|
Net Zero
Global net-zero emissions is reached when greenhouse gas emissions and removals due to human activities are in balance. It is often called simply net zero. ''Emissions'' can refer to all greenhouse gases or only carbon dioxide (). Reaching net zero is necessary to stop further global warming. It requires deep cuts in emissions, for example by shifting from fossil fuels to sustainable energy, improving energy efficiency and halting deforestation. A small remaining fraction of emissions can then be offset using carbon dioxide removal. People often use the terms ''net-zero emissions'', ''carbon neutrality,'' and ''climate neutrality'' with the same meaning. However, in some cases, these terms have different meanings. For example, some standards for ''carbon neutral certification'' allow a lot of carbon offsetting. But ''net zero standards'' require reducing emissions to more than 90% and then only offsetting the remaining 10% or less to fall in line with 1.5 °C targets. Organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
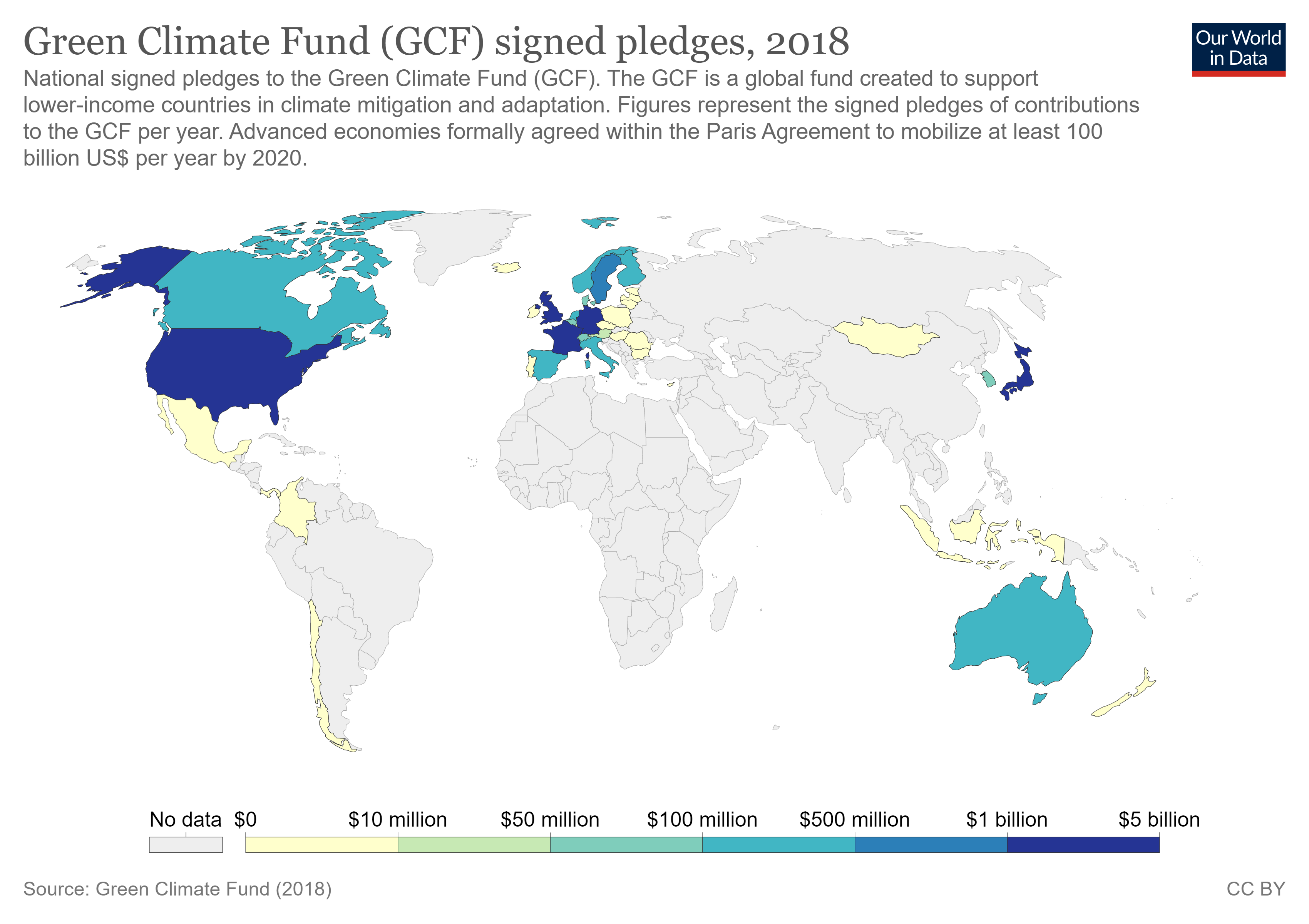
Global CO2 Pathways Using Remaining Carbon Budgets
Global may refer to: General *Globe, a spherical model of celestial bodies *Earth, the third planet from the Sun Entertainment * ''Global'' (Paul van Dyk album), 2003 * ''Global'' (Bunji Garlin album), 2007 * ''Global'' (Humanoid album), 1989 * ''Global'' (Todd Rundgren album), 2015 * Bruno J. Global, a character in the anime series ''The Super Dimension Fortress Marcoss'' Companies and brands Television * Global Television Network, in Canada ** Canwest Global, former parent company of Global Television Network ** Global BC, on-air brand of CHAN-TV, a television station in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada ** Global Calgary ** Global Edmonton ** Global Halifax ** Global Montreal ** Global News, the news division of the Global Television Network ** Global Okanagan, on-air brand of CHBC-TV, a television station in Kelowna, British Columbia, Canada ** Global Toronto, a television station in Toronto * Global TV (Venezuela), a regional channel in Venezuela * Global TV, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNFCC
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is the UN process for negotiating an agreement to limit dangerous climate change. It is an international treaty among countries to combat "dangerous human interference with the climate system". The main way to do this is limiting the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. It was signed in 1992 by 154 states at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), informally known as the Earth Summit, held in Rio de Janeiro. The treaty entered into force on 21 March 1994. "UNFCCC" is also the name of the Secretariat charged with supporting the operation of the convention, with offices on the UN Campus in Bonn, Germany. The convention's main objective is explained in Article 2. It is the "stabilization of greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic .e., human-causedinterference with the climate system". The treaty calls for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrous Oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or factitious air, among others, is a chemical compound, an Nitrogen oxide, oxide of nitrogen with the Chemical formula, formula . At room temperature, it is a colourless Flammability#Definitions, non-flammable gas, and has a slightly sweet scent and taste. At elevated temperatures, nitrous oxide is a powerful Oxidising agent, oxidiser similar to molecular oxygen. Nitrous oxide has significant Nitrous oxide (medication), medical uses, especially in surgery and dentistry, for its Anesthesia, anaesthetic and Analgesic, pain-reducing effects, and it is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Its colloquial name, "laughing gas", coined by Humphry Davy, describes the Euphoria, euphoric effects upon inhaling it, which cause it to be used as a recreational drug inducing a brief "Dissociative, high". When abused chronically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes it an economically attractive fuel, although capturing and storing it is difficult because it is a gas at standard temperature and pressure. In the Earth's atmosphere methane is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Methane is an Organic chemistry, organic Organic compound, compound, and among the simplest of organic compounds. Methane is also a hydrocarbon. Naturally occurring methane is found both below ground and under the seafloor and is formed by both geological and biological processes. The largest reservoir of methane is under the seafloor in the form of methane clathrates. When methane reaches the surface and the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere, it is known as atmospheric methane. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Inertia
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere and the interactions between them. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude, longitude, terrain, altitude, land use and nearby water bodies and their currents. Climates can be classified according to the average and typical variables, most commonly temperature and precipitation. The most widely used classification scheme is the Köppen climate classification. The Thornthwaite system, in use since 1948, incorporates evapotranspiration along with temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
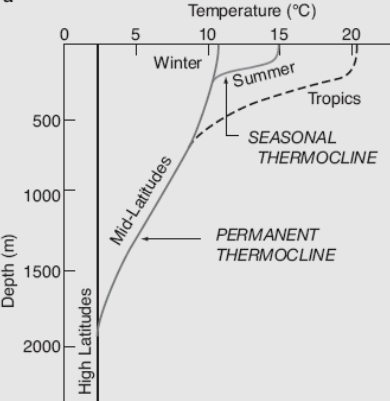
Ocean Temperature
The ocean temperature plays a crucial role in the global climate system, ocean currents and for marine habitats. It varies depending on depth, geographical location and season. Not only does the temperature differ in seawater, so does the salinity. Warm surface water is generally saltier than the cooler deep or polar waters. In polar regions, the upper layers of ocean water are cold and fresh. Deep ocean water is cold, salty water found deep below the surface of Earth's oceans. This water has a uniform temperature of around 0-3°C. The ocean temperature also depends on the amount of solar radiation falling on its surface. In the tropics, with the Sun nearly overhead, the temperature of the surface layers can rise to over . Near the poles the temperature in equilibrium with the sea ice is about . There is a continuous large-scale circulation of water in the oceans. One part of it is the thermohaline circulation (THC). It is driven by global density gradients created by su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Sequestration
Carbon sequestration is the process of storing carbon in a carbon pool. It plays a crucial role in Climate change mitigation, limiting climate change by reducing the amount of Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. There are two main types of carbon sequestration: biologic (also called ''biosequestration'') and geologic. Biologic carbon sequestration is a naturally occurring process as part of the carbon cycle. Humans can enhance it through deliberate actions and use of technology. Carbon dioxide () is naturally captured from the atmosphere through biological, chemical, and physical processes. These processes can be accelerated for example through changes in land use and agricultural practices, called carbon farming. Artificial processes have also been devised to produce similar effects. This approach is called carbon capture and storage. It involves using technology to capture and sequester (store) that is produced from human activities under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Framework Convention On Climate Change
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is the UN process for negotiating an agreement to limit dangerous climate change. It is an international treaty among countries to combat "dangerous human interference with the climate system". The main way to do this is limiting the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. It was signed in 1992 by 154 states at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), informally known as the Earth Summit, held in Rio de Janeiro. The treaty entered into force on 21 March 1994. "UNFCCC" is also the name of the Secretariat charged with supporting the operation of the convention, with offices on the UN Campus in Bonn, Germany. The convention's main objective is explained in Article 2. It is the "stabilization of greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic .e., human-causedinterference with the climate system". The treaty calls for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiative Forcing
Radiative forcing (or climate forcing) is a concept used to quantify a change to the balance of energy flowing through a planetary atmosphere. Various factors contribute to this change in energy balance, such as concentrations of greenhouse gases and aerosols, and changes in surface albedo and solar irradiance. In more technical terms, it is defined as "the change in the net, downward minus upward, radiative flux (expressed in W/m2) due to a change in an external driver of climate change." These external drivers are distinguished from feedbacks and variability that are internal to the climate system, and that further influence the direction and magnitude of imbalance. Radiative forcing on Earth is meaningfully evaluated at the tropopause and at the top of the stratosphere. It is quantified in units of watts per square meter, and often summarized as an average over the total surface area of the globe. A planet in radiative equilibrium with its parent star and the rest of sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Report On Global Warming Of 1
Special or specials may refer to: Policing * Specials, Ulster Special Constabulary, the Northern Ireland police force * Specials, Special Constable, an auxiliary, volunteer, or temporary; police worker or police officer * Special police forces Military * Special forces * Special operations Literature * ''Specials'' (novel), a novel by Scott Westerfeld * ''Specials'', the comic book heroes, see ''Rising Stars'' (comic) Film and television * Special (lighting), a stage light that is used for a single, specific purpose * ''Special'' (film), a 2006 scifi dramedy * ''The Specials'' (2000 film), a comedy film about a group of superheroes * Special 26, a 2013 Indian Hindi-language period heist thriller film * ''The Specials'' (2019 film), a film by Olivier Nakache and Éric Toledano * Television special, television programming that temporarily replaces scheduled programming * ''Special'' (TV series), a 2019 Netflix Original TV series * ''Specials'' (TV series), a 1991 TV se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergovernmental Panel On Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to "provide governments at all levels with scientific information that they can use to develop climate policies". The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) set up the IPCC in 1988. The United Nations General Assembly, United Nations endorsed the creation of the IPCC later that year. It has a secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland, hosted by the WMO. It has 195 Member states of the United Nations, member states who govern the IPCC. The member states elect a bureau of scientists to serve through an assessment cycle. A cycle is usually six to seven years. The bureau selects experts in their fields to prepare IPCC reports. There is a formal nomination process by governments and observer organizations to find these experts. The IPCC has three working groups and a task force, which carry out its scientific work. The IPCC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinks, Sources,and Reservoirs
The carbon cycle is a part of the biogeochemical cycle where carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of Earth. Other major biogeochemical cycles include the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major component of many rocks such as limestone. The carbon cycle comprises a sequence of events that are key to making Earth capable of sustaining life. It describes the movement of carbon as it is recycled and reused throughout the biosphere, as well as long-term processes of carbon sequestration (storage) to and release from carbon sinks. To describe the dynamics of the carbon cycle, a distinction can be made between the ''fast'' and ''slow'' carbon cycle. The fast cycle is also referred to as the ''biological carbon cycle''. Fast cycles can complete within years, moving substances from atmosphere to biosphere, then back to the atmosphere. Slow or geological cycles (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |