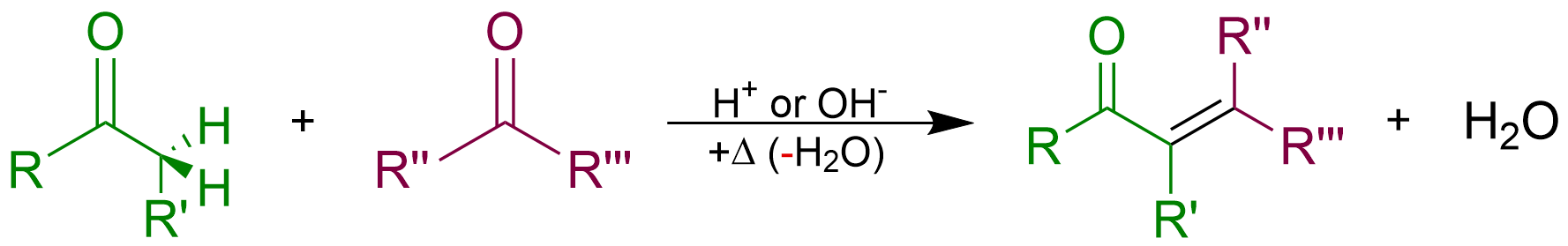|
Neopentyl Glycol
Neopentyl glycol (IUPAC name: 2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diol) is an organic chemical compound. It is used in the synthesis of polyesters, paints, lubricants, and plasticizers. When used in the manufacture of polyesters, it enhances the stability of the product towards heat, light, and water. By esterification reaction with fatty or carboxylic acids, synthetic lubricating esters with reduced potential for oxidation or hydrolysis, compared to natural esters, can be produced. Reactions Neopentyl glycol is synthesized industrially by the aldol reaction of formaldehyde and isobutyraldehyde. This creates the intermediate hydroxypivaldehyde, which can be converted to neopentyl glycol by either a Cannizzaro reaction with excess formaldehyde, or by hydrogenation using palladium on carbon. Owing to its tendency to form cyclic derivatives (see Thorpe-Ingold Effect), it is used as a protecting group for ketones, for example in gestodene synthesis. Similarly it gives boronic acid ester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon. Benzene is a natural constituent of petroleum and is one of the elementary petrochemicals. Due to the cyclic continuous pi bonds between the carbon atoms, benzene is classed as an aromatic hydrocarbon. Benzene is a colorless and highly Combustibility and flammability, flammable liquid with a sweet smell, and is partially responsible for the aroma of gasoline. It is used primarily as a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to the manufacture of chemicals with more complex structures, such as ethylbenzene and cumene, of which billions of kilograms are produced annually. Although benzene is a major Chemical industry, industrial che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldol Reaction
The aldol reaction (aldol addition) is a Chemical reaction, reaction in organic chemistry that combines two Carbonyl group, carbonyl compounds (e.g. aldehydes or ketones) to form a new β-hydroxy carbonyl compound. Its simplest form might involve the nucleophilic addition of an Enolate, enolized ketone to another: These products are known as ''aldols'', from the ''ald''ehyde + alcoh''ol'', a structural motif seen in many of the products. The use of aldehyde in the name comes from its history: aldehydes are more reactive than ketones, so that the reaction was discovered first with them. The aldol reaction is paradigmatic in organic chemistry and one of the most common means of forming carbon–carbon bonds in organic chemistry. It lends its name to the family of aldol reactions and similar techniques analyze a whole family of carbonyl α-substitution reactions, as well as the Claisen condensation, diketone condensations. Scope Aldol structural units are found in many importa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neopentyl Glycol Diglycidyl Ether
Neopentyl glycol diglycidyl ether (NPGDGE) is an organic chemical in the glycidyl ether family. It is aliphatic and a colorless liquid. It has the formula C11H20O4 and the CAS registry number of 17557-23-2. It has two oxirane groups per molecule. Its principle use is in modifying epoxy resins. It is REACH registered. The IUPAC name is 2- 2,2-dimethyl-3-(oxiran-2-ylmethoxy)propoxyethyl]oxirane. Synthesis Neopentyl glycol and epichlorohydrin are reacted in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst to form a halohydrin. This is followed by washing with sodium hydroxide in dehydrochlorination step. This forms Neopentyl glycol diglycidyl ether. The waste products are water and sodium chloride and excess caustic soda. One of the quality control tests would involve measuring the Epoxy value by determination of the epoxy equivalent weight. Uses A key use is modifying the viscosity and properties of epoxy resins. As an Epoxy modifier it is classed as an epoxy reactive diluent. which may then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CGP-7930
CGP-7930 was the first positive allosteric modulator of GABAB receptors described in literature. CGP7930 is also a GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator and a blocker of Potassium channels. CGP7930 was developed in Novartis and has been used extensively for scientific research. It has anxiolytic effects in animal studies, and has a synergistic effect with GABAB agonists such as baclofen and GHB, as well as reducing self-administration of alcoholic drinks and cocaine. CNS Review: Synthesis The chemical synthesis has been described: Starting material: Product of first step: 2,6-Di-tert-butylphenol is treated with formaldehyde, base and methanol to give 7-97-8(2). Base catalyzed reaction with isobutaldehyde gives CGP-13501 (3). Hydride reduction of the aldehyde gives the primary alcohol. According to Krysin (Russia), 2,6-Di-tert-butylphenol is reacted with Neopentyl glycol Neopentyl glycol (IUPAC name: 2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diol) is an organic chemical compound. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2,6-Di-tert-butylphenol
2,6-Di-''tert''-butylphenol is an organic compound with the structural formula 2,6-((CH3)3C)2C6H3OH. This colorless solid alkylated phenol and its derivatives are used industrially as UV stabilizers and antioxidants for hydrocarbon-based products ranging from petrochemicals to plastics. Illustrative of its usefulness, it prevents gumming in aviation fuels. Production 2,6-Di-''tert''-butylphenol is prepared industrially via the Friedel–Crafts alkylation of phenol with isobutene catalyzed by aluminium phenoxide: :C6H5OH + 2 CH2=C(CH3)2 → ((CH3)3C)2C6H3OH In this way, approximately 2.5M kg/y are produced. Alkylation of phenol usually favours the para-position, and a strong lewis acid such as the Al3+ ion is necessary to give selective ortho‑alkylation. If a conventional brønsted acid is used then 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol will be produced instead. Natural occurrence Two species of plants, '' Jastropa curcas'' and '' Metaplexis japonica'', contain 2,6-DTBP in seed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation Reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis. However other molecules can also be lost, such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid and hydrogen sulfide. The addition of the two molecules typically proceeds in a step-wise fashion to the addition product, usually in equilibrium, and with loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). The reaction may otherwise involve the functional groups of the molecule, and is a versatile class of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic conditions or in the presence of a catalyst. This class of reactions is a vital part of life as it is essential to the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids and to the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Many variations of condensation reactions exist. Common examples include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
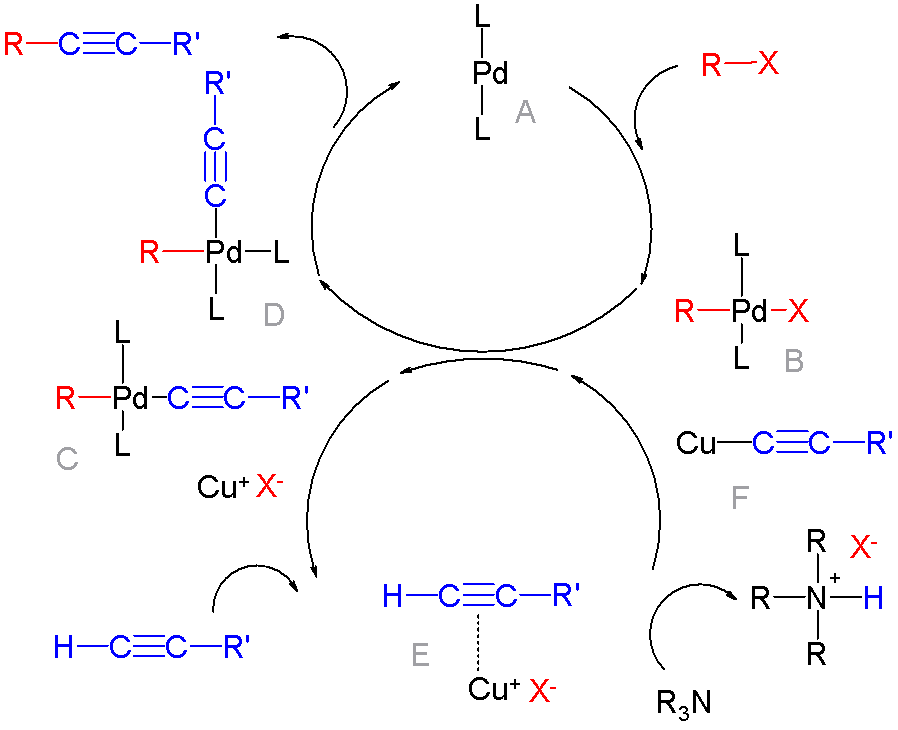
Cross Coupling Reaction
In organic chemistry, a cross-coupling reaction is a reaction where two different fragments are joined. Cross-couplings are a subset of the more general coupling reactions. Often cross-coupling reactions require metal catalysts. One important reaction type is this: : (R, R' = organic fragments, usually aryl; M = main group center such as Li or MgX; X = halide) These reactions are used to form carbon–carbon bonds but also carbon-heteroatom bonds. Cross-coupling reaction are a subset of coupling reactions. Richard F. Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki were awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for developing palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions. Mechanism Many mechanisms exist reflecting the myriad types of cross-couplings, including those that do not require metal catalysts. Often, however, cross-coupling refers to a metal-catalyzed reaction of a nucleophilic partner with an electrophilic partner. In such cases, the mechanism generally involves reductive elimin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boronic Ester
A boronic acid is an organic compound related to boric acid () in which one of the three hydroxyl groups () is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group (represented by R in the general formula ). As a compound containing a carbon–boron bond, members of this class thus belong to the larger class of organoboranes. Boronic acids act as Lewis acids. Their unique feature is that they are capable of forming reversible covalent complexes with sugars, amino acids, hydroxamic acids, etc. (molecules with vicinal, (1,2) or occasionally (1,3) substituted Lewis base donors (alcohol, amine, carboxylate)). The p''K''a of a boronic acid is ~9, but they can form tetrahedral boronate complexes with p''K''a ~7. They are occasionally used in the area of molecular recognition to bind to saccharides for fluorescent detection or selective transport of saccharides across membranes. Boronic acids are used extensively in organic chemistry as chemical building blocks and intermediates predominantly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestodene
Gestodene, sold under the brand names Femodene and Minulet among others, is a progestin medication which is used in birth control pills for women. It is also used in menopausal hormone therapy. The medication is available almost exclusively in combination with an estrogen. It is taken by mouth. Side effects of the combination of an estrogen and gestodene include menstrual irregularities, headaches, nausea, breast tenderness, mood changes, and others. Gestodene is a progestin, or a synthetic progestogen, and hence is an agonist of the progesterone receptor, the biological target of progestogens like progesterone. It has weak androgenic activity, weak antimineralocorticoid activity, and weak glucocorticoid activity. Gestodene was discovered in 1975 and was introduced for medical use, specifically in birth control pills, in 1987. It was subsequently introduced for use in menopausal hormone therapy as well. Gestodene is sometimes referred to as a "third-generation" progestin. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
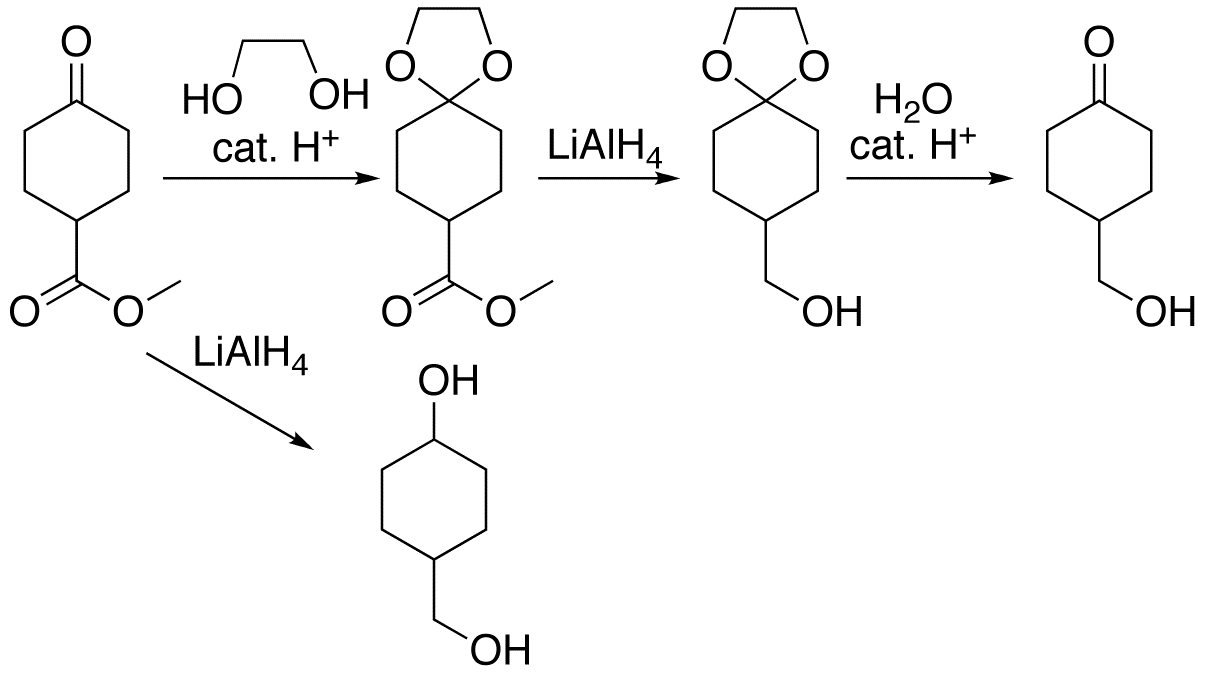
Protecting Group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds, specific parts of the molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments. These parts (functional groups) must be protected. For example, lithium aluminium hydride is a highly reactive reagent that usefully reduces esters to alcohols. It always reacts with carbonyl groups, and cannot be discouraged by any means. When an ester must be reduced in the presence of a carbonyl, hydride attack on the carbonyl must be prevented. One way to do so converts the carbonyl into an acetal, which does not react with hydrides. The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl. After the hydride step is complete, aqueous acid removes the acetal, restoring the carbonyl. This step ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannizzaro Reaction
The Cannizzaro reaction, named after its discoverer Stanislao Cannizzaro, is a chemical reaction which involves the base-induced disproportionation of two molecules of a non-enolizable aldehyde to give a primary alcohol and a carboxylic acid. : Cannizzaro first accomplished this transformation in 1853, when he obtained benzyl alcohol and potassium benzoate from the treatment of benzaldehyde with potash (potassium carbonate). More typically, the reaction would be conducted with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, giving the sodium or potassium carboxylate salt of the carboxylic-acid product: :2 C6H5CHO + KOH → C6H5CH2OH + C6H5COOK The process is a redox reaction involving transfer of a hydride from one substrate molecule to the other: one aldehyde is oxidized to form the acid, the other is reduced to form the alcohol. Mechanism The reaction involves a nucleophilic acyl substitution on an aldehyde, with the leaving group concurrently attacking another aldehy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |