|
Ngounié Province
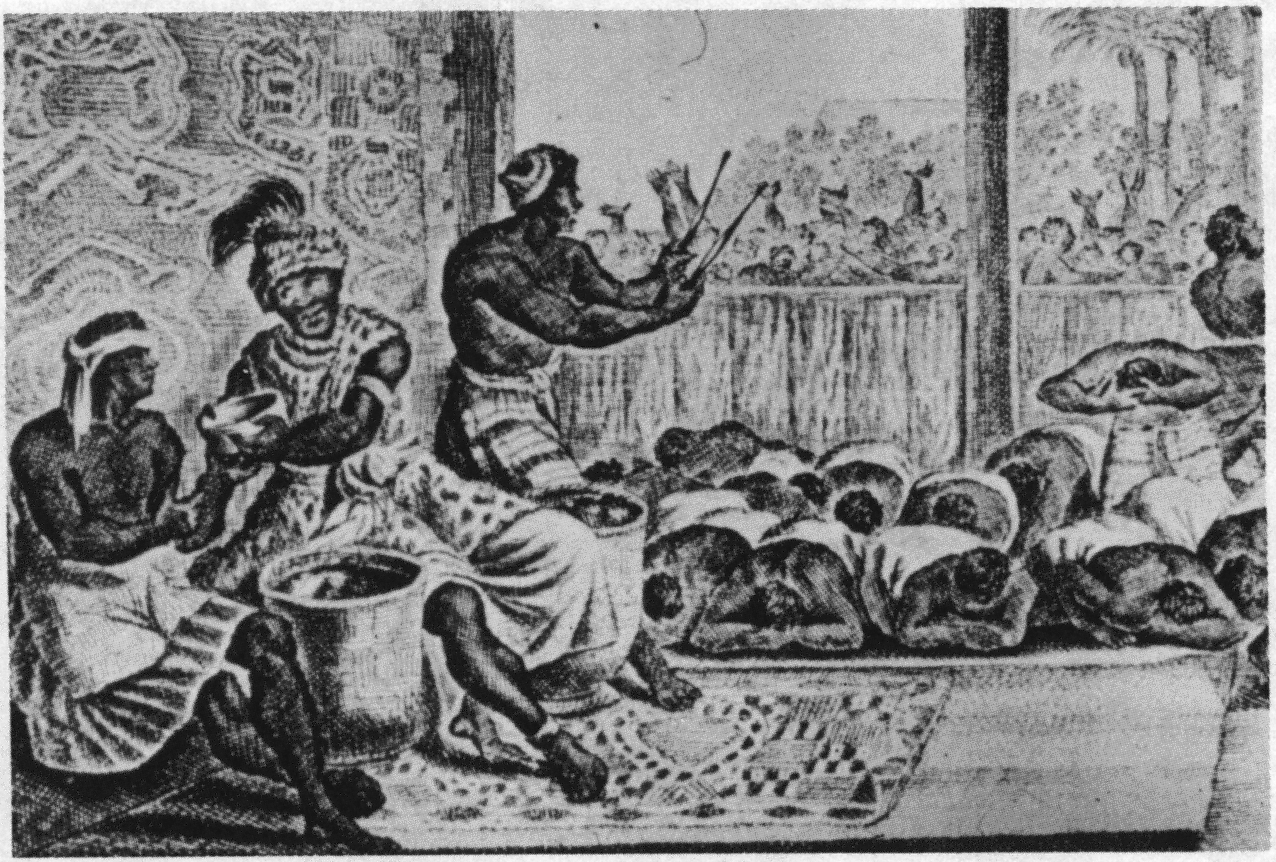
Ngounié is a province of south-central Gabon covering an area of . Its capital is Mouila. At the 2013 census it had 100,838 inhabitants. In 2016, its governor was Benjamin Nzigou. History The province is named after the Ngounié River, which crosses it with its many tributaries. In December 1858 the French explorer Paul Du Chaillu navigated the Nguoiné river upstream to Fougamou. On his journey, he met several local tribes whom he described in his diaries of his second voyage. Later, Catholic missions were built in Mandji, Sindara, and Saint Martin, whose architecture attracts many tourists. Geography The geography varies from large expanses of savannah and forest to the Monts de Cristal in the north to the Chaillu and Ikoundou ranges further south. Steep sloping mountains abut plains and dense forests, savannah, lakes, and rich farmland. Population Estimated at 101,415 inhabitants, the population of the Ngounié includes significant ethnic diversity including Eshir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Gabon
Gabon ( ; ), officially the Gabonese Republic (), is a country on the Atlantic coast of Central Africa, on the equator, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and the Gulf of Guinea to the west. It has an area of and a population of million people. There are coastal plains, mountains (the Cristal Mountains and the Chaillu Massif in the centre), and a savanna in the east. Libreville is the country's capital and largest city. Gabon's original inhabitants were the Bambenga. In the 14th century, Bantu migrants also began settling in the area. The Kingdom of Orungu was established around 1700. France colonised the region in the late 19th century. Since its independence from France in 1960, Gabon has had four presidents. In the 1990s, it introduced a multi-party system and a democratic constitution that aimed for a more transparent electoral process and reformed some governmental institutions. Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantu Peoples
The Bantu peoples are an Indigenous peoples of Africa, indigenous ethnolinguistic grouping of approximately 400 distinct native Demographics of Africa, African List of ethnic groups of Africa, ethnic groups who speak Bantu languages. The languages are native to countries spread over a vast area from West Africa, to Central Africa, Southeast Africa and into Southern Africa. Bantu people also inhabit southern areas of Northeast African states. There are several hundred Bantu languages. Depending on the definition of Dialect#Dialect or language, "language" or "dialect", it is estimated that there are between 440 and 680 distinct languages. The total number of speakers is in the hundreds of millions, ranging at roughly 350 million in the mid-2010s (roughly 30% of the demographics of Africa, population of Africa, or roughly 5% of world population, the total world population). About 90 million speakers (2015), divided into some 400 ethnic or tribal groups, are found in the Democratic Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogooué-Ivindo Province
Ogooué-Ivindo Province is the northeasternmost of Gabon's nine provinces, though its Lopé Department is in the very center of the country. It gets its name from two rivers, the Ogooué and the Ivindo. This province, containing thousands of square kilometres of rainforest, is the largest and most sparsely populated and much less developed than the rest of the country. As of 2013 it had a population of 63,293 people. The principal town is Makokou. History In 1873–4, Antoine-Alfred Marche and Victor de Compiègne (the Marquis de Compiegné) explored the Ogooué River region. They arrived in Lopé in 1874 but encountered hostility from the Fang-Meke people at the mouth of the Ivindo. Pierre Savorgnan de Brazza similarly made excursion to the region in November 1875 and between 1879 and 1882. In January 1995, a bout of the Ebola virus broke out in the forests of Ogooué-Ivindo. Nine out of 19 people died in the cases registered out of a population of 350 people. In 2010 it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
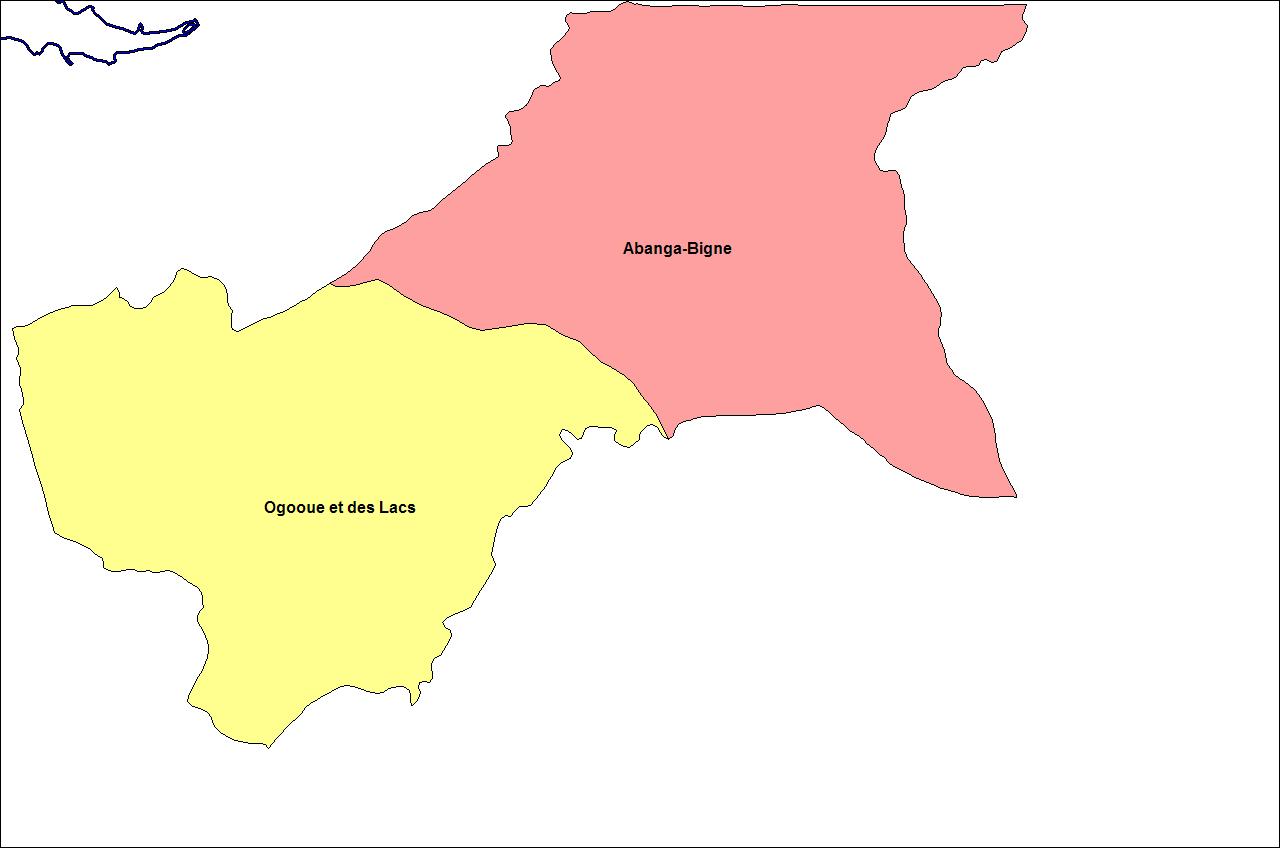
Moyen-Ogooué Province
Moyen-Ogooué is one of Gabon's nine provinces. It covers an area of . The provincial capital is Lambaréné. As of 2013, 69,287 people lived there. Unlike any other province of Gabon, Moyen-Ogooué has neither seacoast nor a foreign border. It borders the following provinces: *Estuaire Province – northwest *Woleu-Ntem Province – north-northeast * Ogooué-Ivindo Province – east * Ogooué-Lolo Province – southeast, at a quadripoint *Ngounié Province Ngounié is a province of south-central Gabon covering an area of . Its capital is Mouila. At the 2013 census it had 100,838 inhabitants. In 2016, its governor was Benjamin Nzigou. History The province is named after the Ngounié River, which ... – south * Ogooué-Maritime Province – west-southwest Moyen-Ogooué borders all but two of the rest of Gabon's provinces, thus more than any other province. Departments Moyen-Ogooué is divided into 2 departments: * Abanga-Bigne Department (capital Ndjolé) * Ogooué e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogooué-Maritime Province
Ogooué-Maritime is the westernmost of Gabon's nine provinces. It covers an area of 22,890 km. The provincial capital is Port-Gentil. It has a 2013 census population of 157,562. The shores of Ogooué-Maritime are of the Gulf of Guinea to the northwest and the South Atlantic Ocean The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ... to the southwest. It is the only coastal province without a foreign border. On land, it borders the following provinces: * Estuaire – north * Moyen-Ogooué – northeast * Ngounié – east * Nyanga – southeast Departments Ogooué-Maritime is divided into 3 departments: * Bendje Department ( Port-Gentil) * Etimboue Department ( Omboue) * Ndougou Department ( Gamba) Economy * Rabi Kounga oil field References Provinces of Gabon [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyanga Province
Nyanga is the southernmost of Gabon's nine provinces. The provincial capital is Tchibanga, which had a total of 31294 inhabitants in 2013 (more than the half of the province population). Nyanga is the least populated province of the nine and the other least developed, besides Ogooué-Ivindo. It is bordered by Ogooué-Maritime in the northwest, Ngounié in the north, and the Congo to the south ( Kouilou Region) and east ( Niari Region). The Atlantic Ocean—the lowest point in both Gabon and Nyanga Province—borders it in the west. Departments Nyanga is divided into 6 departments: * Basse-Banio Department ( Mayumba) * Douigni Department ( Moabi) * Doutsila Department (Mabanda) * Haute-Banio Department (Ndindi) * Mongo Department (Moulengui-Binza) * Mougoutsi Department ( Tchibanga) Statistics *Area: 21,285 km² *2-letter abbreviation/HASC: GA-NY *ISO 3166-2 ISO 3166-2 is part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of The Congo
The Republic of the Congo, also known as Congo-Brazzaville, the Congo Republic or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Democratic Republic of the Congo), is a country located on the western coast of Central Africa to the west of the Congo River. It is bordered to the west by Gabon, to the northwest by Cameroon, to the northeast by the Central African Republic, to the southeast by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south by the Angolan exclave of Cabinda Province, Cabinda, and to the southwest by the Atlantic Ocean. The region was dominated by Bantu peoples, Bantu-speaking tribes at least 3,000 years ago, who built trade links leading into the Congo River basin. From the 13th century, the present-day territory was dominated by a confederation led by Vungu which included Kakongo and Ngoyo. Kingdom of Loango, Loango emerged in the 16th century. In the late 19th century France colonised the region and incorporated it into French Equato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niari
Niari are a caste in Odisha. They are similar to the Dewar caste, and belong to the Sebc category. History The Niari have a history of being unemployed and poor, and alongside a few other castes, mostly adopted the profession of preparing flattened rice, which has traditionally been an offering to the deity Prasad. According to the Hindu scriptures the caste known as uranas-Ganga DynastyRadhi/Niari (Region du Niari) belonged to lower medium caste. In early times they were involved in govt offices but later the kayastha's were moved to this position and then they were moved out of the offices. Later they started their business like running sugar mills and preparing flattened rice. Modern Era: A return has been filed by the State. In paragraph-3 of the counter affidavit it has been averred that: "............ It has been seen from the Record-of-Rights of the Tahasil that caste "Kaibarta" has been recorded against some individual tenants and Niari against some other individual ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ndendé
Ndendé is a town and capital of the Dola Department in Ngounié Province, southern Gabon. It is located 549 kilometres southeast of Libreville Libreville (; ) is the capital and largest city of Gabon, located on the Gabon Estuary. Libreville occupies of the northwestern province of Estuaire Province, Estuaire. Libreville is also a port on the Gabon Estuary, near the Gulf of Guinea. A ... at the junction of the N1 and N6 roads. In 2006, the population was 6,346. Populated places in Ngounié Province {{Gabon-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dola, Gabon
Dola is a department of Ngounié Province in southern Gabon. The capital lies at Ndendé Ndendé is a town and capital of the Dola Department in Ngounié Province, southern Gabon. It is located 549 kilometres southeast of Libreville Libreville (; ) is the capital and largest city of Gabon, located on the Gabon Estuary. Librevil .... It had a population of 6,979 in 2013. Towns and villages References Ngounié Province Departments of Gabon {{Gabon-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bwiti
Bwiti is a spiritual discipline of the forest-dwelling Punu people and Mitsogo peoples of Gabon (where it is recognized as one of three official religions) and by the Fang people of Gabon. Modern Bwiti incorporates animism, ancestor worship, and in some cases, Christianity, into a syncretistic belief system. Bwiti practitioners use the psychedelic, dissociative root bark of the '' Tabernanthe iboga'' plant, specially cultivated for the religion, to promote radical spiritual growth, to stabilize community and family structure, to meet religious requirements, and to resolve pathological problems. The root bark has been consumed for hundreds of years in a Bwiti rite of passage ceremony, as well as in initiation rites and acts of healing. The experience yields complex visions and insights anticipated to be valuable to the initiate and the chapel. Liturgy Intoxicants in liturgy Taking Iboga brings both open and closed-eye visions which can be made stronger by darkness, ambiance, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kota People (Gabon)
The Bakota (or Kota) are a Bantu peoples, Bantu ethnic group from the northeastern region of Gabon and Republic of the Congo, Congo. The language they speak is called iKota, but is sometimes referred to as Bakota, ikuta, Kota, and among the Beti-Pahuin#Fang, Fang, they are known as Mekora. The language has several dialects, which include: Ndambomo, Mahongwe, Ikota-la-hua, Sake, Menzambi, Bougom. Some of these dialects themselves include regional variations of some kind. Culture The Kota are traditionally a patriarchal society, however some of the sub-groups such as the Mahongwe have over time adopted a matrilineal system of Lineage (anthropology), lineage (Mahongwe means, "from your father"). Another key feature of the Kota people is the originality of its circumcision and widow-purification rituals, which are generally kept secret. The true meaning of Bakota is unclear, however it may be derived from the word kota, which means to bind/to attach/to link, hereby suggesting they v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |