|
Neuroptera
The insect order (biology), order Neuroptera, or net-winged insects, includes the lacewings, mantidflies, antlions, and their relatives. The order consists of some 6,000 species. Neuroptera is grouped together with the Megaloptera (alderflies, fishflies, and dobsonflies) and Raphidioptera (snakeflies) in the unranked taxon Neuropterida (once known as Planipennia). Adult neuropterans have four membranous wings, all about the same size, with many wing vein, veins. They have chewing mouthparts, and undergo complete metamorphosis. Neuropterans first appeared during the Permian Period (geology), period, and continued to diversify through the Mesozoic era. During this time, several unusually large forms evolved, especially in the extinct Family (biology), family Kalligrammatidae, often called "the butterflies of the Jurassic" for their large, patterned wings. Anatomy and biology Neuropterans are soft-bodied insects with relatively few specialized features. They have large lateral co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
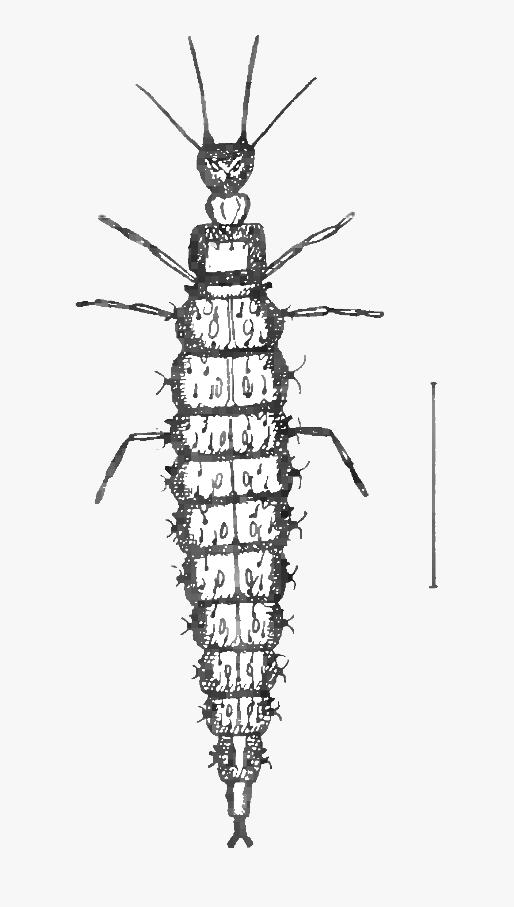
Antlion
The antlions are a group of about 2,000 species of insect in the neuropteran family (biology), family Myrmeleontidae. They are known for the predation, predatory habits of their larvae, which mostly dig pits to trap passing ants or other prey. In North America, the larvae are sometimes referred to as doodlebugs because of the marks they leave in the sand. The adult insects are less well known due to their relatively short lifespans in comparison with the larvae. Adults, sometimes known as antlion lacewings, mostly fly at dusk or just after dark and may be mistakenly identified as dragonfly, dragonflies or damselfly, damselflies. Antlions have a worldwide distribution. The greatest diversity occurs in the tropics, but a few species are found in cold-temperate locations, one such being the European ''Euroleon nostras''. They most commonly occur in dry and sandy habitats where the larvae can easily excavate their pits, but some larvae hide under debris or ambush their prey among le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantidflies
Mantispidae (), commonly known as mantidflies, mantispids, mantid lacewings, mantisflies or mantis-flies, is a family of small to moderate-sized insects in the order Neuroptera. There are many genera with around 400 species worldwide, especially in the tropics and subtropics. Only five species of '' Mantispa'' occur in Europe. As their names suggest, members of the group possess raptorial forelimbs similar to those of the praying mantis, a case of convergent evolution. Description and ecology About long and with a wingspan of , some mantidflies such as '' Climaciella brunnea'', '' Euclimacia nodosa'' are wasp mimics, but most are brownish with green, yellow and sometimes red hues. The vernacular and scientific names are derived from their mantis-like appearance, as their spiny "raptorial" front legs are modified to catch small insect prey and are very similar to the front legs of mantids (the only difference is that the pincers lack footpads and are not used for walking at al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Lacewing
Green lacewings are insects in the large family Chrysopidae of the order Neuroptera. There are about 85 genera and (differing between sources) 1,300–2,000 species in this widespread group. Members of the genera '' Chrysopa'' and '' Chrysoperla'' are very common in North America and Europe; they are very similar and many of their species have been moved from one genus to the other time and again, and in the nonscientific literature assignment to ''Chrysopa'' and ''Chrysoperla'' can rarely be relied upon. Since they are the most familiar neuropterans to many people, they are often simply called " lacewings". Since most of the diversity of Neuroptera are properly referred to as some sort of "lacewing", common lacewings is preferable. Description and ecology Green lacewings are delicate insects with a wingspan of 6 to over 65 mm, though the largest forms are tropical. They are characterized by a wide costal field in their wing venation, which includes the cross-veins. The b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raphidioptera
Snakeflies are a group of predatory insects comprising the order (biology), order Raphidioptera with two extant families: Raphidiidae and Inocelliidae, consisting of roughly 260 species. In the past, the group had a much wider distribution than it does now; snakeflies are found in temperate regions worldwide but are absent from the tropics and the Southern Hemisphere. Recognizable representatives of the group first appeared during the Early Jurassic. They are a Relict (biology), relict group, having reached their apex of diversity during the Cretaceous before undergoing substantial decline. An adult snakefly resembles a Hemerobiiformia, lacewing in appearance but has a notably elongated thorax which, together with the mobile head, gives the group their common name. The body is long and slender and the two pairs of long, membranous wings are prominently veined. Females have a large and sturdy ovipositor which is used to deposit eggs in some concealed location. They are holometabolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacewing
The Hemerobiiformia are a suborder of insects in the order Neuroptera that include most of the lacewings, antlions and their allies. The phylogeny of the Neuroptera was explored in 2014 using mitochondrial DNA sequences. The results indicate that the traditional Hemerobiiformia are paraphyletic, meaning that not all the members of the clade are considered to belong to it, in particular since it would include all the Myrmeleontiformia, with which the Hemerobiiformia were traditionally contrasted. The Osmyloidea, usually included in Hemerobiiformia, actually seem to represent a more ancient lineage basal to Hemerobiiformia as well as Myrmeleontiformia. The broken-up group is shown in the cladogram A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ...: See also * Stephanitis pyri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalligrammatidae
Kalligrammatidae, sometimes known as kalligrammatids or kalligrammatid lacewings, is a family of extinct insects in the order Neuroptera (lacewings) that contains twenty genera and a number of species. The family lived from the Middle Jurassic to the early Late Cretaceous before going extinct. Species of the family are known from Europe, Asia, and South America. The family has been occasionally described as "butterflies of the Jurassic" based on their resemblance to modern butterflies in morphology and ecological niche. Range The known distribution of Kalligrammatidae is widespread both in time and in location. Fossils of the family have been recovered from sediments in Western Europe, the British Isles, Central Asia, and China. The majority of described species, thirty one, are from Jurassic and Cretaceous fossils found in China. Eight species are known from Kazakhstan, the second largest number of species for a single country, while only two species are represented by foss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megaloptera
Megaloptera is an order of insects. It contains the alderflies, dobsonflies and fishflies, and there are about 300 known species. The order's name comes from Ancient Greek, from ''mega-'' (μέγα-) "large" + ''pteryx'' (πτέρυξ) "wing", in reference to the large, clumsy wings of these insects. Megaloptera are relatively unknown insects across much of their range, due to the adults' short lives, the aquatic larvae's often-high tolerance of pollution (so they are not often encountered by swimmers etc.), and the generally crepuscular or nocturnal habits. However, in the Americas the dobsonflies are rather well known, as their males have tusk-like mandibles. These, while formidable in appearance, are relatively harmless to humans and other animals; much like a peacock's feathers, they serve mainly to impress females. However, the mandibles are also used to hold females during mating, and some male dobsonflies spar with each other in courtship displays, trying to flip eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuropterida
The Neuropterida are a clade of holometabolous insects, sometimes placed at the superorder level. The clade contains the orders Neuroptera (lacewings, antlions), Megaloptera (alderflies, dobsonflies), and Raphidioptera (snakeflies), and includes over 5,700 described species. Historically, the name Neuroptera referred to this entire group, but it now refers only to lacewings and their relatives (antlions), which were formerly known as Planipennia. As part of the Holometabola and related to beetles, they can be considered an unranked taxon. Arguably, the Holometabola might instead be considered an unranked clade, and divided into numerous superorders to signify the close relationships of certain holometabolan groups.Haaramo, Mikko (2008): Mikko's Phylogeny ArchiveNeuropterida Version of 11 March 2008. Retrieved 5 May 2008. Some authors formerly included the Mecoptera (scorpionflies) in Neuropterida, but they actually belong to the Mecopteroidea (or Antliophora), the holometabolan c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, Thorax (insect anatomy), thorax and abdomen (insect anatomy), abdomen), three pairs of jointed Arthropod leg, legs, compound eyes, and a pair of antenna (biology), antennae. Insects are the most diverse group of animals, with more than a million described species; they represent more than half of all animal species. The insect nervous system consists of a insect brain, brain and a ventral nerve cord. Most insects reproduce Oviparous, by laying eggs. Insects Respiratory system of insects, breathe air through a system of Spiracle (arthropods), paired openings along their sides, connected to Trachea#Invertebrates, small tubes that take air directly to the tissues. The blood therefore does not carry oxygen; it is only partly contained in ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wing Vein
Insect wings are adult outgrowths of the insect exoskeleton that enable insects to fly. They are found on the second and third thoracic segments (the mesothorax and metathorax), and the two pairs are often referred to as the forewings and hindwings, respectively, though a few insects lack hindwings, even rudiments. The wings are strengthened by a number of longitudinal veins, which often have cross-connections that form closed "cells" in the membrane (extreme examples include the dragonflies and lacewings). The patterns resulting from the fusion and cross-connection of the wing veins are often diagnostic for different evolutionary lineages and can be used for identification to the family or even genus level in many orders of insects. Physically, some insects move their flight muscles directly, others indirectly. In insects with direct flight, the wing muscles directly attach to the wing base, so that a small downward movement of the wing base lifts the wing itself upward. Thos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Edition Of Systema Naturae
The 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' (Latin; the English title is ''A General System of Nature'') is a book written by Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus and published in two volumes in 1758 and 1759, which marks the starting point of zoological nomenclature. In it, Linnaeus introduced binomial nomenclature for animals, something he had already done for plants in his 1753 publication of ''Species Plantarum''. Starting point Before 1758, most biological catalogues had used polynomial names for the taxa included, including earlier editions of ''Systema Naturae''. The first work to consistently apply binomial nomenclature across the animal kingdom was the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae''. The International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature therefore chose 1 January 1758 as the "starting point" for zoological nomenclature and asserted that the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' was to be treated as if published on that date. Names published before that date are unavailable, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alderflies
Alderflies are megalopteran insects of the family Sialidae. They are closely related to the dobsonflies and fishflies as well as to the prehistoric Euchauliodidae. All living alderflies – about 66 species all together – are part of the subfamily Sialinae, which contains nine extant genera. Description Sialinae have a body length of less than 25 mm (1 inch), long filamentous antennae, and four large dark wings of which the anterior pair is slightly longer than the posterior. They lack ocelli and their fourth tarsal segment is dilated and deeply bilobed. Dead alderfly larvae are used as bait in fishing. Life cycle The females lay a vast number of eggs on grass stems near water. When the larvae are born they drop into the water or the ground nearby it and make their way into their new aquatic biome. The larvae are aquatic, active, armed with strong sharp mandibles, and breathe by means of seven pairs of abdominal branchial filaments. When full sized, which takes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |