|
Niko Bartulović
Niko Bartulović (23 December 1890 – 1945) was a Croatian and Yugoslav writer, publisher, journalist and translator known for being one of the founders and ideologists of the Organization of Yugoslav Nationalists in 1921. He joined the Chetniks during World War II. Before World War II Bartulović was born on 23 December 1890 in Stari Grad, Hvar, Kingdom of Dalmatia, Dalmatia, Austria-Hungary (modern-day Croatia). Bartulović was the editor of journal "Pučka sloboda". In 1914, after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand he was arrested. Bartulović initiated and organized the publishing of the literary magazine ''Književni jug'' in 1918 while Branko Mašić provided financial sources. At the end of 1918, after World War I, he publicly proclaimed in Zagreb that Dalmatia would join the Kingdom of Serbia alone, if Zagreb did not want to do so. Bartulović is known as one of founders of the Organization of Yugoslav Nationalists (ORJUNA) in 1921, and one of its main ideol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stari Grad, Hvar
Stari Grad is a town on the northern side of the island of Hvar in Dalmatia, Croatia. One of the oldest towns in Europe, its position at the end of a long, protected bay and next to prime agricultural land has long made it attractive for human settlement. Stari Grad is also a municipality within the Split-Dalmatia County. The most ancient part of Stari Grad falls within the UNESCO Protected World Heritage Site of the Stari Grad Plain, while the entire municipality lies within the surrounding buffer zone. Name Stari Grad was originally named Faros () by the Greek settlers from the island of Paros, who arrived in 384 BC. While the name Faros is strikingly similar to the name of the Greek island the settlers arrived from, there is an alternate theory that it came from the previous inhabitants of the area. A great Battle of Pharos, naval battle was recorded a year after the establishment of Pharos colony by a Greek inscription in Pharos (384 – 383 BC) and by the Greek historian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik, historically known as Ragusa, is a city in southern Dalmatia, Croatia, by the Adriatic Sea. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations in the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean, a Port, seaport and the centre of the Dubrovnik-Neretva County. In 2021, its total population was 41,562. Recognizing its outstanding medieval architecture and fortifications, UNESCO inscribed the Old City of Dubrovnik as a World Heritage Site in 1979. The history of the city probably dates back to the 7th century, when the town known as was founded by refugees from Epidaurum (). It was under protectorate of the Byzantine Empire and later under the sovereignty of the Republic of Venice. Between the 14th and 19th centuries, Dubrovnik ruled itself as a Free state (polity), free state. The prosperity of the city was historically based on trade, maritime trade; as the capital of the maritime Republic of Ragusa, it achieved a high level of development, particularly during the 15th and 16t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ustaše
The Ustaše (), also known by anglicised versions Ustasha or Ustashe, was a Croats, Croatian fascist and ultranationalist organization active, as one organization, between 1929 and 1945, formally known as the Ustaša – Croatian Revolutionary Movement (). From its inception and before the World War II, Second World War, the organization engaged in a series of terrorist activities against the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, including collaborating with Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization, IMRO to assassinate King Alexander I of Yugoslavia#Assassination of Alexander I, Alexander I of Yugoslavia in 1934.The Assassination of Europe, 1918-1942: A Political History, Howard M. Sachar, University of Toronto Press, 2014, , pp. 251–258. During World War II in Yugoslavia, the Ustaše went on to perpetrate The Holocaust in the Independent State of Croatia, the Holocaust and genocide against its Jews, Jewish, Genocide of Serbs in the Independent State of Croatia, Serb and Romani Holoca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Serbs, Croats And Slovenes
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a country in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, but the term "Yugoslavia" () has been its colloquial name as early as 1922 due to its origins. "Kraljevina Jugoslavija! Novi naziv naše države. No, mi smo itak med seboj vedno dejali Jugoslavija, četudi je bilo na vseh uradnih listih Kraljevina Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev. In tudi drugi narodi, kakor Nemci in Francozi, so pisali že prej v svojih listih mnogo o Jugoslaviji. 3. oktobra, ko je kralj Aleksander podpisal "Zakon o nazivu in razdelitvi kraljevine na upravna območja", pa je bil naslov kraljevine Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev za vedno izbrisan." (Naš rod ("Our Generation", a monthly Slovene language periodical), Ljubljana 1929/30, št. 1, str. 22, letnik I.) The official name of the state was changed to "Kingdom of Yugoslavia" by King Alexander I on 3 October 1929. The pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yugoslavism
Yugoslavism, Yugoslavdom, or Yugoslav nationalism is an ideology supporting the notion that the South Slavs, namely the Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians (ethnic group), Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes belong to a single Yugoslavs, Yugoslav nation separated by diverging historical circumstances, forms of speech, and religious divides. During the interwar period, Yugoslavism became predominant in, and then the official ideology of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. There were two major forms of Yugoslavism in the period: the regime favoured integral Yugoslavism promoting Political unitarism, unitarism, Political centralization, centralisation, and unification of the country's Ethnic groups in Yugoslavia, ethnic groups into a single Yugoslav nation, by coercion if necessary. The approach was also applied to Languages of Yugoslavia, languages spoken in the Kingdom. The main alternative was Federalism, federalist Yugoslavism which advocated the autonomy of the historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
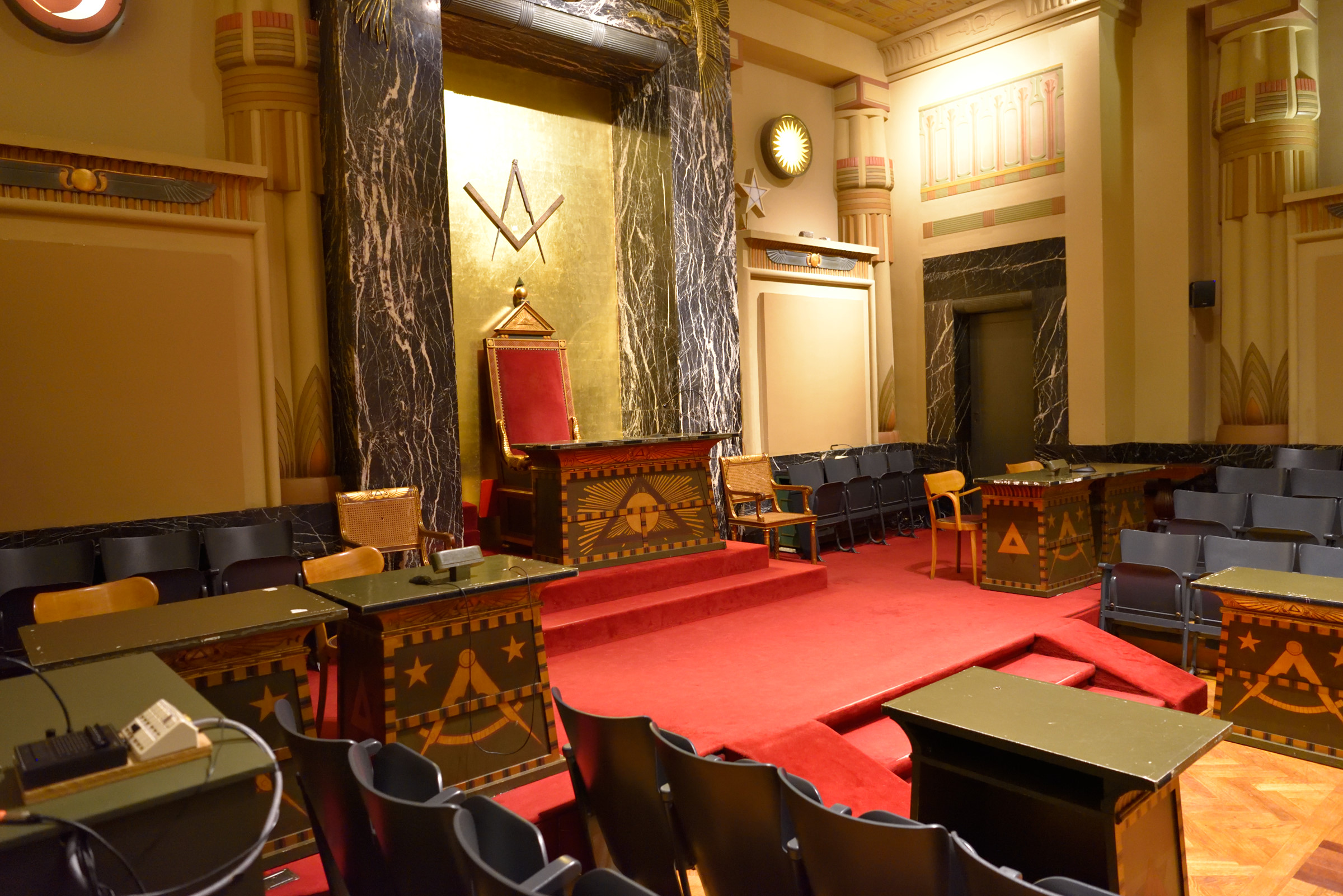
Masonic Lodge
A Masonic lodge (also called Freemasons' lodge, or private lodge or constituent lodge) is the basic organisational unit of Freemasonry. It is also a commonly used term for a building where Freemasons meet and hold their meetings. Every new lodge must be Warrant (finance), warranted or Charter, chartered by a Grand Lodge, but is subject to its direction only by enforcing the published constitution of the jurisdiction. By exception, the three surviving lodges that formed the world's first known grand lodge in London (now merged into the United Grand Lodge of England) have the unique privilege to operate as ''time immemorial'', i.e., without such warrant; only one other lodge operates without a warrant – the Grand Stewards' Lodge in London, although it is not entitled to the "time immemorial" status. A Freemason is generally entitled to visit any lodge in any jurisdiction (''i.e.'', under any Grand Lodge) in amity (recognition of mutual status) with his own Grand Lodge. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grga Novak
Grga Novak (2April 18887September 1978) was a distinguished Croatian historian, archaeologist and geographer, and President of the Yugoslav Academy of Sciences and Arts from 1958 to 1978. Born on the island of Hvar, he was Professor of Ancient History in the University of Zagreb, where he was also Rector between 1946 and 1947. He is best known for pioneering archaeology in Croatia, and his publications on the history of Dalmatia, Split, Dubrovnik, Hvar and the Adriatic Islands. Biography Grga Novak studied history, archaeology, and geography in Zagreb, Prague and Vienna, receiving his doctorate in 1913. From 1920, he taught in the Philosophy Faculty in Skoplje (then part of the University of Belgrade), then moved to the University of Zagreb, where he taught ancient history from 1924 to 1959. Dr Novak was a fellow of the Yugoslav Academy of Sciences and Arts in Zagreb from 1939, serving as its President from 1958 to 1978. Research and publications Grga Novak was the most importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdo Šišić
Ferdo Šišić (, 9 March 1869 – 21 January 1940) was a Croatian historian, the founding figure of the Croatian historiography of the 20th century. He made his most important contributions in the area of the Croatian early Middle Ages. Life Šišić was born in Vinkovci. After graduating from the comprehensive school in Zagreb in 1888, he studied at the Faculty of Philosophy at the University of Zagreb, earning a teacher's diploma in the summer of 1892. He worked as a teacher at high schools in Gospić from 1892 to 1893, Zagreb from 1893 to 1894, Osijek from 1894 to 1902 and again in Zagreb from 1902 to 1906. Šišić continued his studies in Vienna, where he met individuals who informed his vocation, including Vatroslav Jagić. Šišić returned to Zagreb after the 6th semester and attended the lectures of Tadija Smičiklas and Tomislav Maretić. In 1900 he obtained his Ph.D. at the Zagreb University with the work "''Zadar and Venice from 1159 to 1247''". In 1902 he earned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freemason
Freemasonry (sometimes spelled Free-Masonry) consists of fraternal groups that trace their origins to the medieval guilds of stonemasons. Freemasonry is the oldest secular fraternity in the world and among the oldest still-existing organizations in history. Modern Freemasonry broadly consists of three main traditions: *Anglo-American Freemasonry, Anglo-American style Freemasonry, which insists that a "volume of sacred law", such as the Bible, Quran, or other religious text be open in a working Masonic lodge, lodge, that every member professes belief in a God, supreme being, that only men be admitted, and discussion of religion or politics does not take place within the lodge. *Continental Freemasonry or Liberal Freemasonry which has continued to evolve beyond these restrictions, particularly regarding religious belief and political discussion. *Co-Freemasonry, Women Freemasonry or Co-Freemasonry, which includes organizations that either admit women exclusively (such as the Ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Party Of Yugoslavia
The League of Communists of Yugoslavia, known until 1952 as the Communist Party of Yugoslavia, was the founding and ruling party of SFR Yugoslavia. It was formed in 1919 as the main communist opposition party in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes and after its initial successes in the elections, it was proscribed by the royal government and was at times harshly and violently suppressed. It remained an illegal underground group until World War II when, after the invasion of Yugoslavia in 1941, the military arm of the party, the Yugoslav Partisans, became embroiled in a bloody civil war and defeated the Axis powers and their local auxiliaries. After the liberation from foreign occupation in 1945, the party consolidated its power and established a one-party state, which existed in that form of government until 1990, a year prior to the start of the Yugoslav Wars and breakup of Yugoslavia. The party, which was led by Josip Broz Tito from 1937 to 1980, was the first communi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Bakarić
Vladimir Bakarić (; 8 March 1912 – 16 January 1983) was a Yugoslav and Croatian communist revolutionary and a politician. Political career Bakarić helped to organise the partisan resistance in the Independent State of Croatia during World War II. From 1948 to 1969, he was the chairman of the League of Communists of Croatia and as such was a close collaborator of President Josip Broz Tito. Even after stepping down from the top post in communist hierarchy in the Socialist Republic of Croatia, he retained much influence and was even considered to be the most influential politician in Croatia. From 1964 to 1974, he was a member of the Council of the Federation, and since 1974 he has been a member of the Presidency of the SFRY, where he served as vice president from May 15, 1975, to May 15, 1976, and was re-elected to that position in May 1982. Together with Edvard Kardelj, he belonged to the more liberal wing of the Yugoslav political elite and was known for his statement on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Party Of Croatia
League of Communists of Croatia (, SKH) was the Croatian branch of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia (SKJ). It came into power in 1945. Until 1952, it was known as Communist Party of Croatia (, KPH). The party dissolved in 1990. History Kingdom of Yugoslavia The party was formally founded in 1937 with Pavle Gregorić as its first general secretary. The reasons for KPJ to have its specifically Croatian branch were partly ideological, partly practical. Croatia, just as Slovenia, which would have its Communist Party at the same time, was the most industrialised part of the country, with the biggest percentage of working class in the population, and, therefore, more likely to adopt communism than rural Serbia. The other, more practical, reason was in the increased marginalisation of Communists in Croatian political life due to public more preoccupied with ethnic issues and position of Croatia within Yugoslavia (cf. Croatia in the first Yugoslavia). Territorial aspiration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |