|
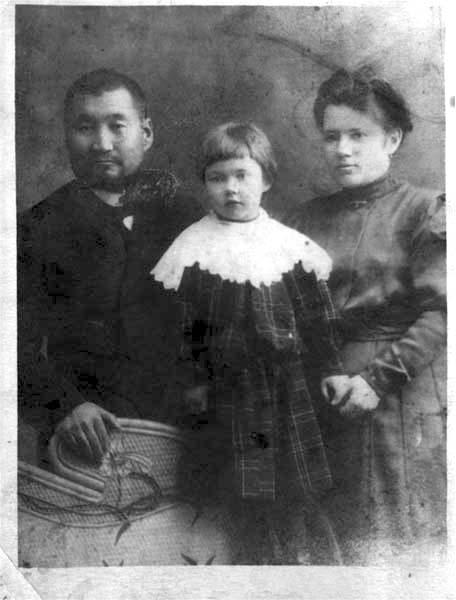
Nikolay Katanov
Nikolai Fedorovich Katanov (; 6 [18] May 1862, Izyum (Uzyum) near the village of Askiz (rural locality), Askiz9 March 1922, Kazan) was a Russian Turkologist, professor at the Kazan Federal University, Imperial Kazan University and the Kazan Theological Academy, doctor of comparative linguistics, Ethnography, ethnographer, folklorist and social activist. Katanov is widely regarded as the first Khakass scientist and was an Active State Councillor in 1915. He was born into the family of an ulus clerk. From 1876 to 1884, he studied at Krasnoyarsk gymnasium, graduating with a gold medal. He then attended the Faculty of Oriental Languages at St. Petersburg University from 1884 to 1888. On the recommendation of Vasily Radlov, he was sent on an ethnographic-linguistic expedition to Siberia and East Turkestan to study the languages and lifestyles of Turkic tribes. From 1889 to 1892, he studied the peoples of Khakassia, Tuva, Jetisu, Zhetysu, Tarbagatai Mountains, Tarbagatai, and Xinjiang. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Askiz (rural Locality)
Askiz (; Khakas language, Khakas: Асхыс, ''Asxıs'') is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, rural locality (a Village#Russia, selo) and the administrative center of Askizsky District of the Khakassia, Republic of Khakassia, Russia. Population: References Notes Sources * * {{Authority control Rural localities in Khakassia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnography
Ethnography is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. It explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject of the study. Ethnography is also a type of social research that involves examining the behavior of the participants in a given social situation and understanding the group members' own interpretation of such behavior. As a form of inquiry, ethnography relies heavily on participant observation, where the researcher participates in the setting or with the people being studied, at least in some marginal role, and seeking to document, in detail, patterns of social interaction and the perspectives of participants, and to understand these in their local contexts. It had its origin in social and cultural anthropology in the early twentieth century, but has, since then, spread to other social science disciplines, notably sociology. Ethnographers mainly use Qualitative research, qualitative methods, though they may also include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finno-Ugrian Society
Finno-Ugrian Society (, ) is a Finnish learned society, dedicated to the study of Uralic and Altaic languages. It was founded in Helsinki in 1883 by the proposal of professor Otto Donner. The society publishes several academic journal An academic journal (or scholarly journal or scientific journal) is a periodical publication in which Scholarly method, scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. They serve as permanent and transparent forums for the ...s, including: * ''Mémoires de la Société Finno-Ougrienne'' (278 volumes ) * ''Finnisch-ugrische Forschungen'' (69 volumes ) * ''Journal de la Société Finno-Ougrienne'' (99 volumes ). External links Home page Uralic languages [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budapest
Budapest is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns of Hungary, most populous city of Hungary. It is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, tenth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the List of cities and towns on the river Danube, second-largest city on the river Danube. The estimated population of the city in 2025 is 1,782,240. This includes the city's population and surrounding suburban areas, over a land area of about . Budapest, which is both a List of cities and towns of Hungary, city and Counties of Hungary, municipality, forms the centre of the Budapest metropolitan area, which has an area of and a population of 3,019,479. It is a primate city, constituting 33% of the population of Hungary. The history of Budapest began when an early Celts, Celtic settlement transformed into the Ancient Rome, Roman town of Aquincum, the capital of Pannonia Inferior, Lower Pannonia. The Hungarian p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leuven
Leuven (, , ), also called Louvain (, , ), is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the deelgemeente, sub-municipalities of Heverlee, Kessel-Lo, Leuven proper, Wilsele, Wijgmaal and part of Haasrode, Leuven, Haasrode and Korbeek-Lo, Leuven, Korbeek-Lo. It is the eighth largest city in Belgium, with more than 100,244 inhabitants. Leuven has been a university city since 1425. This makes it the oldest university city in the Low Countries. KU Leuven, the largest Dutch-speaking university in the world and the largest university in the Low Countries (and thus also Belgium's largest university), has its flagship campus in Leuven. The city is home of the headquarters of Anheuser-Busch InBev, the world's largest beer brewer and sixth-largest fast-moving consumer goods company. History Middle Ages The earli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narkompros
The People's Commissariat for Education (or Narkompros; , directly translated as the "People's Commissariat for Enlightenment") was the Soviet agency charged with the administration of public education and most other issues related to culture. In 1946, it was transformed into the Ministry of Education. Its first head was Anatoly Lunacharsky. However he described Nadezhda Krupskaya as the "soul of Narkompros". Mikhail Pokrovsky, Dmitry Leshchenko and Evgraf Litkens also played important roles. Lunacharsky protected most of the avant-garde artists such as Vladimir Mayakovsky, Kazimir Malevich, Vladimir Tatlin and Vsevolod Meyerhold. Despite his efforts, the official policy after Joseph Stalin put him in disgrace. Narkompros had seventeen sections, in addition to the main ones related to general education, e.g., * Likbez, a section for liquidation of illiteracy, * " Profobr", a section for professional education, * Glavlit, a section for literature and publishing (also in charge o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuvan Language
Tuvan, also spelt Tyvan, is a Turkic language spoken in the Republic of Tuva in South Central Siberia, Russia. There are small groups of Tuvans that speak distinct dialects of Tuvan in China and Mongolia. History The earliest record of Tuvan is from the early 19th century by ''Wūlǐyǎsūtái zhìlüè'' (), Julius Klaproth 1823, Matthias Castrén 1857, Nikolay Katanov, Vasily Radlov, etc. The name Tuva goes back as early as the publication of ''The Secret History of the Mongols''. The Tuva (as they refer to themselves) have historically been referred to as Soyons, Soyots or Uriankhais. Classification Tuvan (also spelled Tyvan) is linguistically classified as a Sayan Turkic language. Its closest relative is the moribund Tofa. Tuvan, as spoken in Tuva, is principally divided into four dialect groups; Western, Central, Northeastern, Southeastern. * Central: forms the basis of the literary language and includes Ovyur and Bii-Khem subdialects. The geographical c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the Northwest China, northwest of the country at the crossroads of Central Asia and East Asia. Being the List of Chinese administrative divisions by area, largest province-level division of China by area and the List of the largest country subdivisions by area, 8th-largest country subdivision in the world, Xinjiang spans over and has about 25 million inhabitants. Xinjiang Borders of China, borders the countries of Afghanistan, India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Pakistan, Russia, and Tajikistan. The rugged Karakoram, Kunlun Mountains, Kunlun and Tian Shan mountain ranges occupy much of Xinjiang's borders, as well as its western and southern regions. The Aksai Chin and Trans-Karakoram Tract regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarbagatai Mountains
The Tarbagatai Mountains are a mountain range straddling the China–Kazakhstan border, located in northwestern Xinjiang, China, and the Abai Region of East Kazakhstan. The name of the mountain derived from the Mongolian word ''tarvaga'', meaning " marmot", with the suffix ''-tai'', literally "to have" or "with". Tarbagan marmots live in this mountain range. An eastern extension of the Tarbagatai is the Saur Mountains. Drainage As is common for mountain ranges, there is more precipitation in the Tarbagatai mountains than in the adjacent flatlands. The mountains are thus an important watershed. Streams from the northern slopes of the Tarbagatai flow into Lake Zaysan, which eventually drains (via the Irtysh) into the Arctic Ocean. The streams of the southern slope, many of which merge into the Emil, flow into the Emin Valley, part of the endorheic Balkhash-Alakol Basin; they are an important source of water for several counties of Tacheng (Tarbagatay) Prefecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jetisu
Jetisu ( ) or Semirechye ( rus, Семиречье, p=sʲɪmʲɪˈrʲetɕje) or Heptopotamia is a historical region in Central Asia corresponding to the southeastern part of modern Kazakhstan. Name Jetisu is also transcribed Jeti-Suu (, ), Zhetisu, Jetisuw, Jetysu, Jeti-su or Jity-su, The name comes from "seven rivers" in Kazakh but meant "abounding in water", in contrast to the dry steppes of the eastern Balkhash area. It owes its name to the rivers that flow from the southeast into Lake Balkhash. Jetisu primarily falls into today's Jetisu Region and Almaty Region and other South-Eastern parts of Kazakhstan and some parts of Northern Kyrgyzstan. Geography The lands of the 19th-century Semirechye Oblast included the steppes south of Lake Balkhash and parts of the Tian Shan Mountains around Lake Issyk Kul. The province had an area of 147,300 km², and was bounded by the province of Semipalatinsk on the north, by China (Xinjiang) on the east and south, and by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuva
Tuva (; ) or Tyva (; ), officially the Republic of Tyva,; , is a Republics of Russia, republic of Russia. Tuva lies at the geographical center of Asia, in southern Siberia. The republic borders the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of the Altai Republic, Buryatia, Irkutsk Oblast, Khakassia, and Krasnoyarsk Krai, and shares an international border with Mongolia to the south. Tuva has a population of 336,651 (Russian Census (2021), 2021 census). Its capital city is Kyzyl, in which more than a third of the population reside. Historically part of Outer Mongolia as Tannu Uriankhai during the Qing dynasty, the last imperial dynasty of China, Tuva broke away in 1911 as the Uryankhay Republic following the 1911 Revolution, Xinhai Revolution, which created the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. It became a Uryankhay Krai, Russian protectorate in 1914 and was replaced by the nominally independent Tuvan People's Republic in 1921 (known officially as Tannu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khakassia
Khakassia (), officially the Republic of Khakassia, is a republic of Russia located in southern Siberia. It is situated between Krasnoyarsk Krai to the north and the Altai Republic to the south. The capital city of Khakassia is Abakan, and the region covers an area of about . The population of Khakassia is approximately 537,000 people, with the majority of the population living in urban areas. The region is known for its natural beauty, with numerous rivers, lakes, and mountains. The Khakassky Nature Reserve is located in the region, and it is home to a wide variety of wildlife, including brown bears, wolves, and sable. The region is also known for its traditional crafts, such as woodworking and embroidery, and for its traditional festivals and celebrations. Geography The republic is located in the southwestern part of Eastern Siberia and borders Krasnoyarsk Krai in the north and east, the Tuva Republic in the southeast and south, the Altai Republic in the south and southwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |