmetric polytopes are scissors congruent, and proved a weak version of Dehn's criterion. In 1897 Bricard published an important investigation on flexible polyhedra. In it he classified all flexible octahedra, now known as Bricard octahedra. This work was the subject of Henri Lebesgue's lectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johns Hopkins University
The Johns Hopkins University (often abbreviated as Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1876 based on the European research institution model, Johns Hopkins is considered to be the first research university in the U.S. The university was named for its first benefactor, the American entrepreneur and Quakers, Quaker philanthropist Johns Hopkins. Hopkins's $7 million bequest (equivalent to $ in ) to establish the university was the largest Philanthropy, philanthropic gift in U.S. history up to that time. Daniel Coit Gilman, who was inaugurated as :Presidents of Johns Hopkins University, Johns Hopkins's first president on February 22, 1876, led the university to revolutionize higher education in the U.S. by integrating teaching and research. In 1900, Johns Hopkins became a founding member of the Association of American Universities. The university has led all Higher education in the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Liouville
Joseph Liouville ( ; ; 24 March 1809 – 8 September 1882) was a French mathematician and engineer. Life and work He was born in Saint-Omer in France on 24 March 1809. His parents were Claude-Joseph Liouville (an army officer) and Thérèse Liouville (née Balland). Liouville gained admission to the École Polytechnique in 1825 and graduated in 1827. Just like Augustin-Louis Cauchy before him, Liouville studied engineering at École des Ponts et Chaussées after graduating from the Polytechnique, but opted instead for a career in mathematics. After some years as an assistant at various institutions including the École Centrale Paris, he was appointed as professor at the École Polytechnique in 1838. He obtained a chair in mathematics at the Collège de France in 1850 and a chair in mechanics at the Faculté des Sciences in 1857. Besides his academic achievements, he was very talented in organisational matters. Liouville founded the ''Journal de Mathématiques Pures et A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal De Mathématiques Pures Et Appliquées
The ''Journal de Mathématiques Pures et Appliquées'' () is a French monthly scientific journal of mathematics, founded in 1836 by Joseph Liouville (editor: 1836–1874). The journal was originally published by Charles Louis Étienne Bachelier. After Bachelier's death in 1853, publishing passed to his son-in-law, Louis Alexandre Joseph Mallet, and the journal was marked Mallet-Bachelier. The publisher was sold to Gauthier-Villars ( fr) in 1863, where it remained for many decades. The journal is currently published by Elsevier. According to the 2018 Journal Citation Reports, its impact factor is 2.464. Articles are written in English or French. References External links * Online access* http://sites.mathdoc.fr/JMPA/ Index of freely available volumes Up to 1945, volumes of Journal de Mathématiques Pures et Appliquées are available online free in their entirety from Internet Archive The Internet Archive is an American 501(c)(3) organization, non-profit organiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics Education
In contemporary education, mathematics education—known in Europe as the didactics or pedagogy of mathematics—is the practice of teaching, learning, and carrying out Scholarly method, scholarly research into the transfer of mathematical knowledge. Although research into mathematics education is primarily concerned with the tools, methods, and approaches that facilitate practice or the study of practice, it also covers an extensive field of study encompassing a variety of different concepts, theories and methods. List of mathematical societies, National and international organisations regularly hold conferences and List of mathematics education journals, publish literature in order to improve mathematics education. History Ancient Elementary mathematics were a core part of education in many ancient civilisations, including ancient Egypt, Babylonia, ancient Babylonia, ancient Greece, ancient Rome, and Vedic civilization, Vedic Ancient India, India. In most cases, formal edu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophia Scientiae
''philoSOPHIA: A Journal of Transcontinental Feminism'' is an international, interdisciplinary, biannual peer-reviewed academic journal covering feminist theory and continental philosophy. Published by SUNY Press, the journal was established by philoSOPHIA: the Society for Continental Feminism, which was founded in 2008."philoSOPHIA – Biannual" SUNY Press. The are Alyson Cole and Kyoo Lee. Established in 2008 as ''philoSOPHIA: A Journal of Continental Feminism'', it was "transcontinentalized" in 2018 to broaden its scope and inclusivity. The new subtitle ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |