|
Neurite
A neurite or neuronal process refers to any projection from the cell body of a neuron. This projection can be either an axon or a dendrite. The term is frequently used when speaking of immature or developing neurons, especially of cells in culture, because it can be difficult to tell axons from dendrites before differentiation is complete. Neurite development The development of a neurite (neuritogenesis) requires a complex interplay of both extracellular and intracellular signals. At every given point along a developing neurite, there are receptors detecting both positive and negative growth cues from every direction in the surrounding space. The developing neurite sums together all of these growth signals in order to determine which direction the neurite will ultimately grow towards. While not all of the growth signals are known, several have been identified and characterized. Among the known extracellular growth signals are netrin, a midline chemoattractant, and semaphorin, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis) or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, spelling differences) is a long, slender cellular extensions, projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in Vertebrate, vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the Soma (biology), nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the peripheral nervous system, periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the Peripheral nervous system, peripheral and Central nervous system, central ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Body
In cellular neuroscience, the soma (: somata or somas; ), neurocyton, or cell body is the bulbous, non-process portion of a neuron or other brain cell type, containing the cell nucleus. Although it is often used to refer to neurons, it can also refer to other cell types as well, including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia. The part of the soma without the nucleus is called perikaryon (: perikarya). There are many different specialized types of neurons, and their sizes vary from as small as about 5 micrometres to over 10 millimetres for some of the smallest and largest neurons of invertebrates, respectively. The soma of a neuron (i.e., the main part of the neuron in which the dendrites branch off of) contains many organelles, including granules called Nissl granules, which are composed largely of rough endoplasmic reticulum and free polyribosomes. The cell nucleus is a key feature of the soma. The nucleus is the source of most of the RNA that is produced in neuron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule
Neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM), also called CD56, is a homophilic binding glycoprotein expressed on the surface of neurons, glia and skeletal muscle. Although CD56 is often considered a marker of neural lineage commitment due to its discovery site, CD56 expression is also found in, among others, the hematopoietic system. Here, the expression of CD56 is mostly associated with, but not limited to, natural killer cells. CD56 has been detected on other lymphoid cells, including gamma delta (γδ) Τ cells and activated CD8+ T cells, as well as on dendritic cells. NCAM has been implicated as having a role in cell–cell adhesion, neurite outgrowth, synaptic plasticity, and learning and memory. Forms, domains and homophilic binding NCAM is a glycoprotein of Immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. At least 27 alternatively spliced NCAM mRNAs are produced, giving a wide diversity of NCAM isoforms. The three main isoforms of NCAM vary only in their cytoplasmic domain: * NCAM-120kDa (GP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewy Neurites
Lewy may refer to: * Lewy (surname) * Levi, a biblical personage * Lewy body, abnormal aggregates of protein that develop inside nerve cells of the brain * Dementia with Lewy bodies, progressive brain disease associated with degenerative dementia in the elderly * A nickname for Polish footballer Robert Lewandowski (born 1988) See also * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic AMP
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger, or cellular signal occurring within cells, that is important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal transduction in many different organisms, conveying the cAMP-dependent pathway. History Earl Sutherland of Vanderbilt University won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1971 "for his discoveries concerning the mechanisms of the action of hormones", especially epinephrine, via second messengers (such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cyclic AMP). Synthesis The synthesis of cAMP is stimulated by trophic hormones that bind to receptors on the cell surface. cAMP levels reach maximal levels within minutes and decrease gradually over an hour in cultured cells. Cyclic AMP is synthesized from ATP by adenylate cyclase located on the inner side of the plasma membrane and anchored at vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotrophin
Neurotrophins are a family of proteins that induce the survival, development, and function of neurons. They belong to a class of growth factors, secreted proteins that can signal particular cells to survive, differentiate, or grow. Growth factors such as neurotrophins that promote the survival of neurons are known as neurotrophic factors. Neurotrophic factors are secreted by target tissue and act by preventing the associated neuron from initiating programmed cell death – allowing the neurons to survive. Neurotrophins also induce differentiation of progenitor cells, to ''form'' neurons. Although the vast majority of neurons in the mammalian brain are formed prenatally, parts of the adult brain (for example, the hippocampus) retain the ability to grow new neurons from neural stem cells, a process known as neurogenesis. Neurotrophins are chemicals that help to stimulate and control neurogenesis. Terminology According to the United States National Library of Medicine's medical su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glial
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cell (biology), cells in the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord) and in the peripheral nervous system that do not produce Action potential, electrical impulses. The neuroglia make up more than one half the volume of neural Tissue (biology), tissue in the human body. They maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and provide support and protection for neurons. In the central nervous system, glial cells include oligodendrocytes (that produce myelin), astrocytes, ependymal cells and microglia, and in the peripheral nervous system they include Schwann cells (that produce myelin), and Satellite glial cell, satellite cells. Function They have four main functions: * to surround neurons and hold them in place * to supply nutrients and oxygen to neurons * to Myelination, insulate one neuron from another * to destroy pathogens and remove dead neurons. They also play a role in neurotransmission and Synaps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenopus
''Xenopus'' () (Gk., ξενος, ''xenos'' = strange, πους, ''pous'' = foot, commonly known as the clawed frog) is a genus of highly aquatic frogs native to sub-Saharan Africa. Twenty species are currently described within it. The two best-known species of this genus are '' Xenopus laevis'' and '' Xenopus tropicalis'', which are commonly studied as model organisms for developmental biology, cell biology, toxicology, neuroscience and for modelling human disease and birth defects. The genus is also known for its polyploidy, with some species having up to 12 sets of chromosomes. Characteristics ''Xenopus laevis'' is a rather inactive creature. It is incredibly hardy and can live up to 15 years. At times the ponds that ''Xenopus laevis'' is found in dry up, compelling it, in the dry season, to burrow into the mud, leaving a tunnel for air. It may lie dormant for up to a year. If the pond dries up in the rainy season, ''Xenopus laevis'' may migrate long di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mouse
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus''). Mice are also popular as pets. In some places, certain kinds of Apodemus, field mice are locally common. They are known to invade homes for food and shelter. Mice are typically distinguished from rats by their size. Generally, when a muroid rodent is discovered, its common name includes the term ''mouse'' if it is smaller, or ''rat'' if it is larger. The common terms ''rat'' and ''mouse'' are not Taxonomy (biology), taxonomically specific. Typical mice are classified in the genus ''Mus (genus), Mus'', but the term ''mouse'' is not confined to members of ''Mus'' and can also apply to species from other genera such as the deer mouse, deer mouse (''Peromyscus''). Fancy mouse, Domestic mice sold as pets often differ substantially in size f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
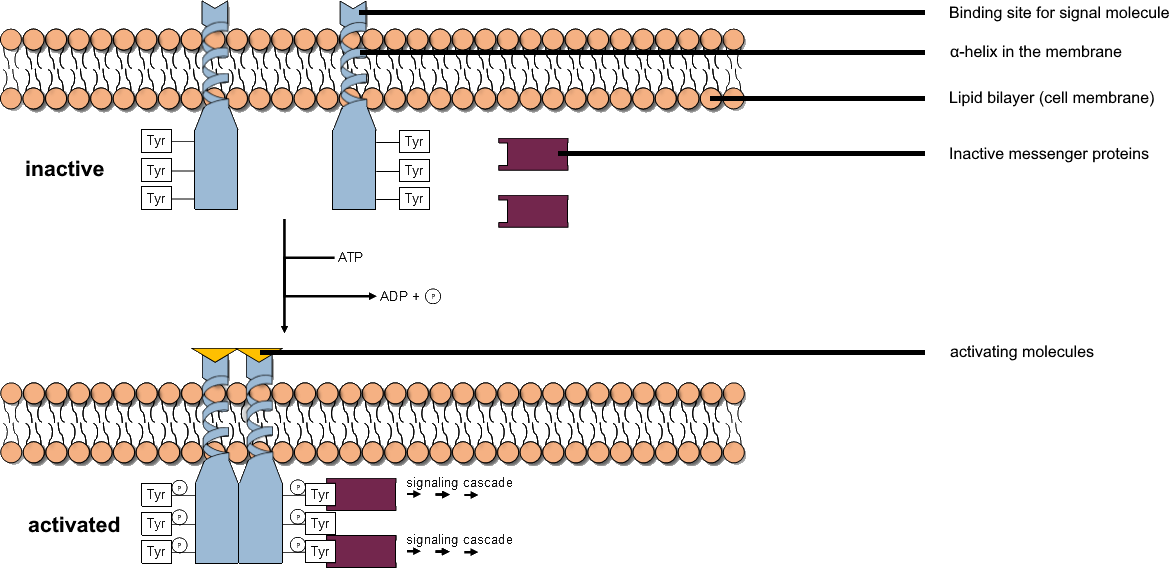
Tyrosine Kinase
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions. Tyrosine kinases belong to a larger class of enzymes known as protein kinases which also attach phosphates to other amino acids such as serine and threonine. Phosphorylation of proteins by kinases is an important mechanism for communicating signals within a cell (signal transduction) and regulating cellular activity, such as cell division. Protein kinases can become mutated, stuck in the "on" position, and cause unregulated growth of the cell, which is a necessary step for the development of cancer. Therefore, kinase inhibitors, such as imatinib and osimertinib, are often effective cancer treatments. Most tyrosine kinases have an associated protein tyrosine phosphatase, which removes the phosphate group. Reaction Protein kinases are a group of enzymes that possess a ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor
The fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFR) are, as their name implies, receptors that bind to members of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family of proteins. Some of these receptors are involved in pathological conditions. For example, a point mutation in FGFR3 can lead to achondroplasia. Structure The fibroblast growth factor receptors consist of an extracellular ligand domain composed of three immunoglobulin-like domains, a single transmembrane helix domain, and an intracellular domain with tyrosine kinase activity. These receptors bind fibroblast growth factors, members of the largest family of growth factor ligands, comprising 22 members. The natural alternate splicing of four fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) genes results in the production of over 48 different isoforms of FGFR. These isoforms vary in their ligand-binding properties and kinase domains, however all share the common extracellular region composed of three immunoglobulin(Ig)-like domains (D1-D3), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |