|
Neurocan
Neurocan core protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NCAN'' gene. Neurocan is a member of the lectican / chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan protein families and consists of neurocan core protein and chondroitin sulfate. It is thought to be involved in the modulation of cell adhesion and migration. Role in bipolar disorder Neurocan is a significant component of the extracellular matrix, and its levels are modulated by a variety of factors, but mice in which the NCAN gene has been knocked out show no easily observable defects in brain development or behavior. However, a genome-wide association study published in 2011 identified Neurocan as a susceptibility factor for bipolar disorder Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in .... A more comprehensive study pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan
Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs) are proteoglycans consisting of a protein core and a chondroitin sulfate side chain. They are known to be structural components of a variety of human tissues, including cartilage, and also play key roles in neural development and glial scar formation. They are known to be involved in certain cell processes, such as cell adhesion, cell growth, receptor binding, cell migration, and interaction with other extracellular matrix constituents. They are also known to interact with laminin, fibronectin, tenascin, and collagen. CSPGs are generally secreted from cells. Importantly, CSPGs are known to inhibit axon regeneration after spinal cord injury. CSPGs contribute to glial scar formation post injury, acting as a barrier against new axons growing into the injury site. CSPGs play a crucial role in explaining why the spinal cord doesn't self-regenerate after an injury. General structure Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans are composed of a core protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lectican
Lecticans, also known as hyalectans, are a family of large chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans found in the extracellular matrix. There are four members of the lectican family: aggrecan, brevican, neurocan, and versican. Lecticans interact with hyaluronic acid and tenascin-R to form a ternary complex. Tissue distribution Aggregan and versican are widely distributed throughout all tissues. Where aggrecan is a major extracellular matrix constituent in cartilage, versican is widely expressed in a number of connective tissues, including those in vascular smooth muscle, skin, and the cells of central and peripheral nervous systems. Brevican and neurocan are primarily restricted to the central nervous system (CNS) and are particularly abundant in perineuronal nets. Structure All four lecticans contain an N-terminal globular domain (G1 domain) that in turn contains an immunoglobulin V-set domain and a Link domain that binds hyaluronic acid; a long extended central domain (CS) that is mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondroitin Sulfate
Chondroitin sulfate is a sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) composed of a chain of alternating sugars (N-Acetylgalactosamine, N-acetylgalactosamine and glucuronic acid). It is usually found attached to proteins as part of a proteoglycan. A chondroitin chain can have over 100 individual sugars, each of which can be sulfated in variable positions and quantities. Chondroitin sulfate is an important structural component of cartilage, and provides much of its resistance to compressive stress, compression. Along with glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate has become a widely used dietary supplement for treatment of osteoarthritis, although large clinical trials failed to demonstrate any symptomatic benefit of chondroitin. Fragments of chondroitin chains suspended in water elicit a fear response in many fishes, similar to schreckstoff, hypoxanthine-3N-oxide. Medical use Chondroitin is used in dietary supplements as an alternative medicine to treat osteoarthritis. It is also approved and regula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
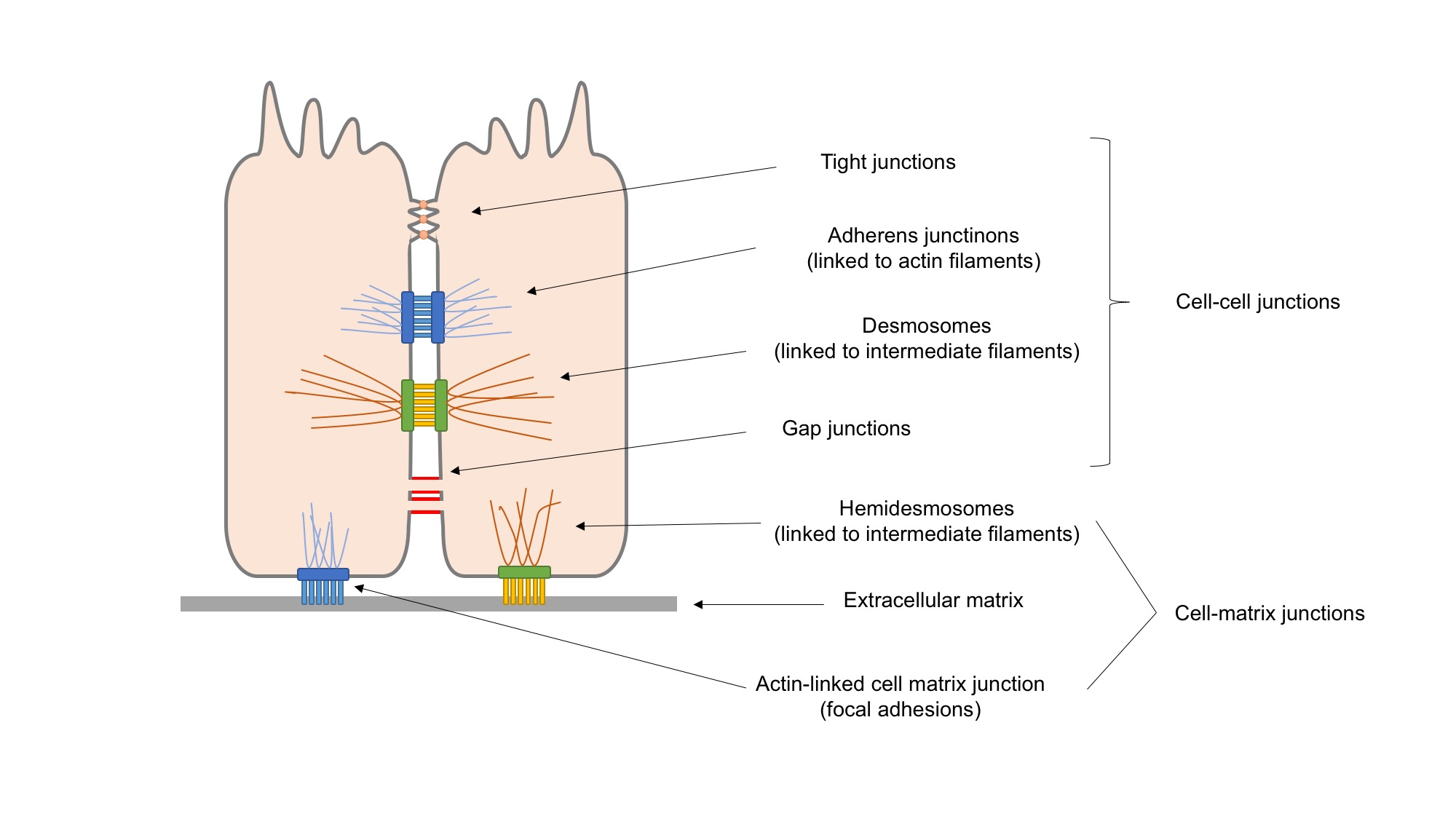
Cell Adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as Cell_junction, cell junctions or indirect interaction, where cells attach to surrounding extracellular matrix (ECM), a gel-like structure containing molecules released by cells into spaces between them. Cells adhesion occurs from the interactions between cell adhesion molecules, cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface. Cell adhesion links cells in different ways and can be involved in signal transduction for cells to detect and respond to changes in the surroundings. Other cellular processes regulated by cell adhesion include cell migration and tissue development in multicellular organisms. Alterations in cell adhesion can disrupt important cellular processes and lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and arthrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in some cases months. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called ''mania''; if it is less severe and does not significantly affect functioning, it is called ''hypomania''. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy, or irritable, and they often make impulsive decisions with little regard for the consequences. There is usually, but not always, a Sleep deprivation, reduced need for sleep during manic phases. During periods of depression, the individual may experience crying, have a negative outlook on life, and demonstrate poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide is high. Over a period of 20 years, 6% of those with bipolar disorder died by suicide, with about one-third Suicide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |