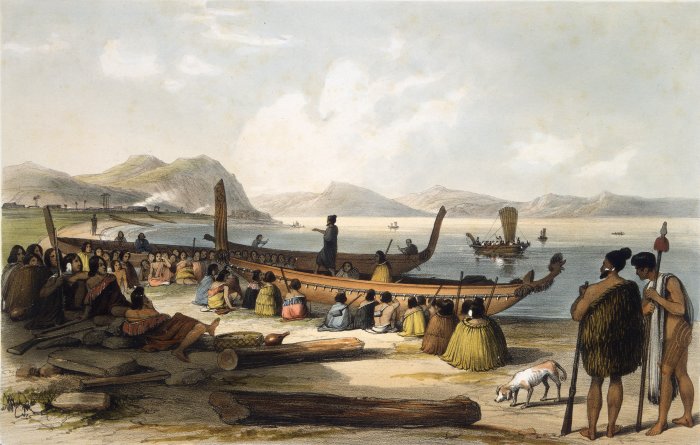|
Ngāti Tūmatakōkiri
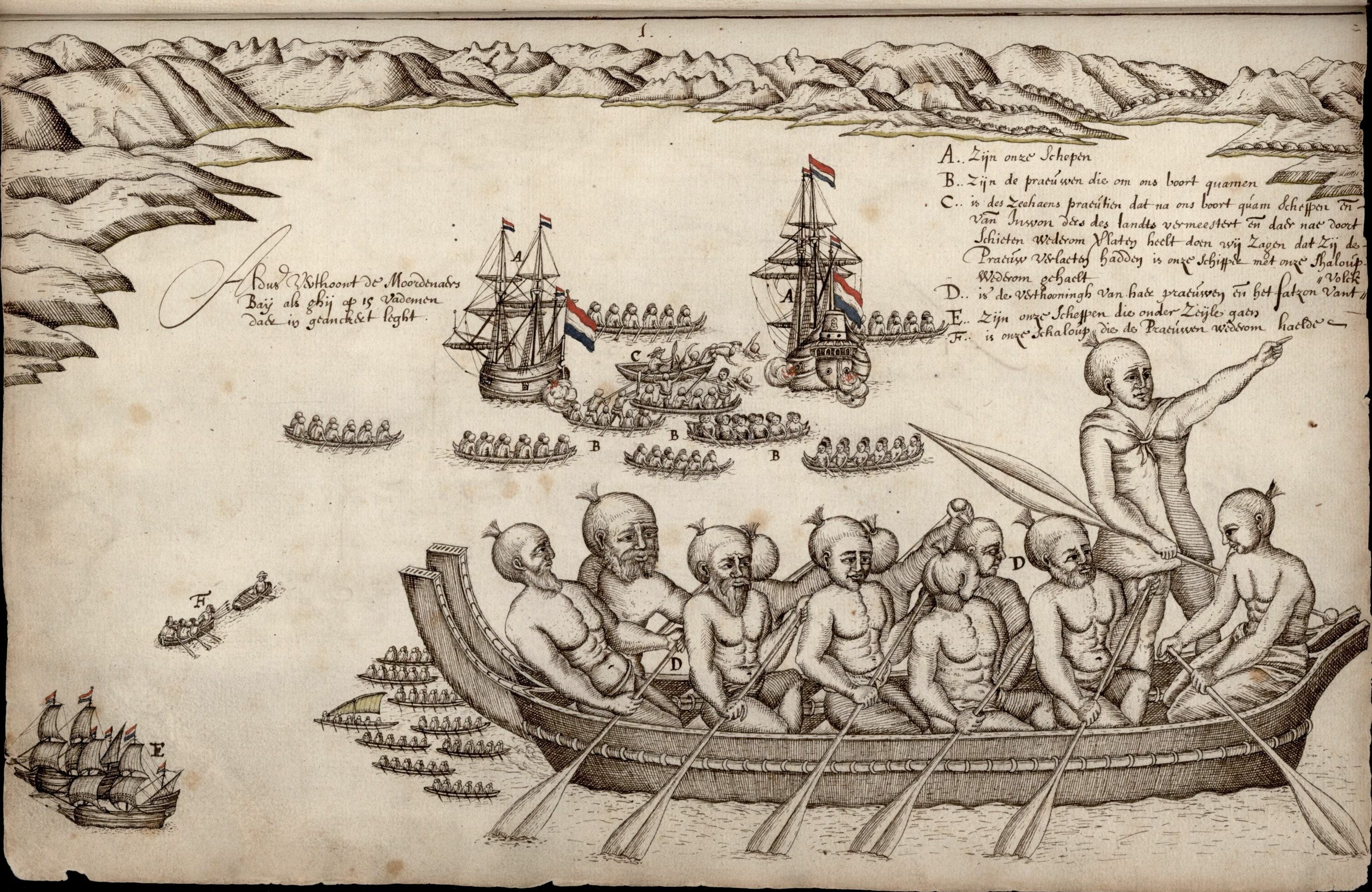
Ngāti Tūmatakōkiri is a Māori iwi (tribe) of New Zealand, who arrived on the '' Kurahaupō'' waka. In the 1600s the iwi settled northwestern South Island, becoming a major power in the region until the 1800s. In 1642, members of Ngāti Tūmatakōkiri made the first known contact between Europeans and Māori, when Dutch explorer Abel Tasman visited Golden Bay / Mohua. History The members of the '' Kurahaupō'' waka initially settled in the Bay of Plenty, and after several generations moved inland towards Taupō District and along the Whanganui River. In the late 1500s, the iwi began settling the Marlborough Sounds, however later moved westwards. By the 1600s, the rohe of Ngāti Tūmatakōkiri had expanded to include most of the northwest of the South Island, spanning from Māwhera (Greymouth) in the west to Whangarae ( Croisilles Harbour in the Marlborough Sounds), displacing Ngāti Wairangi ( Hauāuru Māori) to move south of Māwhera (Greymouth). Ngāti Tūmatakōkiri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasman District
Tasman District () is a local government district in the northwest of the South Island of New Zealand. It borders the Canterbury Region, West Coast Region, Marlborough Region and Nelson City. It is administered by the Tasman District Council, a unitary authority, which sits at Richmond, with community boards serving outlying communities in Motueka and Golden Bay / Mohua. The city of Nelson has its own unitary authority separate from Tasman District, and together they comprise a single region in some contexts, but not for local government functions or resource management (planning) functions. Name Tasman Bay, the largest indentation in the north coast of the South Island, was named after Dutch seafarer, explorer and merchant Abel Tasman. He was the first European to discover New Zealand on 13 December 1642 while on an expedition for the Dutch East India Company. Tasman Bay passed the name on to the adjoining district, which was formed in 1989 largely from the merger of Wai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croisilles Harbour
Croisilles Harbour (formerly spelt Croixelles Harbour) is a natural inlet north of Nelson at the westernmost edge of the Marlborough Sounds on the northern coast of New Zealand's South Island. It has two major arms, Ōkiwi Bay and Squally Cove. The inlet was named by early explorer Dumont D'Urville after his mother's home village of Croisilles, Calvados Croisilles () is a Communes of France, commune in the Calvados (department), Calvados Departments of France, department in the Normandy (administrative region), Normandy Regions of France, region in northwestern France. The mother of explorer D .... Reed, A.W., (1975) ''Place Names of New Zealand.'' Wellington: A.H. & A.W. Reed. p.94. References Marlborough Sounds Landforms of the Marlborough District {{Marlborough-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapiti Island
Kapiti Island (), sometimes written as Kāpiti Island, is an island nature reserve located off the west coast of the lower North Island of New Zealand and within the Kāpiti Coast District. Parts of the island were previously farmed, but it is now a predator-free sanctuary for endemic birds, including many endangered birds. The island is long, running southwest/northeast, and roughly wide, being more or less rectangular in shape, and has an area of . The island is separated from the North Island by the Rauoterangi Channel. The highest point on the island is Tūteremoana, . The seaward (west) side of the island is particularly rocky and has high cliffs, some hundreds of metres high, that drop straight into the sea. The cliffs are subject to very strong prevailing westerly winds and the scrubby vegetation that grows there is low and stunted by the harsh environmental conditions. A cross-section of the island would show almost a right-angled triangle, revealing its origins fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pounamu
Pounamu is a term for several types of hard and durable stone found in the South Island of New Zealand. They are highly valued in New Zealand, and carvings made from pounamu play an important role in Māori culture. Name The Māori word is derived from ''namu'', an archaic word that describes blue-green (or 'grue') cognate with Tahitian ''ninamu''. , also used in New Zealand English, in itself refers to two main types of green stone valued for carving: nephrite jade, classified by Māori as , , , and other names depending on colour; and translucent bowenite, a type of serpentine, known as . The collective term pounamu is preferred, as the other names in common use are misleading, such as New Zealand jade (not all pounamu is jade) and greenstone (a generic term used for unrelated stone from many countries). Pounamu is only found in New Zealand, whereas much of the carved "greenstone" sold in souvenir shops is jade sourced overseas. The Māori classification of pouna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngāti Kuia
Ngāti Kuia is a Māori iwi of the Northern South Island in New Zealand. They first settled in the Pelorus Sound / Te Hoiere, and later spread to the Marlborough Sounds, Nelson and Tasman districts to Taitapu on the West Coast, and as far south as the Nelson Lakes National Park. Ngāti Kuia tradition states that their founding tupuna Matua Hautere, a descendant of Kupe, came to Te Waipounamu in his waka Te Hoiere, guided by the kaitiaki (tribal guardian) Kaikaiawaro. Ngāti Kuia are the largest and oldest iwi of Te Tauihu o Te Waka a Māui in Te Waipounamu (The Prow of the Canoe of Māui). Also known as The Top of the South Island of New Zealand. The founding tipuna is Matua Hautere, a descendant of Kupe, who came to Te Waipounamu in his waka Te Hoiere. According to Ngāti Kuia whakapapa, Matua Hautere was guided by the kaitiaki Kaikaiāwaro and Ruamano who took the form of dolphins. Hinepopo/Hinepoupou, a Ngāti Kuia tipuna credited as being the first woman to swim R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapiti Coast
Kapiti or Kāpiti may refer to: * Kapiti (New Zealand electorate), a former Parliamentary electorate *Kāpiti Coast District, a local government district *Kapiti Island * Kapiti Coast Airport * Kāpiti College *Kāpiti Expressway * Kapiti Fine Foods, a company *Kapiti Line Metlink's Kapiti Line is the Railway electrification system, electrified southern portion of the North Island Main Trunk railway between New Zealand's capital city, Wellington, and Waikanae on the Kāpiti Coast, operated by Transdev Wellington o ..., a railway line * Kapiti Urban Area See also * {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngāti Apa
Ngāti Apa is a Māori iwi (tribe) in Rangitikei District of New Zealand. Its rohe (traditional tribal lands) extend between the Mangawhero, Whangaehu, Turakina and Rangitīkei rivers. This area is bounded by Whanganui River in the north-west, and Manawatū River in the south-east. The marae in this district include Tini wai tara, Whangaehu, Kauangaroa, and Parewanui. History Ngāti Apa take their name from the ancestor Apa-hāpai-taketake, who was the son of Ruatea. Stories of Apa's deeds place the tribe's origins in the Bay of Plenty. To the west of Pūtauaki mountain is a place known to Māori Māori or Maori can refer to: Relating to the Māori people * Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group * Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand * Māori culture * Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Co ... as Te Takanga-a-Apa (the place where Apa fell), so named because, according to one account, it was where Apa was kicked to the gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matukituki Valley, 1847
The Matukituki River is a short braided river in the Southern Alps of New Zealand's South Island. Both its West Branch and East Branch originate from the Main Divide mountain ranges near Mount Aspiring / Tititea. Their largely glacier-fed waters each flow for approximately before joining near Camerons Flat. After this confluence, the Matukituki River leaves the boundaries of Mount Aspiring National Park and continues for another to exit into Lake Wānaka at the lake's southwestern edge. Six glaciers feed tributary streams to the Matukituki River, the largest being the Upper Volta Glacier, Rob Roy Glacier, Maud Francis Glacier, and the Avalanche Glacier. From Camerons Flat onwards, the river is increasingly braided until it passes through a narrow gorge and under the West Wanaka bridge just before Lake Wānaka. History Most of the Southern Alps started over 220 million years ago as sediment and rock on top of volcanic rocks on the seafloor. Intense heat and pressure cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waka (canoe)
Waka () are Māori people, Māori watercraft, usually canoes ranging in size from small, unornamented canoes (''waka tīwai'') used for fishing and river travel to large, decorated war canoes (''waka taua'') up to long. The earliest remains of a canoe in New Zealand were found near the Anaweka River, Anaweka estuary in a remote part of the Tasman District and Radiocarbon dating, radiocarbon-dated to about 1400. The canoe was constructed in New Zealand, but was a sophisticated canoe, compatible with the style of other Polynesian voyaging canoes at that time. Since the 1970s, about eight large double-hulled canoes of about 20 metres have been constructed for oceanic voyaging to other parts of the Pacific Ocean, Pacific. They are made of a blend of modern and traditional materials, incorporating features from ancient Melanesia, as well as Polynesia. Waka taua (war canoes) ''Waka taua'' (in Māori language, Māori, ''waka'' means "canoe" and ''taua'' means "army" or "war party") a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch People
The Dutch, or Netherlanders (Dutch language, Dutch: ) are an ethnic group native to the Netherlands. They share a common ancestry and culture and speak the Dutch language. Dutch people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Argentina, Aruba, Australia, Brazil, Canada,Based on Statistics Canada, Canada 2001 Census]Linkto Canadian statistics. Caribbean Netherlands, Curaçao, Germany, Guyana, Indonesia, New Zealand, Sint Maarten, South Africa, Suriname, and the United States.According tFactfinder.census.gov The Low Countries were situated around the border of France and the Holy Roman Empire, forming a part of their respective peripheries and the various territories of which they consisted had become virtually autonomous by the 13th century. Under the Habsburgs, the Netherlands were organised into a single administrative unit, and in the 16th and 17th centuries the Northern Netherlands gained independence from Spain as the Dutch Republic. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Longfin Eel
The New Zealand longfin eel (''Anguilla dieffenbachii'') is a species of freshwater eel that is endemic to New Zealand. It is the largest freshwater eel in New Zealand and the only endemic species – the other eels found in New Zealand are the native shortfin eel (''Anguilla australis''), also found in Australia, and the naturally introduced Australian longfin eel (''Anguilla reinhardtii''). Longfin eels are long-lived, migrating to the Pacific Ocean near Tonga to breed at the end of their lives. They are good climbers as juveniles and so are found in streams and lakes a long way inland. An important traditional food source for Māori (who name them ), longfin eel numbers are declining and they are classified as endangered, but over one hundred tonnes are still commercially fished each year. Description The easiest way to identify the longfin eel is by the length of its fins: the dorsal (top) fin is about two-thirds the length of the body and starts significantly further tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngāi Tahu
Ngāi Tahu, or Kāi Tahu, is the principal Māori people, Māori (tribe) of the South Island. Its (tribal area) is the largest in New Zealand, and extends from the White Bluffs / Te Parinui o Whiti (southeast of Blenheim, New Zealand, Blenheim), Mount Māhanga and Kahurangi Point in the north to Stewart Island / Rakiura in the south. The comprises 18 (governance areas) corresponding to traditional settlements. According to the 2023 New Zealand census, 2023 census an estimated 84,000 people affiliated with the Kāi Tahu iwi. Ngāi Tahu originated in the Gisborne District of the North Island, along with Ngāti Porou and Ngāti Kahungunu, who all intermarried amongst the local Ngāti Ira. Over time, all but Ngāti Porou would migrate away from the district. Several were already occupying the South Island prior to Ngāi Tahu's arrival, with Kāti Māmoe only having arrived about a century earlier from the Hastings, New Zealand, Hastings District, and already having conquered W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |