|
Niccolò Fontana Tartaglia
Nicolo, known as Tartaglia (; 1499/1500 – 13 December 1557), was an Italian mathematician, engineer (designing fortifications), a surveyor (of topography, seeking the best means of defense or offense) and a bookkeeper from the then Republic of Venice. He published many books, including the first Italian translations of Archimedes and Euclid, and an acclaimed compilation of mathematics. Tartaglia was the first to apply mathematics to the investigation of the paths of cannonballs, known as ballistics, in his ''Nova Scientia'' (''A New Science'', 1537); his work was later partially validated and partially superseded by Galileo's studies on falling bodies. He also published a treatise on retrieving sunken ships. Personal life Nicolo was born in Brescia, the son of Michele, a dispatch rider who travelled to neighbouring towns to deliver mail. In 1506, Michele was murdered by robbers, and Nicolo, his two siblings, and his mother were left impoverished. Nicolo experienced further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Galle
Philip (or Philips) Galle (1537 – March 1612) was a Dutch publisher, best known for publishing old master prints, which he also produced as designer and engraver. He is especially known for his reproductive engravings of paintings. Life Galle was born in Haarlem in the Netherlands, where he was a pupil of the humanist and engraver Dirck Volckertszoon Coornhert, Dirck Volkertsz. Coornhert. According to the RKD, he married Catharina van Rollant on 9 June 1569. They had five children who later became active as artists: Theodoor Galle, Theodoor, Cornelis Galle the Elder, Cornelis, Philips Galle II, Philips II, Justa (who married the engraver Adriaen Collaert) and Catharina (who married the engraver Karel de Mallery).Philips Galle in the RKD In Haarlem he engraved several works of the Haarlem painter Maarten van Heemskerck. Even while he worked fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, mathematical structure, structure, space, Mathematical model, models, and mathematics#Calculus and analysis, change. History One of the earliest known mathematicians was Thales of Miletus (); he has been hailed as the first true mathematician and the first known individual to whom a mathematical discovery has been attributed. He is credited with the first use of deductive reasoning applied to geometry, by deriving four corollaries to Thales's theorem. The number of known mathematicians grew when Pythagoras of Samos () established the Pythagorean school, whose doctrine it was that mathematics ruled the universe and whose motto was "All is number". It was the Pythagoreans who coined the term "mathematics", and with whom the study of mathematics for its own sake begins. The first woman math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euclid's Elements
The ''Elements'' ( ) is a mathematics, mathematical treatise written 300 BC by the Ancient Greek mathematics, Ancient Greek mathematician Euclid. ''Elements'' is the oldest extant large-scale deductive treatment of mathematics. Drawing on the works of earlier mathematicians such as Hippocrates of Chios, Eudoxus of Cnidus and Theaetetus (mathematician), Theaetetus, the ''Elements'' is a collection in 13 books of definitions, postulates, propositions and mathematical proofs that covers plane and solid Euclidean geometry, elementary number theory, and Commensurability (mathematics), incommensurable lines. These include Pythagorean theorem, Thales' theorem, the Euclidean algorithm for greatest common divisors, Euclid's theorem that there are infinitely many prime numbers, and the Compass-and-straightedge construction, construction of regular polygons and Regular polyhedra, polyhedra. Often referred to as the most successful textbook ever written, the ''Elements'' has continued to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federigo Commandino
Federico Commandino (1509 – 5 September 1575) was an Italian humanist and mathematician. Born in Urbino, he studied at Padua and then at Ferrara, where he received his doctorate in medicine under Antonio Musa Brassavola. He had numerous patrons throughout his life. Initially, aided by Grassi, the bishop of Viterbo, he then came under the patronage of Pope Clement VIII. In Urbino, he was sponsored by Guidobaldo II della Rovere, but then came to Rome with cardinal Ranuccio Farnese. In Rome, he was patronized by Cardinal Cervini, who served briefly as Pope. Lured back to Urbino by Francesco Maria II della Rovere. In Urbino, he putatively met John Dee, and corresponded with the scholars Conrad Dasypodius (il Dasipodio), Gerolamo Cardano, Francesco Maurolico, and Christopher Clavius. He was most famous for his central role as translator of works of ancient mathematicians. In this, his sources were primarily written in Greek and secondarily in Arabic, while his translations were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projectile Trajectories From Tartaglia's Nova Scientia
A projectile is an object that is propelled by the application of an external force and then moves freely under the influence of gravity and air resistance. Although any objects in motion through space are projectiles, they are commonly found in warfare and sports (for example, a thrown baseball, kicked football, fired bullet, shot arrow, stone released from catapult). In ballistics, mathematical equations of motion are used to analyze projectile trajectories through launch, flight, and impact. Motive force Blowguns and pneumatic rifles use compressed gases, while most other guns and cannons utilize expanding gases liberated by sudden chemical reactions by propellants like smokeless powder. Light-gas guns use a combination of these mechanisms. Railguns utilize electromagnetic fields to provide acceleration along the entire length of the device, greatly increasing the muzzle velocity. Some projectiles provide propulsion during flight by means of a rocket engine or jet engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abacus School
Abacus school is a term applied to any Italian school or tutorial after the 13th century, whose commerce-directed curriculum placed special emphasis on mathematics, such as algebra, among other subjects. These schools sprang up after the publication of Fibonacci's '' Book of the Abacus'' and his introduction of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. In Fibonacci's viewpoint, this system, originating in India around 400 BCE, and later adopted by the Arabs, was simpler and more practical than using the existing Roman numeric tradition. Italian merchants and traders quickly adopted the structure as a means of producing accountants, clerks, and so on, and subsequently abacus schools for students were established. These were done in many ways: communes could appeal to patrons to support the institution and find masters; religious institutions could finance and oversee the curriculum; independent masters could teach pupils. Unless they were selected for teaching occupations that were salaried, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
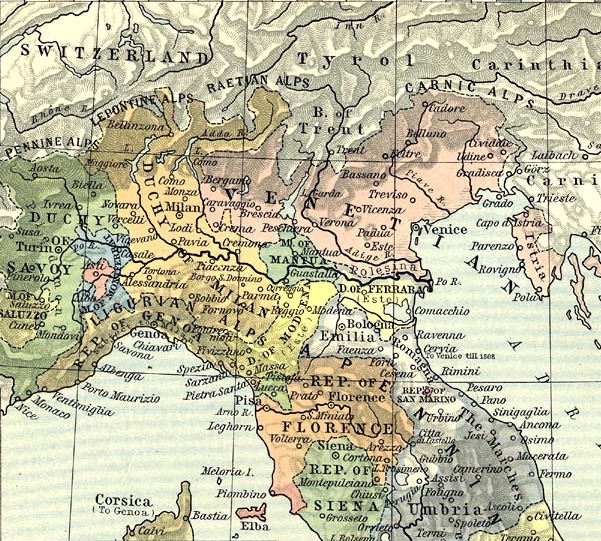
Verona
Verona ( ; ; or ) is a city on the Adige, River Adige in Veneto, Italy, with 255,131 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region, and is the largest city Comune, municipality in the region and in Northeast Italy, northeastern Italy. The metropolitan area of Verona covers an area of and has a population of 714,310 inhabitants. It is one of the main tourist destinations in Northern Italy because of its artistic heritage and several annual fairs and shows as well as the Opera, opera season in the Verona Arena, Arena, an ancient Ancient Rome, Roman Amphitheatre, amphitheater. Between the 13th and 14th centuries, the city was ruled by the Scaliger, della Scala family. Under the rule of the family, in particular of Cangrande I della Scala, the city experienced great prosperity, becoming rich and powerful and being surrounded by new walls. The della Scala era is preserved in numerous monuments around Verona. Two of William Shakespeare's plays are set in Ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The League Of Cambrai
The War of the League of Cambrai, sometimes known as the War of the Holy League and several other names, was fought from February 1508 to December 1516 as part of the Italian Wars of 1494–1559. The main participants of the war, who fought for its entire duration, were Early modern France, France, the Papal States, and the Republic of Venice; they were joined at various times by nearly every significant power in Western Europe, including Spain, the Holy Roman Empire, Kingdom of England, England, the Duchy of Milan, the Republic of Florence, the Duchy of Ferrara, and the Swiss mercenaries, Swiss. The war started with the ''Italienzug'' of Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, Maximilian I, King of the Romans, crossing into Venetian territory in February 1508 with his army on the way to be Coronation of the Holy Roman Emperor, crowned Holy Roman emperor by the pope in Rome. Meanwhile, Pope Julius II, intending to curb Venetian influence in northern History of Italy during foreig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falling Bodies
A set of equations describing the trajectories of objects subject to a constant gravitational force under normal Earth-bound conditions. Assuming constant acceleration ''g'' due to Earth's gravity, Newton's law of universal gravitation simplifies to ''F'' = ''mg'', where ''F'' is the force exerted on a mass ''m'' by the Earth's gravitational field of strength ''g''. Assuming constant ''g'' is reasonable for objects falling to Earth over the relatively short vertical distances of our everyday experience, but is not valid for greater distances involved in calculating more distant effects, such as spacecraft trajectories. History Galileo was the first to demonstrate and then formulate these equations. He used a ramp to study rolling balls, the ramp slowing the acceleration enough to measure the time taken for the ball to roll a known distance. He measured elapsed time with a water clock, using an "extremely accurate balance" to measure the amount of water.See the works of Stillman D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. He was born in the city of Pisa, then part of the Duchy of Florence. Galileo has been called the father of observational astronomy, modern-era classical physics, the scientific method, and modern science. Galileo studied speed and velocity, gravity and free fall, the principle of relativity, inertia, projectile motion and also worked in applied science and technology, describing the properties of the pendulum and "hydrostatic balances". He was one of the earliest Renaissance developers of the thermoscope and the inventor of various sector (instrument), military compasses. With an improved telescope he built, he observed the stars of the Milky Way, the phases of Venus, the Galilean moons, four largest satellites of Jupiter, Saturn's r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |