|
Navier–Stokes Existence And Smoothness
The Navier–Stokes existence and smoothness problem concerns the mathematical properties of solutions to the Navier–Stokes equations, a system of partial differential equations that describe the motion of a fluid in space. Solutions to the Navier–Stokes equations are used in many practical applications. However, theoretical understanding of the solutions to these equations is incomplete. In particular, solutions of the Navier–Stokes equations often include turbulence, which remains one of the greatest unsolved problems in physics, despite its immense importance in science and engineering. Even more basic (and seemingly intuitive) properties of the solutions to Navier–Stokes have never been proven. For the three-dimensional system of equations, and given some initial conditions, mathematicians have neither proved that smooth solutions always exist, nor found any counter-examples. This is called the ''Navier–Stokes existence and smoothness'' problem. Since underst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
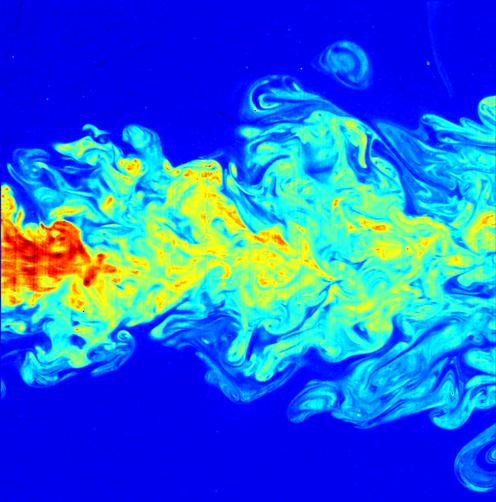
False Color Image Of The Far Field Of A Submerged Turbulent Jet
False or falsehood may refer to: *False (logic), the negation of truth in classical logic *Lie or falsehood, a type of deception in the form of an untruthful statement *False statement, aka a falsehood, falsity, misstatement or untruth, is a statement that is false *false (Unix), a Unix command * ''False'' (album), a 1992 album by Gorefest *Matthew Dear Matthew Dear (born April 4, 1979) is an American electronic music producer and DJ. History Texas-born Dear moved to Michigan as a teenager, where he was inspired by the sound of Detroit techno. Dear met Sam Valenti IV at a party while attendin ... or False (born 1979), American DJ and producer * ''Falsehood'' (1952 film), an Italian melodrama film * ''Falsehood'' (2001 film), an American short film See also * * Anrita, falsehood in Hindu mythology {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent drag (physics), resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. Thus its SI units are newton-seconds per metre squared, or pascal-seconds. Viscosity quantifies the internal friction, frictional force between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. For instance, when a viscous fluid is forced through a tube, it flows more quickly near the tube's center line than near its walls. Experiments show that some stress (physics), stress (such as a pressure difference between the two ends of the tube) is needed to sustain the flow. This is because a force is required to overcome the friction between the layers of the fluid which are in relative motion. For a tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vorticity Equation
The vorticity equation of fluid dynamics describes the evolution of the vorticity of a particle of a fluid dynamics, fluid as it moves with its flow (fluid), flow; that is, the local rotation of the fluid (in terms of vector calculus this is the curl (mathematics), curl of the flow velocity). The governing equation is:where is the material derivative operator, is the flow velocity, is the local fluid density, is the local pressure, is the viscous stress tensor and represents the sum of the external body forces. The first source term on the right hand side represents vortex stretching. The equation is valid in the absence of any concentrated torques and line forces for a Compressibility, compressible, Newtonian fluid. In the case of incompressible flow (i.e., low Mach number) and isotropic fluids, with conservative force, conservative body forces, the equation simplifies to the vorticity transport equation: :\frac = \left(\boldsymbol \cdot \nabla\right) \mathbf + \nu \nabla^ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curl (mathematics)
In vector calculus, the curl, also known as rotor, is a vector operator that describes the Differential (infinitesimal), infinitesimal Circulation (physics), circulation of a vector field in three-dimensional Euclidean space. The curl at a point in the field is represented by a vector (geometry), vector whose length and direction denote the Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude and axis of the maximum circulation. The curl of a field is formally defined as the circulation density at each point of the field. A vector field whose curl is zero is called irrotational. The curl is a form of derivative, differentiation for vector fields. The corresponding form of the fundamental theorem of calculus is Kelvin–Stokes theorem, Stokes' theorem, which relates the surface integral of the curl of a vector field to the line integral of the vector field around the boundary curve. The notation is more common in North America. In the rest of the world, particularly in 20th century scientific li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divergence
In vector calculus, divergence is a vector operator that operates on a vector field, producing a scalar field giving the rate that the vector field alters the volume in an infinitesimal neighborhood of each point. (In 2D this "volume" refers to area.) More precisely, the divergence at a point is the rate that the flow of the vector field modifies a volume about the point ''in the limit'', as a small volume shrinks down to the point. As an example, consider air as it is heated or cooled. The velocity of the air at each point defines a vector field. While air is heated in a region, it expands in all directions, and thus the velocity field points outward from that region. The divergence of the velocity field in that region would thus have a positive value. While the air is cooled and thus contracting, the divergence of the velocity has a negative value. Physical interpretation of divergence In physical terms, the divergence of a vector field is the extent to which the vector fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solenoidal Vector Field
In vector calculus a solenoidal vector field (also known as an incompressible vector field, a divergence-free vector field, or a transverse vector field) is a vector field v with divergence zero at all points in the field: \nabla \cdot \mathbf = 0. A common way of expressing this property is to say that the field has no sources or sinks.This statement does not mean that the field lines of a solenoidal field must be closed, neither that they cannot begin or end. For a detailed discussion of the subject, see J. Slepian: "Lines of Force in Electric and Magnetic Fields", American Journal of Physics, vol. 19, pp. 87-90, 1951, and L. Zilberti: "The Misconception of Closed Magnetic Flux Lines", IEEE Magnetics Letters, vol. 8, art. 1306005, 2017. Properties The divergence theorem gives an equivalent integral definition of a solenoidal field; namely that for any closed surface, the net total flux through the surface must be zero: where d\mathbf is the outward normal to each surface el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Of Mass
In physics and chemistry, the law of conservation of mass or principle of mass conservation states that for any system closed to all transfers of matter the mass of the system must remain constant over time. The law implies that mass can neither be created nor destroyed, although it may be rearranged in space, or the entities associated with it may be changed in form. For example, in chemical reactions, the mass of the chemical components before the reaction is equal to the mass of the components after the reaction. Thus, during any chemical reaction and low-energy thermodynamic processes in an isolated system, the total mass of the reactants, or starting materials, must be equal to the mass of the products. The concept of mass conservation is widely used in many fields such as chemistry, mechanics, and fluid dynamics. Historically, mass conservation in chemical reactions was primarily demonstrated in the 17th century and finally confirmed by Antoine Lavoisier in the late 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuity Equation
A continuity equation or transport equation is an equation that describes the transport of some quantity. It is particularly simple and powerful when applied to a conserved quantity, but it can be generalized to apply to any extensive quantity. Since mass, energy, momentum, electric charge and other natural quantities are conserved under their respective appropriate conditions, a variety of physical phenomena may be described using continuity equations. Continuity equations are a stronger, local form of conservation laws. For example, a weak version of the law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed—i.e., the total amount of energy in the universe is fixed. This statement does not rule out the possibility that a quantity of energy could disappear from one point while simultaneously appearing at another point. A stronger statement is that energy is ''locally'' conserved: energy can neither be created nor destroyed, ''nor'' can it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laplacian
In mathematics, the Laplace operator or Laplacian is a differential operator given by the divergence of the gradient of a scalar function on Euclidean space. It is usually denoted by the symbols \nabla\cdot\nabla, \nabla^2 (where \nabla is the nabla operator), or \Delta. In a Cartesian coordinate system, the Laplacian is given by the sum of second partial derivatives of the function with respect to each independent variable. In other coordinate systems, such as cylindrical and spherical coordinates, the Laplacian also has a useful form. Informally, the Laplacian of a function at a point measures by how much the average value of over small spheres or balls centered at deviates from . The Laplace operator is named after the French mathematician Pierre-Simon de Laplace (1749–1827), who first applied the operator to the study of celestial mechanics: the Laplacian of the gravitational potential due to a given mass density distribution is a constant multiple of that de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar-valued differentiable function f of several variables is the vector field (or vector-valued function) \nabla f whose value at a point p gives the direction and the rate of fastest increase. The gradient transforms like a vector under change of basis of the space of variables of f. If the gradient of a function is non-zero at a point p, the direction of the gradient is the direction in which the function increases most quickly from p, and the magnitude of the gradient is the rate of increase in that direction, the greatest absolute directional derivative. Further, a point where the gradient is the zero vector is known as a stationary point. The gradient thus plays a fundamental role in optimization theory, where it is used to minimize a function by gradient descent. In coordinate-free terms, the gradient of a function f(\mathbf) may be defined by: df=\nabla f \cdot d\mathbf where df is the total infinitesimal change in f for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinematic Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent drag (physics), resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. Thus its SI units are newton-seconds per metre squared, or pascal-seconds. Viscosity quantifies the internal friction, frictional force between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. For instance, when a viscous fluid is forced through a tube, it flows more quickly near the tube's center line than near its walls. Experiments show that some stress (physics), stress (such as a pressure difference between the two ends of the tube) is needed to sustain the flow. This is because a force is required to overcome the friction between the layers of the fluid which are in relative motion. For a tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be used: \rho = \frac, where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance, the density is equal to its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium is the densest known element at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different systems of units, it is sometimes replaced by the dimensionless quantity "relative den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |