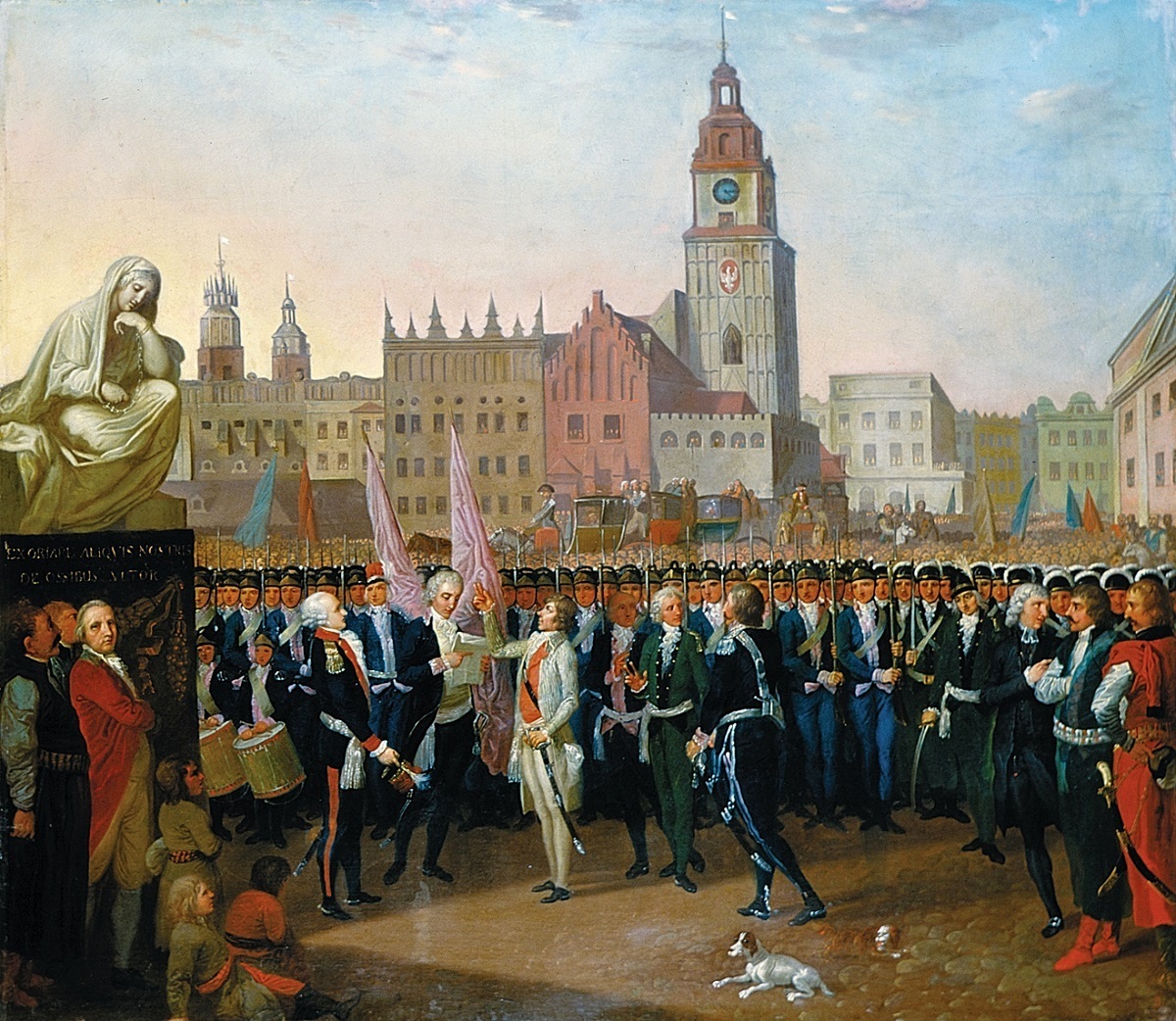|
Nemunėlio Radviliškis
Nemunėlio Radviliškis is a town in Biržai district municipality, in Panevėžys County, northern Lithuania. According to the 2011 census, the town has a population of 566 people. Etymology The name Radviliškis is a place name derived from the last name Radvila. The town was founded in the 16th century by the Dukes of Biržai and Dubingiai, the Radvila family, and is thus named after them. To distinguish it from the town of Radviliškis, the town was given the designation Nemunėlis, thus referring to the river flowing through the town. History Two ancient Roman enamelled bronze brooches were found in the settlement, during archeological excavations. A flat, symmetrical one with an animal head ornament and a similar round one. Nemunėlio Radviliškis was first mentioned in 4 November 1586. It was founded by the Radvila noble family. The Evangelical Reformed Church of was built in 1590, a Catholic chapel in 1719, and the Catholic Church of the Virgin Mary was established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutherans
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched the Reformation in 1517. The Lutheran Churches adhere to the Bible and the Ecumenical Creeds, with Lutheran doctrine being explicated in the Book of Concord. Lutherans hold themselves to be in continuity with the apostolic church and affirm the writings of the Church Fathers and the first four ecumenical councils. The schism between Roman Catholicism and Lutheranism, which was formalized in the Edict of Worms of 1521, centered around two points: the proper source of authority in the church, often called the formal principle of the Reformation, and the doctrine of justification, the material principle of Lutheran theology. Lutheranism advocates a doctrine of justification "by Grace alone through faith alone on the basis of Scripture alone", the doctrine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Press Ban
The Lithuanian press ban () was a ban on all Lithuanian language publications printed in the Latin alphabet, in force from 1865 to 1904, within the Russian Empire, which controlled Lithuania proper at the time. Lithuanian-language publications that used Cyrillic script, Cyrillic were allowed and even encouraged by those seeking the Russification of Lithuanians. The concept arose after the failed January Uprising of 1863, taking the form of an administrative order in 1864, and was not lifted until 24 April 1904. The Russian courts reversed two convictions in press ban cases in 1902 and 1903, and the setbacks of the Russo-Japanese War in early 1904 brought about a loosened Russian policy towards minorities.Lithuanian Resistance Spaudos.lt, reprinted from Encyclopedia Lituanica, Boston, 1970–1978. Retrieved on 2009-03-17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kościuszko Uprising
The Kościuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794, Second Polish War, Polish Campaign of 1794, and the Polish Revolution of 1794, was an uprising against the Russian and Prussian influence on the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, led by Tadeusz Kościuszko in Poland-Lithuania and the Prussian partition in 1794. It was a failed attempt to liberate the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from external influence after the Second Partition of Poland (1793) and the creation of the Targowica Confederation. Background Decline of the Commonwealth By the early 18th century, the magnates of Poland and Lithuania controlled the state – or rather, they managed to ensure that no reforms would be carried out that might weaken their privileged status (the " Golden Freedoms"). Through the abuse of the '' liberum veto'' rule which enabled any deputy to paralyze the Sejm (Commonwealth's parliament) proceedings, deputies bribed by magnates or foreign powers or those sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasvalys
Pasvalys () is a city in Panevėžys County, Lithuania, located near the bank of the Svalia River. History In 1557, the Treaty of Pasvalys was signed in the town, which provoked Ivan IV of Russia to start the Livonian War. Pasvalys has mineral spring waters – in 1923 physician K. Armonas created a small sanatorium. At this time about 200 people spent time in sanatorium yearly. Soviet occupation and mass deportations in 1941 were devastating – most of the most active teachers and civil servants, intellectuals were deported to remote regions in Russia and Central Asia. In August 1941, 1349 Jews from the village and the surroundings were executed by an Einsatzgruppen of Germans and local collaborators as mentioned in the Jäger Report. After 1944 Soviet mass deportations started again – the main target were farmers and their families. Hundreds of families were deported. The program of forced collectivisation has started. Since 1947 partisans of Pasvalys district fought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Šventoji, Lithuania
Šventoji ( Samogitian: ''Švėntuojė''; ) is a resort town on the coast of the Baltic Sea in Lithuania. Administratively it is part of Palanga City Municipality. The total population of Šventoji as of 2012 was 2631. The town is located about 12 km north of Palanga center and close to the border with Latvia. Further north of the town is Būtingė and its oil terminal. Šventoji River flows into the Baltic sea at the town. The town also has a famous lighthouse, which is located 780 meters from the sea. Its height is 39 meters. The town is a popular summer resort for families, during summer it has many cafes, restaurants and various attractions for the visitors. Šventoji is an important archaeological site as the first artefacts are dated about 3000 BC. A famous cane shaped as moose head was also found in the town. It is a former fishing village now turned into a tourist town. The town always struggled to develop a port, which had to compete with nearby Klaipėda and Lie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palanga
Palanga (; ; ) is a resort town, resort city in western Lithuania, on the shore of the Baltic Sea. Palanga is the busiest and the largest summer resort in Lithuania and has sand, sandy beaches (18 km, 11 miles long and up to 300 metres, 1000 ft wide) and sand dunes. Officially Palanga has the status of a city municipality and includes Šventoji, Lithuania, Šventoji, Nemirseta, Būtingė, Palanga International Airport and other settlements, which are considered as part of the city of Palanga. Etymology The name of the town is likely of Curonian language, Curonian origin, as proposed by the linguist Kazimieras Būga. The primary argument is the suffix "''-ng-''", which is particularly distinctive of Curonian toponyms (Gandinga, Ablinga, Būtingė, etc.). The root ''pal-'', furthermore, is also associated with the landscape of lowlands or marshes. This is exemplified by the Lithuanian ''palios'', which translates to "large marsh", and the Latvian language, Latvian ''pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biržai Castle
Biržai Castle (, ) is a 16th century castle in Biržai, northern Lithuania. It is located in Aukštaitija region, Panevėžys County. The castle was the first Italian-style bastion fort in Lithuania and one of the first in North-Eastern Europe. The well-preserved castle (most recently restored in 2013) now houses a museum, a library and a restaurant. Construction of the earth bastion-type castle started in 1586 by the order of Krzysztof "Piorun" Radziwiłł (Kristupas Radvila „Perkūnas“). In 1575, preparing for this construction, a dam was built on the Agluona and Apaščia rivers at their confluence, and the artificial Lake Širvėna, covering about , was created. Major works were finished in 1589. Since the second half of the 17th century, the castle has been the main seat of the Biržai-Dubingiai Radziwiłł (Radvila) family line, which was transferred here from the Dubingiai Castle. Biržai Castle served as an essential Lithuanian stronghold during the Polish–Swedish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deluge (history)
The Deluge was a series of mid-17th-century military campaigns in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In a wider sense, it applies to the period between the Khmelnytsky Uprising of 1648 and the Truce of Andrusovo in 1667, comprising the Polish theatres of the Russo-Polish and Second Northern Wars. In a stricter sense, the term refers to the Swedish invasion and occupation of the Commonwealth as a theatre of the Second Northern War (1655–1660) only; in Poland and Lithuania this period is called the Swedish Deluge (, Lithuanian: š''vedų tvanas'', ), or less commonly the Russo–Swedish Deluge () due to the simultaneous Russo-Polish War. The term "deluge" (''potop'' in Polish) was popularized by Henryk Sienkiewicz in his novel '' The Deluge'' (1886). During the wars the Commonwealth lost approximately one third of its population as well as its status as a great power due to invasions by Sweden and Russia. According to Professor Andrzej Rottermund, manager of the Roya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |