|
Niğde Archaeological Museum
Niğde Archaeological Museum () is located in the centre of the Turkey, Turkish provincial capital, Niğde between ''Dışarı Cami Sokak'' and ''Öğretmenler Caddesi''. It contains objects found at sites in the surrounding area, including the tell of Köşk Höyük and the Graeco-Roman city of Tyana, both in the nearby town of Kemerhisar. History From the Second World War until 1950, part of the collection of the Istanbul Archaeology Museums, Istanbul Archaeological Museum was kept in the ''Akmedrese'', the main Quran school in Niğde, on ''Ak Medrese Caddesi''. The building continued to be used as a museum after that. Because that space ceased to be sufficient for the collection, work began on a new museum building in 1971. The Akmedrese was closed in 1977and the new museum was opened to visitors on 12 November 1982. Soon the collection outgrew this building as well and it was accordingly rebuilt and renovated. The re-opening of the present museum occurred in 2001. The museum i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karum (trade Post)
Karum ( Akkadian: ''kārum'' "quay, port, commercial district", plural ''kārū'', from Sumerian ''kar'' "fortification (of a harbor), break-water") is the name given to ancient Old Assyrian period trade posts in Anatolia (modern Turkey) from the 20th to 18th centuries BC. The main centre of ''karum'' trading was at the ancient town of Kanesh. History Early references to ''karu'' come from the Ebla tablets; in particular, a vizier known as Ebrium concluded the earliest treaty fully known to archaeology, known as the Treaty between Ebla and Abarsal. Nevertheless, it is also sometimes referred to as the "Treaty between Ebla and Aššur", because some scholars have disputed whether the text refers to Aššur or to Abarsal, an unknown location. In any case, the other city contracted to establish ''karu'' in Eblaite territory (Syria), among other things. The word ''karu'' "... derives from the mercantile quarter of Mesopotamian cities, which were usually just beyond the city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luwian Hieroglyphic
Anatolian hieroglyphs are an indigenous logographic script native to central Anatolia, consisting of some 500 signs. They were once commonly known as Hittite hieroglyphs, but the language they encode proved to be Luwian, not Hittite, and the term Luwian hieroglyphs is used in English publications. They are typologically similar to Egyptian hieroglyphs, but do not derive graphically from that script, and they are not known to have played the sacred role of hieroglyphs in Egypt. There is no demonstrable connection to Hittite cuneiform. History Individual Anatolian hieroglyphs are attested from the second and early first millennia BC across Anatolia and into modern Syria. A biconvex bronze personal seal was found in the Troy VIIb level (later half of the 12th century BC) inscribed with Luwian Hieroglyphs. The earliest examples occur on personal seals, but these consist only of names, titles, and auspicious signs, and it is not certain that they represent language. Most actual tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aktaş, Niğde
Aktaş is a town (''belde'') in the Niğde District, Niğde Province, Turkey Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen .... Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 1 March 2023. Its population is 2,024 (2022). References Populated places in Niğde District Town municipalities in Turkey {{Niğde-geo-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altunhisar
Altunhisar is a town in Niğde Province in the Central Anatolia region of Turkey. It is the seat of Altunhisar District.İlçe Belediyesi Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 1 March 2023. Its population is 3,171 (2022). Located on the Niğde plain to the north of the Melendiz mountains, 16 km for Bor and 30 km from the city of Niğde
Niğde (; ; Hittite: Nahita, Naxita) is a city and is located in the Central Anatolia region of Turkey. It is the seat of Niğde Province and Niğde District.
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
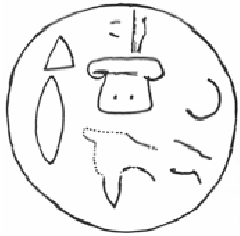
Keşlik Stele
The Keşlik Stele is a Neo-Hittite monument from northern Tyana, near Niğde discovered in 1962 in southern Turkey, which dates from the 8th century BC. Discovery The stele was discovered by Vural Sezer in the ''Bayındır Yaylası'' summer pasture of the village of Keşlik, a plateau north of Altunhisar in Niğde Province and was installed in the Niğde Museum. The location of discovery was part of the Iron Age Luwian kingdom of Tuwana. According to the testimony of local landowner Abdullah Tanik about the find, it was discovered by Turkish archaeologist Aykut Çınaroğlu in a 1962 survey. The stele had probably fallen from a hill which rises 25 m above the surrounding fields, since a depression has been found there which could have contained the pedestal of a stele. The monument is now in the Niğde Archaeological Museum and has the inventory number 51. Description The brown Basalt stele is 1.45 m high, 69 cm wide and about 27 cm thick. The upper surface is sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warpalawas
Warpalawas II () was a Luwian king of the Syro-Hittite kingdom of Tuwana in the region of Tabal who reigned during the late 8th century BC, from around to . Name Etymology The Luwian name was pronounced and was derived by adding the adjectival suffix to the adjective / (), meaning and , and cognate with the Hittite term (), meaning . According to the linguist Ilya Yakubovich, / could also be used as a title meaning "warrior," while the denoted status, thus giving the name the meaning of . The linguist Rostyslav Oreshko meanwhile interprets / as a substantivised epithet of the Luwian Storm-god Tarḫunzas, meaning , therefore giving to the name the meaning of , that is , being thus semantically similar to the name (), meaning . Cognates A Lydian cognate of the name is attested in the form () or () recorded in Phrygia. A Pisidian cognate of is also attested in the form (). In Akkadian Warpallawas II is referred to in Neo-Assyrian Akkadian sources as () and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarḫunz
Tarḫunz (stem: ''Tarḫunt-'') was the weather god and chief god of the Luwians, a people of Bronze Age and early Iron Age Anatolia. He is closely associated with the Hittite god Tarḫunna and the Hurrian god Teshub. Name The name of the Proto-Anatolian weather god can be reconstructed as ''*Tṛḫu-ent-'' ("conquering"), a participle form of the Proto-Indo-European root ''*terh2'', "to cross over, pass through, overcome". It has cognates in Hittite language, Hittite ''tarḫu-'', Latin ''trans-'', Dutch ''door'', German language, German ''durch'', and English ''through''. The same name was used in almost all Anatolian languages: Hittite ''Tarḫunna-''; Carian language, Carian ''Trquδ-''; Milyan language, Milyan ''Trqqñt-'', and Lycian language, Lycian: ''Trqqas'' (A), ''Trqqiz'' (B), who has been identified with Zeus. Norbert Oettinger has argued that the functions of the Anatolian weather god ultimately come from the Proto-Indo-European mythology, Proto-Indo-European go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather God
A weather god or goddess, also frequently known as a storm god or goddess, is a deity in mythology associated with weather phenomena such as thunder, snow, lightning, rain, wind, storms, tornadoes, and hurricanes. Should they only be in charge of one feature of a storm, they will be called after that attribute, such as a rain god or a lightning/thunder god. This singular attribute might then be emphasized more than the generic, all-encompassing term "storm god", though with thunder/lightning gods, the two terms seem interchangeable. They feature commonly in polytheism, polytheistic religions, especially in Proto-Indo-European mythology, Proto-Indo-European ones. Storm gods are most often conceived of as wielding thunder and/or lightning (some lightning gods' names actually mean "thunder", but since one cannot have thunder without lightning, they presumably wielded both). The ancients didn't seem to differentiate between the two, which is presumably why both the words "lightning bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niğde Stele
The Niğde Stele is a Neo-Hittite monument from the modern Turkish city of Niğde, which dates from the end of the 8th century BC. Discovery The stele was found on 24 September 1975 near the citadel of Niğde in the Çelebi Hüsamettin Bey Mosque (now Dışarı Camii), where it was reused, carved side down, as a step in front of the entrance to the mosque. It is now in the Niğde Archaeological Museum (inventory no. 22.1.75). Description The black basalt stele is 2.18 metres high and about a metre wide and belongs to a type which developed in the 10th century BC. It depicts the weather god Tarhunzas, holding an axe and a thunderbolt in his raised hands. Vines sprout from the ground to his left and grain to the right, similar to the İvriz relief. A very similar depiction of the same god appears on the Gökbez relief, relief in the village of Gökbez, Bor, Gökbez, some 22 km to the south. The figure is depicted with clothing, hair and beard of the Assyrian art, Assyrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuwanuwa
Tyana, earlier known as Tuwana during the Iron Age, and Tūwanuwa during the Bronze Age, was an ancient city in the Anatolian region of Cappadocia, in modern Kemerhisar, Niğde Province, Central Anatolia, Turkey. It was the capital of a Luwian-speaking Neo-Hittite kingdom in the 1st millennium BC. Name The name of the city was () during the Hittite Empire, and () in the Luwian language during the Syro-Hittite period. From the Luwian name were derived: * the Neo-Assyrian Akkadian name of the city, (), * and the Ancient Greek name of the city, (; ). Geography Location The location of the Hittite Tūwanuwa/Neo-Hittite Tuwana/Classical Tyana corresponds to the modern-day town of Kemerhisar in Niğde Province, Turkey. Surroundings The region around Tyana, which corresponded to roughly the same area as the former Iron Age kingdom of Tuwana, was known in Classical Antiquity as Tyanitis. History According to later Hittite sources, Tūwanuwa was an important cult centre, and it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luwian
Luwian (), sometimes known as Luvian or Luish, is an ancient language, or group of languages, within the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family. The ethnonym Luwian comes from ''Luwiya'' (also spelled ''Luwia'' or ''Luvia'') – the name of the region in which the Luwians lived. Luwiya is attested, for example, in the Hittite laws. The two varieties of Luwian are known after the scripts in which they were written: Cuneiform Luwian (''CLuwian'') and Hieroglyphic Luwian (''HLuwian''). There is no consensus as to whether these were a single language or two closely related languages. Classification Several other Anatolian languages – particularly Carian, Lycian, and Milyan (also known as Lycian B or Lycian II) – are now usually identified as related to Luwian – and as mutually connected more closely than other constituents of the Anatolian branch.Anna Bauer, 2014, ''Morphosyntax of the Noun Phrase in Hieroglyphic Luwian'', Leiden, Brill NV, pp. 9–10. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |