|
Northland Tusked Wētā
The Northland tusked wētā, ''Anisoura nicobarica'', is a rare monotypic wētā of the family Anostostomatidae, endemic to the northern half of Northland in New Zealand, and originally described in 1932. The type specimen was wrongly labelled as coming from the Nicobar Islands, so the species was named ''Anisoura nicobarica''. It was erroneously described again in 1950 by a different author, who placed it in the ground wētā genus '' Hemiandrus'' (as ''Hemiandrus monstrosus)''. Description Tusked wētā are distinctive because of the long curved "tusks" adult males have projecting forward from their jaws. The tusks are not used for biting but are used to push an opponent. Among the three species of tusked wētā, the Northland tusked wētā, ''Anisoura nicobarica,'' is the smallest measuring up to 21mm in body length. The Middle Island tusked wētā, ''Motuweta isolata,'' being the biggest measuring up to 70 mm in body length and the Raukumara tusked wētā, ''Motuwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northland Tusked Weta DOC
Northland may refer to: Corporations * Northland Organic Foods Corporation, headquartered in Saint Paul, Minnesota * Northland Resources, a mining business * Northland Communications, an American cable television, telephone and internet service provider * Northland Properties, the parent company of multiple hotel chains, restaurants, sports teams and properties Places Australia * Northland Shopping Centre, in Melbourne Canada * Northland Village Mall, in Calgary, Alberta * Northland Pyrite Mine, in Temagami, Ontario New Zealand * Northland (New Zealand electorate), northern New Zealand * Northland Peninsula, northern New Zealand * Northland region, northern New Zealand * Northland, Wellington, suburb Singapore * Northland Primary School United States * Northland, Waupaca County, Wisconsin, an unincorporated community * The Northland, a section of the Kansas City metropolitan area * Northland Center, in Southfield, Michigan * Buzz Westfall Plaza on the Boulev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury Islands Tusked Wētā
The Mercury Islands tusked wētā, (''Motuweta isolata''), also known as the Middle Island tusked wētā, is a large flightless insect in the family (biology), family Anostostomatidae, discovered in 1970 living on a single small island in New Zealand. Distinguished by the enormous tusks with which males fight, it was saved from extinction by a captive breeding programme and translocation: the entire world population is descended from a male and two females captured and bred in captivity in 1998, just before the species went extinct in the wild. ''Motuweta isolata'' is the largest of the three Wētā#Tusked wētā, tusked wētā species, and the most endangered wētā, ranked New Zealand Threat Classification System, Nationally Critical by the Department of Conservation (New Zealand), Department of Conservation. Taxonomy ''Motuweta isolata'' was discovered in 1970 on Middle Island (Atiu in Māori language, Māori) in the Mercury Islands group by herpetologist Anthony Whitaker, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Threat Classification System
The New Zealand Threat Classification System is used by the Department of Conservation to assess conservation priorities of species in New Zealand. The system was developed because the IUCN Red List, a similar conservation status system, had some shortcomings for the unique requirements of conservation ranking in New Zealand. plants, animals, and fungi are evaluated, though the lattermost has yet to be published. Algae were assessed in 2005 but not reassessed since. Other protist A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancest ...s have not been evaluated. Categories Species that are ranked are assigned categories: ;Threatened :This category has three major divisions: :*Nationally Critical - equivalent to the IUCN category of Critically endangered :*Nationally Endangered - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Wētā
Tree wētā (pūtangatanga) are insects in the genus ''Hemideina'' of the family (biology), family Anostostomatidae. The genus is endemic (ecology), endemic to New Zealand. There are seven species within the wētā genus ''Hemideina'', found throughout the country except lowland Otago and Southland, New Zealand, Southland. Because many pūtangatanga species are common and widespread they have been used extensively in studies of ecology and evolution. Habitat Tree wētā are commonly encountered in forests and suburban gardens throughout most of New Zealand. They are up to 40 mm long and most commonly live in holes in trees formed by beetle and moth larvae or where rot has set in after a twig has broken off. The hole, called a gallery, is maintained by the wētā and any growth of the bark surrounding the opening is chewed away. They readily occupy a preformed gallery in a piece of wood (a "wētā motel") and can be kept in a suburban garden as pets. A gallery might house ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
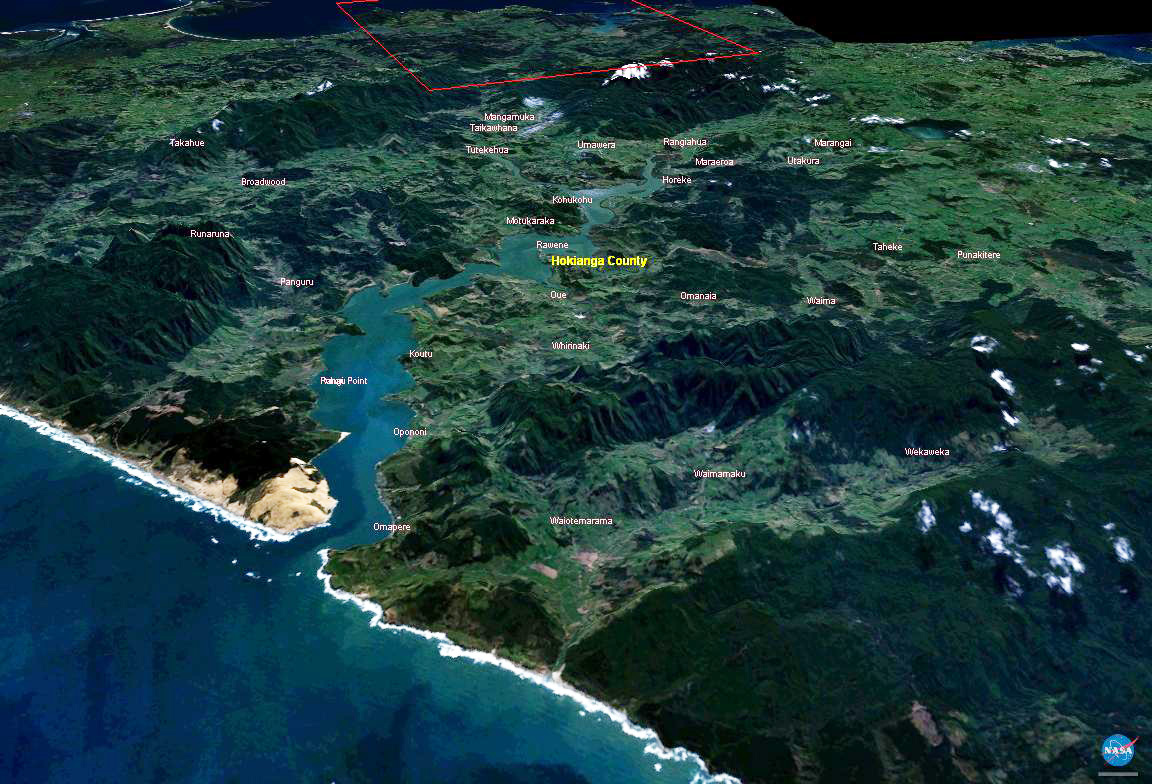
Hokianga
The Hokianga is an area surrounding the Hokianga Harbour, also known as the Hokianga River, a long Estuary, estuarine drowned valley on the west coast in the north of the North Island of New Zealand. The original name, still used by local Māori people, Māori, is ''Te Kohanga o Te Tai Tokerau'' ("the nest of the northern people") or ''Te Puna o Te Ao Marama'' ("the wellspring in the world of light"). The full name of the harbour is Te Hokianga-nui-a-Kupe — "the place of Kupe's great return". Geography The Hokianga is in the Far North (district), New Zealand, Far North District, which is in the Northland Region. The area is northwest of Whangārei City—and west of Kaikohe—by road. The estuary extends inland for from the Tasman Sea. It is navigable for small craft for much of its length, although there is a bar across the mouth. In its upper reaches the Rangiora Narrows separate the mouths of the Waihou and Mangamuka Rivers from the lower parts of the harbour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Islands
The Bay of Islands is an area on the east coast of the Far North District of the North Island of New Zealand. It is one of the most popular fishing, sailing and tourist destinations in the country, and has been renowned internationally for its big-game fishing since American author Zane Grey publicised it in the 1930s. It is north-west of the city of Whangārei. Cape Reinga, at the northern tip of the country, is about by road further to the north-west. Etymology The bay is known in Māori language, Māori as Tokerau, a name given by early Māori ancestors referencing a place in the Hawaiki, Māori homeland. The wider Bay of Islands area, including the plain surrounding Waimate North, is traditionally known as Taiamai, a name shortened from the Ngāpuhi (proverb) ("the Vitex lucens, pūriri trees are laughing with joy"), a phrase used to express delight in the world, or to welcome an honoured guest. The bay's English name was given on 27 November 1769 by Captain James ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptospermum Scoparium
''Leptospermum'' is a genus of shrubs and small trees in the myrtle family Myrtaceae commonly known as tea trees, although this name is sometimes also used for some species of '' Melaleuca''. Most species are endemic to Australia, with the greatest diversity in the south of the continent, but some are native to other parts of the world, including New Zealand and Southeast Asia. Leptospermums all have five conspicuous petals and five groups of stamens which alternate with the petals. There is a single style in the centre of the flower and the fruit is a woody capsule. The first formal description of a leptospermum was published in 1776 by the German botanists Johann Reinhold Forster and his son Johann Georg Adam Forster, but an unambiguous definition of individual species in the genus was not achieved until 1979. Leptospermums grow in a wide range of habitats but are most commonly found in moist, low-nutrient soils. They have important uses in horticulture, in the produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemideina Thoracica
''Hemideina thoracica'', commonly known as the Auckland tree wētā or tokoriro is a cricket-like insect (within the family Anostostomatidae). It is endemic to New Zealand and is found over most of the North Island, except for the Wellington region and regions 900 metres above sea level. This species is an arboreal, herbivorous generalist however, it is also thought to be polyphagous and is found in all wooded habitats, including forest, scrub and suburban gardens. ''H. thoracica'' is morphologically uniform but chromosomally polymorphic. It comprises at least eight chromosomal races with diploid numbers from 2n=11 (XO) to 2n=23 (XO). There are hybrid zones where some of the chromosomal races meet. Phylogenetically, it is most closely related to the other North Island species ('' H. crassidens'' and '' H. trewicki''). The conservation status of ''H. thoracica'' is " not threatened" however, the chromosome race on Karikari Peninsular (2n=23/24) is listed as " nationally vu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arboreal Locomotion
Arboreal locomotion is the animal locomotion, locomotion of animals in trees. In habitats in which trees are present, animals have evolution, evolved to move in them. Some animals may scale trees only occasionally (scansorial), but others are exclusively arboreal. The habitats pose numerous mechanical challenges to animals moving through them and lead to a variety of anatomical, behavioral and ecological consequences as well as variations throughout different species.Matt Cartmill, Cartmill, M. (1985). "Climbing". pp. 73–88 ''In'': Hildebrand, Milton; Bramble, Dennis M.; species:Karel Frederik Liem, Liem, Karel F.; David B. Wake, Wake, David B. (editors) (1985). ''Functional Vertebrate Morphology''. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, Belknap Press. 544 pp. . Furthermore, many of these same principles may be applied to climbing without trees, such as on rock piles or mountains. Some animals are exclusively arboreal in habitat, such as tree snails. Biomechanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Taxon
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of Genus, genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. Theoretical implications Monotypic taxa present several important theoretical challenges in biological classification. One key issue is known as "Gregg's Paradox": if a single species is the only member of multiple hierarchical levels (for example, being the only species in its genus, which is the only genus in its family), then each level needs a distinct definition to maintain logical structure. Otherwise, the different taxonomic ranks become effectively identical, which creates problems for organizing biological diversity in a hierarchical o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |