|
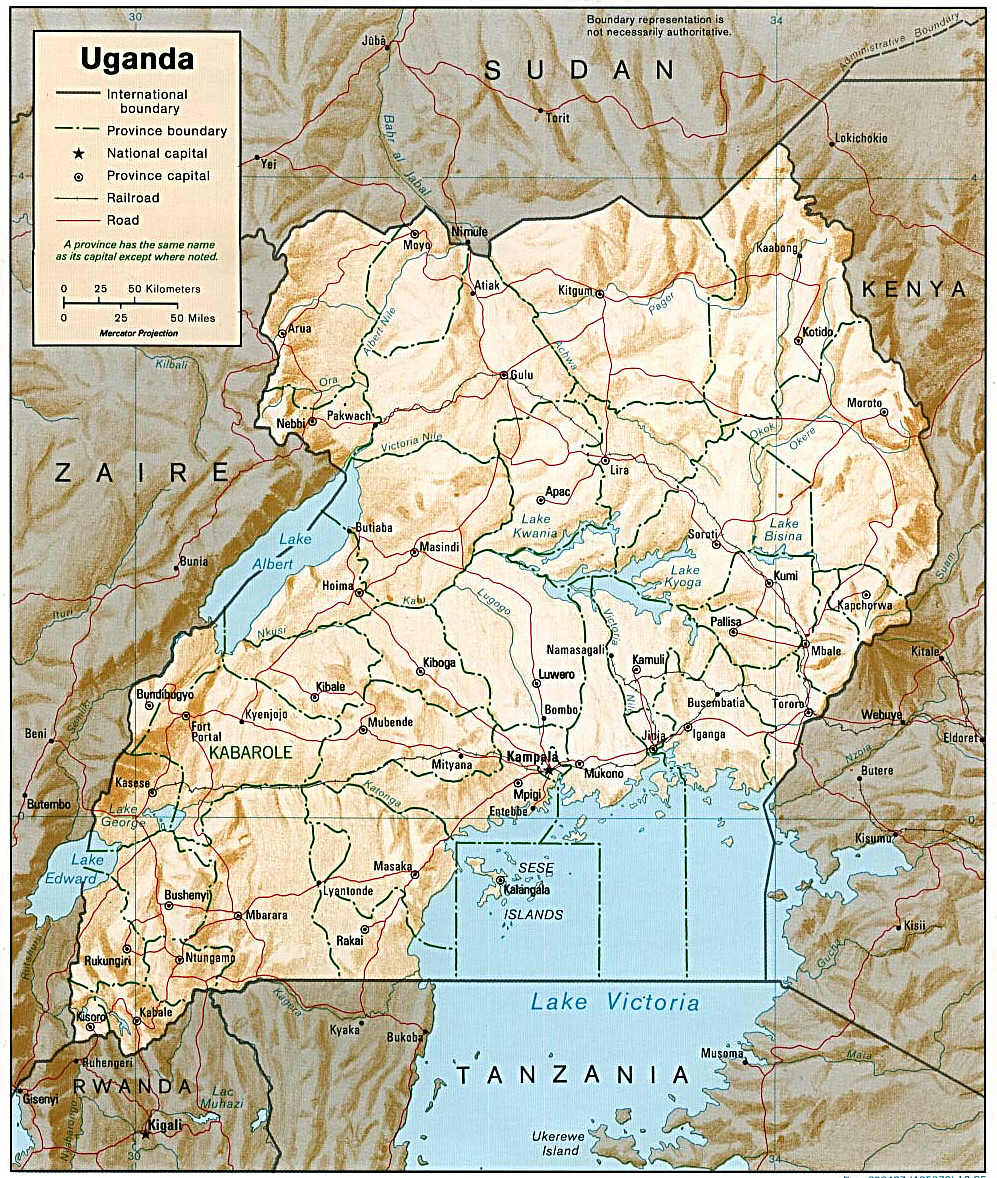
Northern Uganda Campaign (January–March 1986)
In the last phase of the Ugandan Bush War from January to March 1986, the National Resistance Army (NRA) conducted a military campaign to conquer northern Uganda beyond the Nile, an area still held by the Uganda National Liberation Army (UNLA) and allied militias that had previously been loyal to the recently deposed government of Ugandan President Tito Okello. After heavy fighting, the NRA emerged victorious, capturing all of the country. The UNLA and its allies largely disbanded their forces or surrendered, though a substantial number also fled into exile to continue resistance. The conquest of northern Uganda by the NRA marked the formal end of the Ugandan Bush War, though another civil war erupted a few months later. Background In April 1979 Tanzanian forces and the Uganda National Liberation Army (UNLA), a coalition of armed rebel groups united under the Uganda National Liberation Front (UNLF), deposed the President of Uganda, Idi Amin. A new UNLF government was installed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ugandan Bush War
The Ugandan Bush War was a civil war fought in Uganda by the official Ugandan government and its armed wing, the Uganda National Liberation Army (UNLA), against a number of rebel groups, most importantly the National Resistance Army (NRA), from 1980 to 1986. The unpopular President Milton Obote was overthrown in a coup d'état in 1971 by General Idi Amin, who established a military dictatorship. Amin was overthrown in 1979 following the Uganda–Tanzania War, Uganda-Tanzania War, but his loyalists started the Bush War by launching an insurgency in the West Nile sub-region, West Nile region in 1980. 1980 Ugandan general election, Subsequent elections saw Obote return to power in a UNLA-ruled government. Several opposition groups claimed the Rigged election, elections were rigged, and united as the NRA under the leadership of Yoweri Museveni to start an armed uprising against Obote's government on 6 February 1981. Obote was overthrown and replaced as president by his general Tito Oke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tito Okello
Tito Lutwa Okello (15 October 1914 – 3 June 1996) was a Ugandan military officer and politician who served as the eighth president of Uganda from 29 July 1985 until 26 January 1986. Background Tito Okello was born into an ethnic Acholi family in circa 1914 in Namukora, Kitgum District. He joined the King's African Rifles in 1940 and served in the East African Campaign of World War II. As a career military officer, he had a variety of assignments. As a follower of President Milton Obote, Okello went into exile following the 1971 coup d'état that resulted in Idi Amin becoming Uganda's new ruler. In 1972, 1972 invasion of Uganda, rebels invaded Uganda to restore Obote. Okello was one of the leaders of an insurgent group which targeted Masaka. The invasion was defeated by loyalist Uganda Army (1971–1980), Uganda Army troops. Okello took part in the Uganda–Tanzania War. He was one of the commanders in the coalition between the Tanzania People's Defence Force and the Ug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Press International
United Press International (UPI) is an American international news agency whose newswires, photo, news film, and audio services provided news material to thousands of newspapers, magazines, radio and television stations for most of the 20th century until its eventual decline beginning in the early 1980s. At its peak, it had more than 6,000 media subscribers. Since the first of several sales and staff cutbacks in 1982, and the 1999 sale of its broadcast client list to its main U.S. rival, the Associated Press, UPI has concentrated on smaller information-market niches. History Formally named United Press Associations for incorporation and legal purposes but publicly known and identified as United Press or UP, the news agency was created by the 1907 uniting of three smaller news syndicates by the Midwest newspaper publisher E. W. Scripps. It was headed by Hugh Baillie (1890–1966) from 1935 to 1955. At the time of his retirement, UP had 2,900 clients in the United States, and 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Army
A regular army is the official army of a state or country (the official armed forces), contrasting with irregular forces, such as volunteer irregular militias, private armies, mercenaries, etc. A regular army usually has the following: * a standing army, the permanent force of the regular army that is maintained under arms during peacetime. * a military reserve force that can be mobilized when needed to expand the effectiveness of the regular army by complementing the standing army. A regular army may be: * a ''conscript army'', including professionals, volunteers and also conscripts (presence of enforced conscription, including recruits for the standing army and also a compulsory reserve). * a ''professional army'', with no conscripts (absence of compulsory service, and presence of a voluntary reserve), is not exactly the same as a standing army, as there are standing armies both in the conscript and the professional models. In the United Kingdom and the United States, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kampala
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nairobi Agreement, 1985
The Nairobi Agreement was a peace deal between the Ugandan government of Tito Okello and the National Resistance Army (NRA) rebel group led by Yoweri Museveni. The accords were signed in Nairobi, Kenya in December 1985. Background On July 27, 1985, an army brigade of the Ugandan army ( UNLA), commanded by Brigadier Bazilio Olara-Okello, staged a coup d'état against Milton Obote's government. The National Assembly was dissolved and a Military Council was established to rule the country, first with Olara Okello, and later General Tito Okello as Chairman. Meanwhile, Yoweri Museveni's NRA rebels were gaining ground, having taken advantage of the chaotic situation in the country, caused by power struggles within the government and a demoralized and disintegrating UNLA. "A Country Study: Uganda" '' |
1985 Ugandan Coup D'état
The 1985 Ugandan coup d'état was an ethnically motivated military takeover in Uganda involving dissident Acholi elements within the Uganda National Liberation Army (UNLA), led by Brigadier Basilio Olara Okello, which successfully ousted the second Milton Obote government. The army promptly named General Tito Okello Lutwa as President of the Military Council, only for him to be ousted six months later by Yoweri Museveni and his National Resistance Army (NRA). Background Following the overthrow of dictator Idi Amin by the Tanzania People's Defence Force (TPDF) and the Uganda National Liberation Army (UNLA) rebel coalition, a new government led by President Yusuf Lule was formed by the Uganda National Liberation Front (UNLF) and the Tanzanians. However, the UNLF government proved to be weak and unstable, and quickly became embroiled in a series of crises. As he tried to exert his power, Lule was removed from office by the UNLF's powerful National Consultative Committee on 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoweri Museveni
Yoweri Kaguta Museveni Tibuhaburwa (born 15 September 1944) is a Ugandan politician and Officer (armed forces), military officer who is the ninth and current president of Uganda since 1986. As of 2025, he is the third-List of current state leaders by date of assumption of office, longest consecutively serving current non-royal national leader in the world (after Teodoro Obiang Nguema Mbasogo in Equatorial Guinea and Paul Biya in Cameroon). Born in Ntungamo, Museveni studied political science from the University of Dar es Salaam where he initiated the University Students' African Revolutionary Front. In 1972, he participated in the abortive 1972 invasion of Uganda, invasion of Uganda against the regime of President Idi Amin. The next year, Museveni established the Front for National Salvation and fought alongside Tanzania People's Defence Force, Tanzanian forces in the Uganda–Tanzania War, Tanzania–Uganda War, which overthrew Amin. Museveni contested the subsequent 1980 Ugan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Britannica
An encyclopedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into article (publishing), articles or entries that are arranged Alphabetical order, alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionary, dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on ''factual information'' concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on Linguistics, linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammar, grammatical forms.Béjoint, Henri (2000)''Modern Lexicography'', pp. 30–31. Oxford University Press. Encyclopedias have existed for around 2,000 years and have evolved considerably during that time as regards language (written in a major inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1980 Ugandan General Election
General elections were held in Uganda on 10 and 11 December 1980. They followed the overthrow of Idi Amin the previous year and were the first since the pre-independence elections in 1962. The result was a victory for the Uganda People's Congress (UPC) of President Milton Obote, which won 75 of the 126 seats. Voter turnout was 85%.Dieter Nohlen, Michael Krennerich & Bernhard Thibaut (1999) ''Elections in Africa: A data handbook'', p933 The UPC was the only party to contest all 126 seats, and its candidates were returned unopposed in seventeen constituencies. The opposition claimed that the UPC had only won through widespread fraud. Several opposition groups united as the National Resistance Army (NRA) under the leadership of Yoweri Museveni to start an armed uprising against Obote's government on 6 February 1981. Results References {{Ugandan elections General Parliamentary elections in Uganda Uganda Uganda Uganda, officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milton Obote
Apollo Milton Obote (28 December 1925 – 10 October 2005) was a Ugandan politician who served as the second prime minister of Uganda from 1962 to 1966 and the second president of Uganda from 1966 to 1971 and later from 1980 to 1985. A Lango, Obote studied at the Busoga College and Makerere University. In 1956, he joined the Uganda National Congress (UNC) and later split away by founding the Uganda People's Congress (UPC) in 1960. After Uganda gained independence from British colonial rule in 1962, Obote was sworn in as prime minister in a coalition with the Kabaka Yekka, whose leader Mutesa II was named president. Due to a rift with Mutesa over the 1964 Ugandan lost counties referendum and later getting implicated in a gold smuggling scandal, Obote overthrew him in 1966 and declared himself president, establishing a dictatorial regime with the UPC as the sole official party in 1969. As president, Obote implemented ostensibly socialist policies, under which the coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idi Amin
Idi Amin Dada Oumee (, ; 30 May 192816 August 2003) was a Ugandan military officer and politician who served as the third president of Uganda from 1971 until Uganda–Tanzania War, his overthrow in 1979. He ruled as a Military dictatorship, military dictator and is considered one of the most brutal Despotism, despots in modern world history. Amin was born to a Kakwa people, Kakwa father and Lugbara people, Lugbara mother. In 1946, he joined the King's African Rifles (KAR) of the British Colonial Army as a cook. He rose to the rank of lieutenant, taking part in British Empire, British actions against Somali rebels and then the Mau Mau rebellion, Mau Mau Uprising in Kenya Colony, Kenya. Uganda gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1962, and Amin remained in the Uganda Army (1962–1971), army, rising to the position of deputy army commander in 1964 and being appointed commander two years later. He became aware that Ugandan president Milton Obote was planning to arrest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |