|
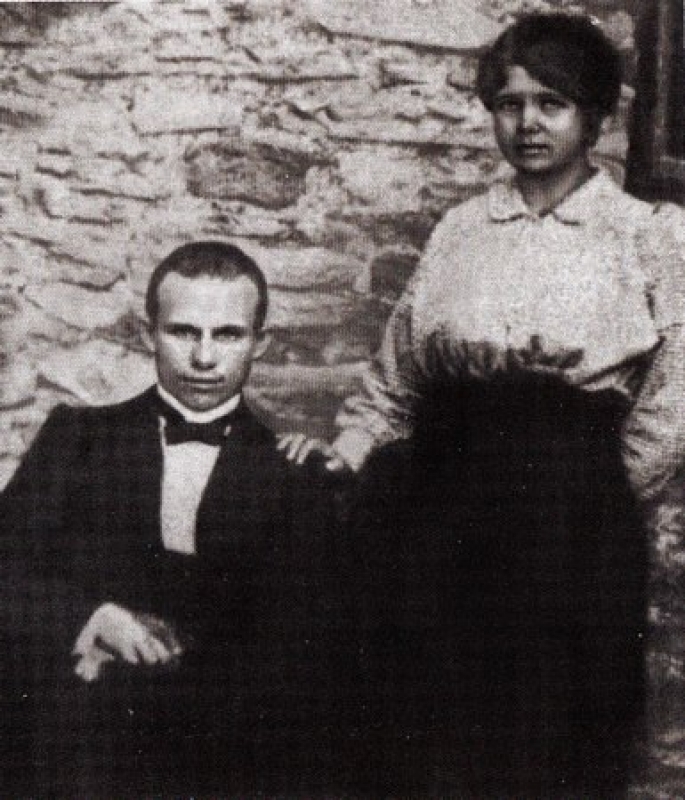
Nicolae Labiș
Nicolae Labiș () (December 2, 1935 in Poiana Mărului, Suceava County, Romania – December 22, 1956 in Bucharest) was a Romanian poet. Early life His father, Eugen, was the son of a forest brigade soldier and himself fought in World War II; he became a schoolteacher in 1931. His mother Ana-Profira, the daughter of a peasant killed in the Battle of Mărășești, was also a schoolteacher. He had two sisters, Margareta and Dorina. He grew up surrounded by mountains and forests. Labiș learned to read around age five from his mother's pupils. He also liked to draw as a child. He entered primary school in his native village (in his mother's class), then as a war refugee took third grade in Văcarea, Argeș, receiving top marks. Classmates of his later recalled that he would write poems and little plays and liked to declaim in public in this period. The family moved back to a village neighbouring his native one in May 1945. From 1946 to 1951, Labiș attended the Nicu Gane High S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Template:Infobox Writer/doc
Infobox writer may be used to summarize information about a person who is a writer/author (includes screenwriters). If the writer-specific fields here are not needed, consider using the more general ; other infoboxes there can be found in :People and person infobox templates. This template may also be used as a module (or sub-template) of ; see WikiProject Infoboxes/embed for guidance on such usage. Syntax The infobox may be added by pasting the template as shown below into an article. All fields are optional. Any unused parameter names can be left blank or omitted. Parameters Please remove any parameters from an article's infobox that are unlikely to be used. All parameters are optional. Unless otherwise specified, if a parameter has multiple values, they should be comma-separated using the template: : which produces: : , language= If any of the individual values contain commas already, add to use semi-colons as separators: : which produces: : , pseu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mihai Eminescu
Mihai Eminescu (; born Mihail Eminovici; 15 January 1850 – 15 June 1889) was a Romanians, Romanian Romanticism, Romantic poet, novelist, and journalist from Moldavia, generally regarded as the most famous and influential Romanian poet. Eminescu was an active member of the Junimea literary society and worked as an editor for the newspaper ''Timpul'' ("The Time"), the official newspaper of the Conservative Party (Romania, 1880–1918), Conservative Party (1880–1918). His poetry was first published when he was 16 and he went to Vienna, Austria to study when he was 19. The poet's manuscripts, containing 46 volumes and approximately 14,000 pages, were offered by Titu Maiorescu as a gift to the Romanian Academy during the meeting that was held on 25 January 1902. Notable works include ''Luceafărul (poem), Luceafărul'', ''Odă în metru antic'' (''Ode in Ancient Meter''), and the five ''Letters'' (''Epistles/Satires''). In his poems, he frequently used metaphysical, mythological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
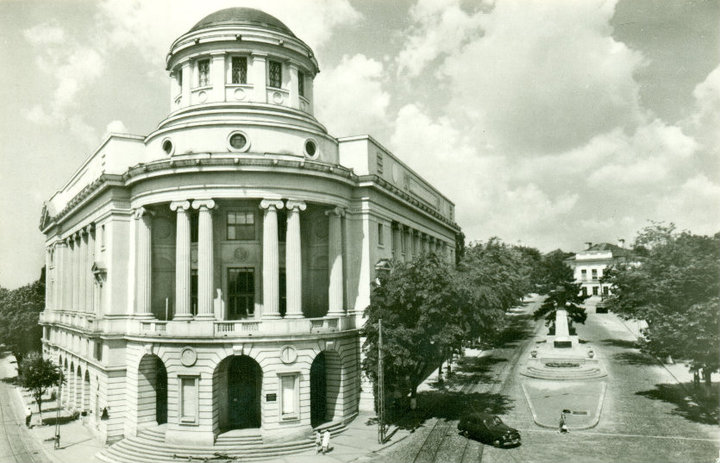
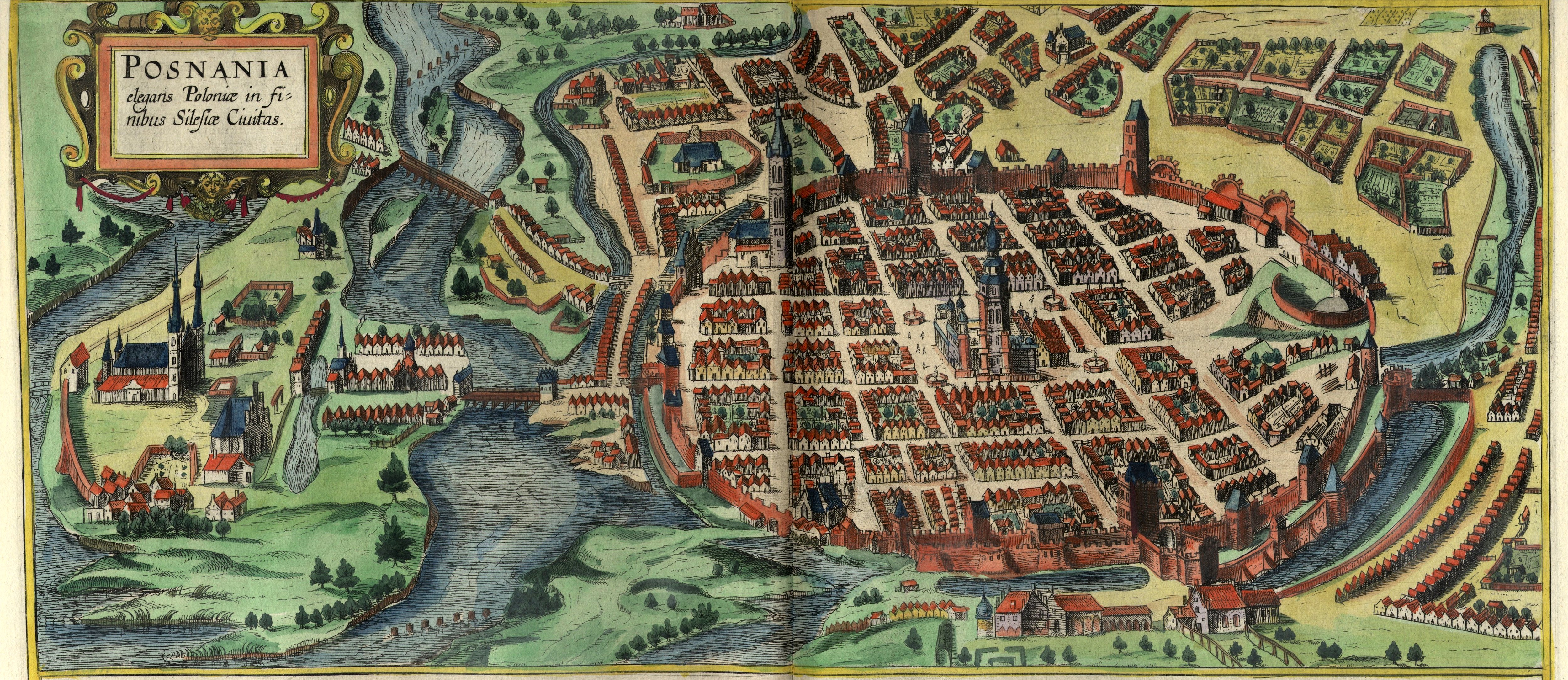
Poznań 1956 Protests
Poznań ( ) is a city on the River Warta in west Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business center and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's Fair (''Jarmark Świętojański''), traditional Saint Martin's croissants and a local dialect. Among its most important heritage sites are the Renaissance Old Town, Town Hall and Poznań Cathedral. Poznań is the fifth-largest city in Poland. As of 2023, the city's population is 540,146, while the Poznań metropolitan area (''Metropolia Poznań'') comprising Poznań County and several other communities is inhabited by over 1.029 million people. It is one of four historical capitals of medieval Poland and the ancient capital of the Greater Poland region, currently the administrative capital of the province called Greater Poland Voivodeship. Poznań is a center of trade, sports, education, technology and tourism. It is an important aca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
On The Personality Cult And Its Consequences
"On the Cult of Personality and Its Consequences" () was a report by Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev, First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, made to the 20th Congress of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union on 25 February 1956. Popularly known as the Secret Speech (), this is something of a misnomer, as copies of the speech were read out at thousands of meetings of Communist Party and Komsomol organisations across the country. Khrushchev's speech was sharply critical of the rule of the deceased General Secretary and Premier Joseph Stalin, particularly with respect to the purges which had especially marked the last years of the 1930s. Khrushchev charged Stalin with having fostered a leadership cult of personality despite ostensibly maintaining support for the ideals of communism. The speech was shocking in its day. There are reports that some of those present suffered heart attacks and that the speech even inspired suicides, due to the shock of all o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and the Premier of the Soviet Union, Chairman of the Council of Ministers (premier) from 1958 to 1964. During his tenure, he stunned the communist world with his denunciation of his predecessor Joseph Stalin and embarked on a campaign of de-Stalinization with his key ally Anastas Mikoyan. Khrushchev sponsored the early Soviet space program and presided over various domestic reforms. After some false starts, and a Cuban Missile Crisis, narrowly avoided nuclear war over Cuba, he conducted successful negotiations with the United States to reduce Cold War tensions. In 1964, the Kremlin circle Nikita Khrushchev#Removal, stripped him of power, replacing him with Leonid Brezhnev as the First Secretary and Alexei Kosygin as the Premier. Khrushchev was born in a village in western Russia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonte Răutu
Leonte Răutu (until 1945 Lev Nikolayevich (Nicolaievici) Oigenstein; February 28, 1910 – September 1993) was a Bessarabian-born Romanian communist activist and propagandist, who served as Deputy Prime Minister of Romania, deputy prime minister in 1969–1972. He was chief ideologist of the Romanian Communist Party ("Workers' Party") during the rule of Gheorghe Gheorghiu-Dej, and one of his country's few high-ranking communists to have studied Marxism from the source. Răutu was of Bessarabian Jews, Jewish origin, though he embraced Jewish atheism, atheism and anti-Zionism. His adventurous youth, with two prison terms served for illegal political activity, culminated in his self-exile to the Soviet Union, where he spent the larger part of World War II. Specializing in agitprop and becoming friends with communist militant Ana Pauker, he joined the Romanian section of Voice of Russia, Radio Moscow. Răutu made his way back to Romania during the communization process of the late 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Securitate
The Department of State Security (), commonly known as the Securitate (, ), was the secret police agency of the Socialist Republic of Romania. It was founded on 30 August 1948 from the '' Siguranța'' with help and direction from the Soviet MGB. The Securitate was, in proportion to Romania's population, one of the largest secret police forces in the Eastern bloc. The first budget of the Securitate in 1948 stipulated a number of 4,641 positions, of which 3,549 were filled by February 1949: 64% were workers, 4% peasants, 28% clerks, 2% persons of unspecified origin, and 2% intellectuals. By 1951, the Securitate's staff had increased fivefold, while in January 1956, the Securitate had 25,468 employees.Cristian Troncota"Securitatea: Începuturile", Magazin Istoric, 1998 At its height, the Securitate employed some 15,000 agents and almost half a million informants for a country with a population of 23 million by 1989. The Securitate under Nicolae Ceaușescu was one of the most br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Bucharest
The University of Bucharest (UB) () is a public university, public research university in Bucharest, Romania. It was founded in its current form on by a decree of Prince Alexandru Ioan Cuza to convert the former Princely Academy of Bucharest, Princely Academy into the current University of Bucharest, making it one of the oldest Romanian universities. It is one of the five members of the ''Universitaria Consortium'' (a group of elite Romanian universities). The University of Bucharest offers study programmes in Romanian and English and is classified as an ''advanced research and education university'' by the Ministry of Education and Scientific Research (Romania), Ministry of Education. History The University of Bucharest was founded by the Decree no. 765 of 4 July 1864 by Alexandru Ioan Cuza and is a leading academic centre and a significant point of reference in society. The University of Bucharest is rich in history and has been actively contributing to the development a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contemporanul
''Contemporanul'' (''The Contemporary'') was a Romanian literary magazine published in Iaşi, Romania Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ..., from 1881 to 1891. It was sponsored by the socialist circle of the city. A new magazine '' Contimporanul'' was published in the 1920s, claiming to continue the tradition of the former newspaper, without having the same political orientation towards Marxism. A new series of the magazine was published in 1946 and continues till present. References External links ''Contemporanul''* Corneliu Senchea - Contemporanul, Trei reviste si un nume care implineste 125 de aniHistory of ''Contemporanul'' on ideeaeuropeana.ro Communism in Romania Mass media in Iași Literary magazines published in Romania Political magazines published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Of Communist Youth
The Union of Communist Youth ( Romanian: '; UTC) was the Romanian Communist Party's youth organisation. Like many Young Communist organisations, it was modelled after the Soviet Komsomol. It aimed to cultivate young cadres into the party, as well as to help create the "new man" envisioned by communist ideologues. History Founded in 1922, the UTC went underground along with the rest of the party when it was banned in 1924. A marginal group under strict control of the Comintern's Young Communist International, it began to emerge as a mass movement in 1944, after the Red Army had entered Romania and the party became legal once again. Nicolae Ceaușescu was the First Secretary of the UTC from August 23, 1944, to June 1945. Beginning in 1948, the Romanian Workers' Party (PMR, as it was then called) began to contemplate merging and purging the country's youth organisations – political, professional, religious, cultural, etc. At the same time, young people were faced with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Communist Party
The Romanian Communist Party ( ; PCR) was a communist party in Romania. The successor to the pro-Bolshevik wing of the Socialist Party of Romania, it gave an ideological endorsement to a communist revolution that would replace the social system of the Kingdom of Romania. After being outlawed in 1924, the PCR remained a minor and illegal grouping for much of the interwar period and submitted to direct Comintern control. During the 1920s and the 1930s, most of its activists were imprisoned or took refuge in the Soviet Union, which led to the creation of competing factions that sometimes came into open conflict. That did not prevent the party from participating in the political life of the country through various front organizations, most notably the Peasant Workers' Bloc. In 1934–1936, PCR reformed itself in the mainland of Romania properly, with foreign observers predicting a possible communist takeover in Romania. The party emerged as a powerful actor on the Romanian political ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |