|
Non-depolarizing
Neuromuscular-blocking drugs, or Neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBAs), block transmission at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the affected skeletal muscles. This is accomplished via their action on the post-synaptic acetylcholine (Nm) receptors. In clinical use, neuromuscular block is used adjunctively to anesthesia to produce paralysis, firstly to paralyze the vocal cords, and permit endotracheal intubation, and secondly to optimize the surgical field by inhibiting spontaneous ventilation, and causing relaxation of skeletal muscles. Because the appropriate dose of neuromuscular-blocking drug may paralyze muscles required for breathing (i.e., the diaphragm), mechanical ventilation should be available to maintain adequate respiration. This class of medications helps to reduce patient movement, breathing, or ventilator dyssynchrony and allows lower insufflation pressures during laparoscopy. It has several indications for use in the intense c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocuronium
Rocuronium bromide (brand names Zemuron, Esmeron) is an aminosteroid non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocker or muscle relaxant used in modern anaesthesia to facilitate tracheal intubation by providing skeletal muscle relaxation for surgery or mechanical ventilation. It is used for standard endotracheal intubation, as well as for rapid sequence induction (RSI). Pharmacology Mechanism of action Rocuronium bromide is a competitive antagonist for the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction. Of the neuromuscular-blocking drugs it is considered to be a non-depolarizing neuromuscular junction blocker, because it acts by dampening the receptor action causing muscle relaxation, instead of continual depolarisation which is the mechanism of action of the depolarizing neuromuscular junction blockers, like succinylcholine. It was designed to be a weaker antagonist at the neuromuscular junction than pancuronium; hence its monoquaternary structure and its hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapacuronium
Rapacuronium bromide (brand name Raplon) is a rapidly acting, non-depolarizing aminosteroid neuromuscular blocker formerly used in modern anaesthesia, to aid and enable endotracheal intubation, which is often necessary to assist in the controlled ventilation of unconscious patients during surgery and sometimes in intensive care. As a non-depolarizing agent it did not cause initial stimulation of muscles before weakening them. Due to risk of fatal bronchospasm it was withdrawn from the United States market by Organon The ''Organon'' (, meaning "instrument, tool, organ") is the standard collection of Aristotle's six works on logical analysis and dialectic. The name ''Organon'' was given by Aristotle's followers, the Peripatetics, who maintained against the ... on March 27, 2001, less than 2 years after its FDA approval in 1999. References Muscle relaxants Nicotinic antagonists Withdrawn drugs Quaternary ammonium compounds 1-Piperidinyl compounds Acetate esters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandonium
Candocuronium iodide ( INN, formerly chandonium, HS-310) is an aminosteroid neuromuscular-blocking drug. It was clinically evaluated in India for use in anesthesia for endotracheal intubation, and for providing skeletal muscle relaxation and assistance mechanical ventilation during surgery. Its development was discontinued due to cardiovascular side effects, primarily tachycardia, the severity of which is similar to the clinically established pancuronium bromide. Candocuronium has a short duration in the body, but a rapid onset of action, with little to no ganglion-blocking activity and greater potency than pancuronium bromide. Background Candocuronium iodide, like other neuromuscular-blocking agents, is a preferential competitive antagonist of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It was developed by the laboratory of Harkishan Singh at Panjab University Panjab University (PU) is an Indian collegiate public state university located in Chandigarh. Funded through both State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancuronium
Pancuronium (trademarked as Pavulon) is an aminosteroid muscle relaxant with various medical uses. It is used in euthanasia and is used in some states as the second of three drugs administered during lethal injections in the United States. Mechanism of action Pancuronium is a typical non-depolarizing curare-mimetic muscle relaxant. It competitively inhibits the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor at the neuromuscular junction by blocking the binding of acetylcholine. It has slight vagolytic activity, causing an increase in heart rate, but no ganglioplegic (i.e., blocking ganglions) activity. It is a very potent muscle relaxant drug, with an ED95 (i.e., the dose that causes 95% depression of muscle twitch response) of only 60 μg/kg body weight. Onset of action is relatively slow compared to other similar drugs, in part due to its low dose: an intubating dose takes 3–6 minutes for full effect. Clinical effects (muscle activity lower than 25% of physiological) last for ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydrochandonium
Dihydrochandonium is an aminosteroid non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent. References Muscle relaxants Nicotinic antagonists Quaternary ammonium compounds Steroids Neuromuscular blockers {{musculoskeletal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vecuronium
Vecuronium bromide, sold under the brand name Norcuron among others, is a medication used as part of general anesthesia to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation. It is also used to help with endotracheal intubation; however, agents such as suxamethonium (succinylcholine) or rocuronium are generally preferred if this needs to be done quickly. It is given by injection into a vein. Effects are greatest at about 4 minutes and last for up to an hour. Side effects may include low blood pressure and prolonged paralysis. Allergic reactions are rare. It is unclear if use in pregnancy is safe for the baby. Vecuronium is in the aminosteroid neuromuscular-blocker family of medications and is of the non-depolarizing type. It works by competitively blocking the action of acetylcholine on skeletal muscles. The effects may be reversed with sugammadex or a combination of neostigmine and glycopyrrolate. To minimize residual blockade, reversal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthesia Awareness
Awareness under anesthesia, also referred to as intraoperative awareness or accidental awareness during general anesthesia (AAGA), is a rare complication of general anesthesia where patients regain varying levels of consciousness during their surgical procedures. While anesthesia awareness is possible without resulting in any long-term memory of the experience, it is also possible for victims to have awareness with explicit recall, where they can remember the events related to their surgery (intraoperative awareness with explicit recall). Intraoperative awareness with explicit recall is an infrequent condition with potentially devastating psychological consequences. While it has gained popular recognition in media, research shows that it only occurs at an incidence rate of 0.1–0.2%. Patients report a variety of experiences, ranging from vague, dreamlike states to being fully awake, immobilized, and in pain from the surgery. Intraoperative awareness is usually caused by the deli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suxamethonium
Suxamethonium chloride (brand names Scoline and Sucostrin, among others), also known as suxamethonium or succinylcholine, or simply sux in medical abbreviation, is a medication used to cause short-term paralysis as part of general anesthesia. This is done to help with tracheal intubation or electroconvulsive therapy. It is administered by injection, either into a vein or into a muscle. When used in a vein, onset of action is generally within one minute and effects last for up to 10 minutes. Common side effects include low blood pressure, increased saliva production, muscle pain, and rash. Serious side effects include malignant hyperthermia, hyperkalemia and allergic reactions. It is not recommended in people who are at risk of high blood potassium or a history of myopathy. Use during pregnancy appears to be safe for the baby. Suxamethonium is in the neuromuscular blocker family of medications and is of the depolarizing type. It works by blocking the action of acetylcholi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
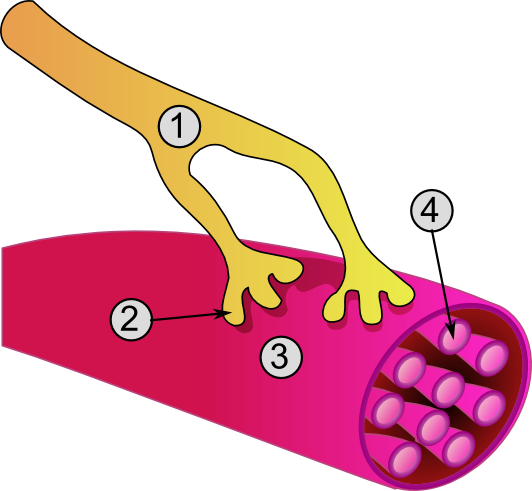
Synapse Diag3
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that allows a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or a target effector cell. Synapses can be classified as either chemical or electrical, depending on the mechanism of signal transmission between neurons. In the case of electrical synapses, neurons are coupled bidirectionally with each other through gap junctions and have a connected cytoplasmic milieu. These types of synapses are known to produce synchronous network activity in the brain, but can also result in complicated, chaotic network level dynamics. Therefore, signal directionality cannot always be defined across electrical synapses. Chemical synapses, on the other hand, communicate through neurotransmitters released from the presynaptic neuron into the synaptic cleft. Upon release, these neurotransmitters bind to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, inducing an electrical or chemical response in the target neuro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymethylene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging (plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including bottles, cups, jars, etc.). , over 100 million tonnes of polyethylene resins are being produced annually, accounting for 34% of the total plastics market. Many kinds of polyethylene are known, with most having the chemical formula (C2H4)''n''. PE is usually a mixture of similar polymers of ethylene, with various values of ''n''. It can be ''low-density'' or ''high-density'' and many variations thereof. Its properties can be modified further by crosslinking or copolymerization. All forms are nontoxic as well as chemically resilient, contributing to polyethylene's popularity as a multi-use plastic. However, polyethylene's chemical resilience also makes it a long-lived and decomposition-resistant pollutant when disposed of improperly. Being a h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pipecuronium
Pipecuronium (Arduan) is a bisquaternary aminosteroid muscle relaxant which blocks nicotinic acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction A neuromuscular junction (or myoneural junction) is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber. It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction. Muscles require innervation to .... It is also an antagonist of M2 and M3 muscarinic receptors and is the most potent neuromuscular blocking agent of the aminosteroid class. It is sold under the trade names Arduan and Pycuron. See also * Pancuronium bromide References Muscle relaxants Quaternary ammonium compounds Piperazines Acetate esters Bromides Nicotinic antagonists Androstanes {{musculoskeletal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |