|
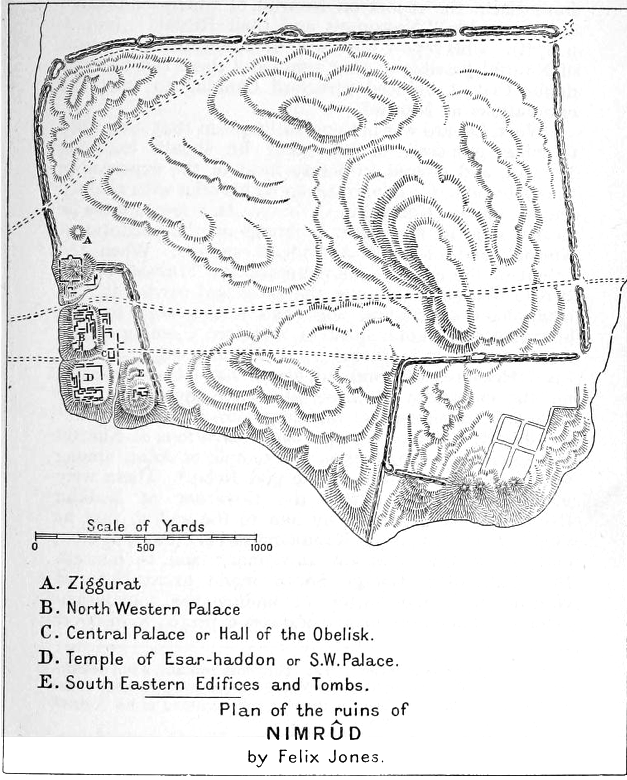
Nimrud
Nimrud (; ) is an ancient Assyrian people, Assyrian city (original Assyrian name Kalḫu, biblical name Calah) located in Iraq, south of the city of Mosul, and south of the village of Selamiyah (), in the Nineveh Plains in Upper Mesopotamia. It was a major Assyrian city between approximately 1350 BC and 610 BC. The city is located in a strategic position north of the point that the river Tigris meets its tributary the Great Zab.Brill's Encyclopedia of Islam 1913-36 p.923 The city covered an area of . The ruins of the city were found within of the modern-day Assyrian people, Assyrian village of Numaniyah, Al-Hamdaniya, Noomanea in Nineveh Governorate, Iraq. The name Nimrud was recorded as the local name by Carsten Niebuhr in the mid-18th century.N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nimrud Plan 1920
Nimrud (; ) is an ancient Assyrian city (original Assyrian name Kalḫu, biblical name Calah) located in Iraq, south of the city of Mosul, and south of the village of Selamiyah (), in the Nineveh Plains in Upper Mesopotamia. It was a major Assyrian city between approximately 1350 BC and 610 BC. The city is located in a strategic position north of the point that the river Tigris meets its tributary the Great Zab.Brill's Encyclopedia of Islam 1913-36 p.923 The city covered an area of . The ruins of the city were found within of the modern-day Assyrian village of Noomanea in |
Ashurnasirpal II
Ashur-nasir-pal II (transliteration: ''Aššur-nāṣir-apli'', meaning " Ashur is guardian of the heir") was the third king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 883 to 859 BC. Ashurnasirpal II succeeded his father, Tukulti-Ninurta II. His son and successor was Shalmaneser III and his queen was Mullissu-mukannišat-Ninua. Reign During his reign he embarked on a vast program of expansion, first conquering the peoples to the north in Asia Minor as far as Nairi and exacting tribute from Phrygia, then invading Aram (modern Syria) conquering the Aramaeans and Neo-Hittites between the Khabur and the Euphrates Rivers. The palaces, temples and other buildings raised by him bear witness to a considerable development of wealth and art. Cruelty Ashurnasirpal II was notorious for his brutality, using enslaved captives to build a new Assyrian capital at Kalhu (Nimrud) in Mesopotamia where he built many impressive monuments. He was also a shrewd administrator, who realized that he could gain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shalmaneser III
Shalmaneser III (''Šulmānu-ašarēdu'', "the god Shulmanu is pre-eminent") was king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 859 BC to 824 BC. His long reign was a constant series of campaigns against the eastern tribes, the Babylonians, the nations of Mesopotamia, Syria, as well as Kizzuwadna and Urartu. His armies penetrated to Lake Van and the Taurus Mountains; the Neo-Hittites of Carchemish were compelled to pay tribute, and the kingdoms of Hamath and Aram Damascus were subdued. It is in the annals of Shalmaneser III from the 850s BC that the Arab people, Arabs and Chaldeans first appear in recorded history. Reign Campaigns Shalmaneser began a campaign against Urartu and reported that in 858 BCE, he destroyed the city of Sugunia, and then in 853 BCE Araškun. Both cities are assumed to have been capitals of Urartu before Tushpa became a center for the Urartians. In 853 BC, a coalition was formed by eleven states, mainly by Hadadezer, King of Aram-Damascus; Irhuleni, king of Hama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamassu
''Lama'', ''Lamma'', or ''Lamassu'' (Cuneiform: , ; Sumerian language, Sumerian: lammař; later in Akkadian language, Akkadian: ''lamassu''; sometimes called a ''lamassuse'') is an Mesopotamia, Assyrian protective deity. Initially depicted as a goddess in Sumerian times, when it was called ''Lamma'', it was later depicted from Assyrian times as a hybrid of a human, bird, and either a bull or lion—specifically having a human head, the body of a bull or a lion, and bird wings, under the name ''Lamassu''. In some writings, it is portrayed to represent a goddess. A less frequently used name is ''shedu'' (Cuneiform: , ; Sumerian: alad; Akkadian, ''šēdu''), which refers to the male counterpart of a ''lamassu''. ''Lamassu'' represent the zodiacs, parent-stars or constellations. Goddess Lama The goddess Lama appears initially as a mediating goddess who precedes the orans and presents them to the deities. The protective deity is clearly labelled as Lam(m)a in a Kassites, Kassite st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assur
Aššur (; AN.ŠAR2KI, Assyrian cuneiform: ''Aš-šurKI'', "City of God Aššur"; ''Āšūr''; ''Aθur'', ''Āšūr''; ', ), also known as Ashur and Qal'at Sherqat, was the capital of the Old Assyrian city-state (2025–1364 BC), the Middle Assyrian Empire (1363–912 BC), and for a time, of the Neo-Assyrian Empire (911–609 BC). The remains of the city lie on the western bank of the Tigris River, north of the confluence with its tributary, the Little Zab, in what is now Iraq, more precisely in the al-Shirqat District of the Saladin Governorate. Occupation of the city itself continued for approximately 3,000 years, from the Early Dynastic Period to the mid-3rd century AD, when the city was sacked by the Sasanian Empire. The site is a World Heritage Site and was added to that organisation's list of sites in danger in 2003 as a result of a proposed dam, which would flood some of the site. It has been further threatened by the conflict that erupted following the US-led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Zab
The Great Zab or Upper Zab (; or ; ; ) is an approximately long river flowing through Turkey and Iraq. It rises in Turkey near Lake Van and joins the Tigris in Iraq south of Mosul. During its course, the river collects water from many tributaries and the drainage basin of the Great Zab covers approximately . The river and its tributaries are primarily fed by rainfall and snowmelt – as a result of which discharge fluctuates highly throughout the year. At least six dams have been planned on the Great Zab and its tributaries, but construction of only one, the Bekhme Dam, has commenced but was halted after the Gulf War. The Zagros Mountains have been occupied since at least the Lower Palaeolithic, and Neanderthal occupation of the Great Zab basin has been testified at the archaeological site of Shanidar Cave. Historical records for the region are available from the end of the third millennium BCE onward. In the Neo-Assyrian period, the Great Zab provided water for irriga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numaniyah, Al-Hamdaniya
Numaniyah () is a village in the Nineveh Governorate, Iraq. It is located near the ruins of the city of Nimrud in the Al-Hamdaniya District in the Nineveh Plains. History Numaniyah came under the occupation of the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) during its campaign in August 2014, but was later retaken by the 9th division of the Iraqi army The Iraqi Ground Forces (Arabic: القوات البرية العراقية), also referred to as the Iraqi Army (Arabic: الجيش العراقي), is the ground force component of the Iraqi Armed Forces. It was formerly known as the Royal Iraq ... on 13 November 2016 amidst the battle of Mosul. The Iraqi army subsequently set about clearing the village of mines and bombs planted by ISIL. References {{Reflist, 3 Populated places in Nineveh Governorate Nineveh Plains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of the modern Middle East. Just beyond it lies southwestern Iran, where the region transitions into the Iranian plateau, Persian plateau, marking the shift from the Arab world to Iran. In the broader sense, the historical region of Mesopotamia also includes parts of present-day Iran (southwest), Turkey (southeast), Syria (northeast), and Kuwait. Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from around 10,000 BC. It has been identified as having "inspired some of the most important developments in human history, including the invention of the wheel, the planting of the first cereal crops, the development of cursive script, mathematics, astronomy, and agriculture". It is recognised as the cradle of some of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosul
Mosul ( ; , , ; ; ; ) is a major city in northern Iraq, serving as the capital of Nineveh Governorate. It is the second largest city in Iraq overall after the capital Baghdad. Situated on the banks of Tigris, the city encloses the ruins of the ancient Old Assyrian Empire, Assyrian city of Nineveh—once the List of largest cities throughout history, largest city in the world—on its east side. Due to its strategic and central location, the city has traditionally served as one of the hubs of international commerce and travel in the region. It is considered as one of the historically and culturally significant cities of the Arab world. The North Mesopotamian dialect of Arabic commonly known as North Mesopotamian Arabic, ''Moslawi'' is named after Mosul, and is widely spoken in the region. Together, with the Nineveh Plains, Mosul is a historical center of the Assyrian people, Assyrians. The surrounding region is ethnically and religiously diverse; a large majority of the city is A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nimrod
Nimrod is a Hebrew Bible, biblical figure mentioned in the Book of Genesis and Books of Chronicles, the Books of Chronicles. The son of Cush (Bible), Cush and therefore the great-grandson of Noah, Nimrod was described as a king in the land of Shinar (Lower Mesopotamia). The Bible states that he was "a mighty hunter before the Lord [and] ... began to be mighty in the earth". Biblical and non-biblical traditions identify Nimrod as the ruler who had commissioned the construction of the Tower of Babel, and that identification led to his reputation as a king who had been rebellious against God. There is no direct evidence that Nimrod was an actual historical person in any of the non-biblical historic records, registers, or king lists (including any of the Mesopotamian ones, which are considered older than the biblical record). Historians have failed to match Nimrod with any real historically attested figure, or to find any historical, linguistic or genetic link between the Sumer, Sume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamshi-Adad V
Shamshi-Adad V () was the King of Assyria from 824 to 811 BC. He was named after the god Adad, who is also known as Hadad. Family Shamshi-Adad was a son and successor of King Shalmaneser III, the husband of Queen Shammuramat (by some identified with the mythical Semiramis), and the father of Adad-nirari III, who succeeded him as king. He was also a grandfather of Shalmaneser IV. Reign The first years of Shamshi-Adad's reign saw a serious struggle for the succession of the aged Shalmaneser. The revolt was led by Shamshi-Adad's brother Assur-danin-pal, and had broken out already by 826 BC. The rebellious brother, according to Shamshi-Adad's own inscriptions, succeeded in bringing to his side 27 important cities, including Nineveh. The rebellion lasted until 820 BC, weakening the Assyrian empire and its ruler; this weakness continued to reverberate in the kingdom until the reforms of Tiglath-Pileser III. Later in his reign, Shamshi-Adad campaigned against Southern Meso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyrian People
Assyrians (, ) are an ethnic group Indigenous peoples, indigenous to Mesopotamia, a geographical region in West Asia. Modern Assyrians Assyrian continuity, share descent directly from the ancient Assyrians, one of the key civilizations of Mesopotamia. While they are distinct from other Mesopotamian groups, such as the Babylonians, they share in the broader cultural heritage of the Mesopotamian region. Modern Assyrians may culturally self-identify as Terms for Syriac Christians#Syriac identity, Syriacs, Chaldean Catholics, Chaldeans, or Terms for Syriac Christians#Aramean identity, Arameans for religious, geographic, and tribal identification. Assyrians speak various dialects of Neo-Aramaic, specifically those known as Suret and Turoyo, which are among the oldest continuously spoken and written languages in the world. Aramaic was the lingua franca of West Asia for centuries and was the language spoken by historical Jesus, Jesus. It has influenced other languages such as Hebrew an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |