|
Natural Language Generator
Natural language generation (NLG) is a software process that produces natural language output. A widely cited survey of NLG methods describes NLG as "the subfield of artificial intelligence and computational linguistics that is concerned with the construction of computer systems that can produce understandable texts in English or other human languages from some underlying non-linguistic representation of information". While it is widely agreed that the output of any NLG process is text, there is some disagreement about whether the inputs of an NLG system need to be non-linguistic. Common applications of NLG methods include the production of various reports, for example weather and patient reports; image captions; and chatbots like ChatGPT. Automated NLG can be compared to the process humans use when they turn ideas into writing or speech. Psycholinguists prefer the term language production for this process, which can also be described in mathematical terms, or modeled in a comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origin Of Language
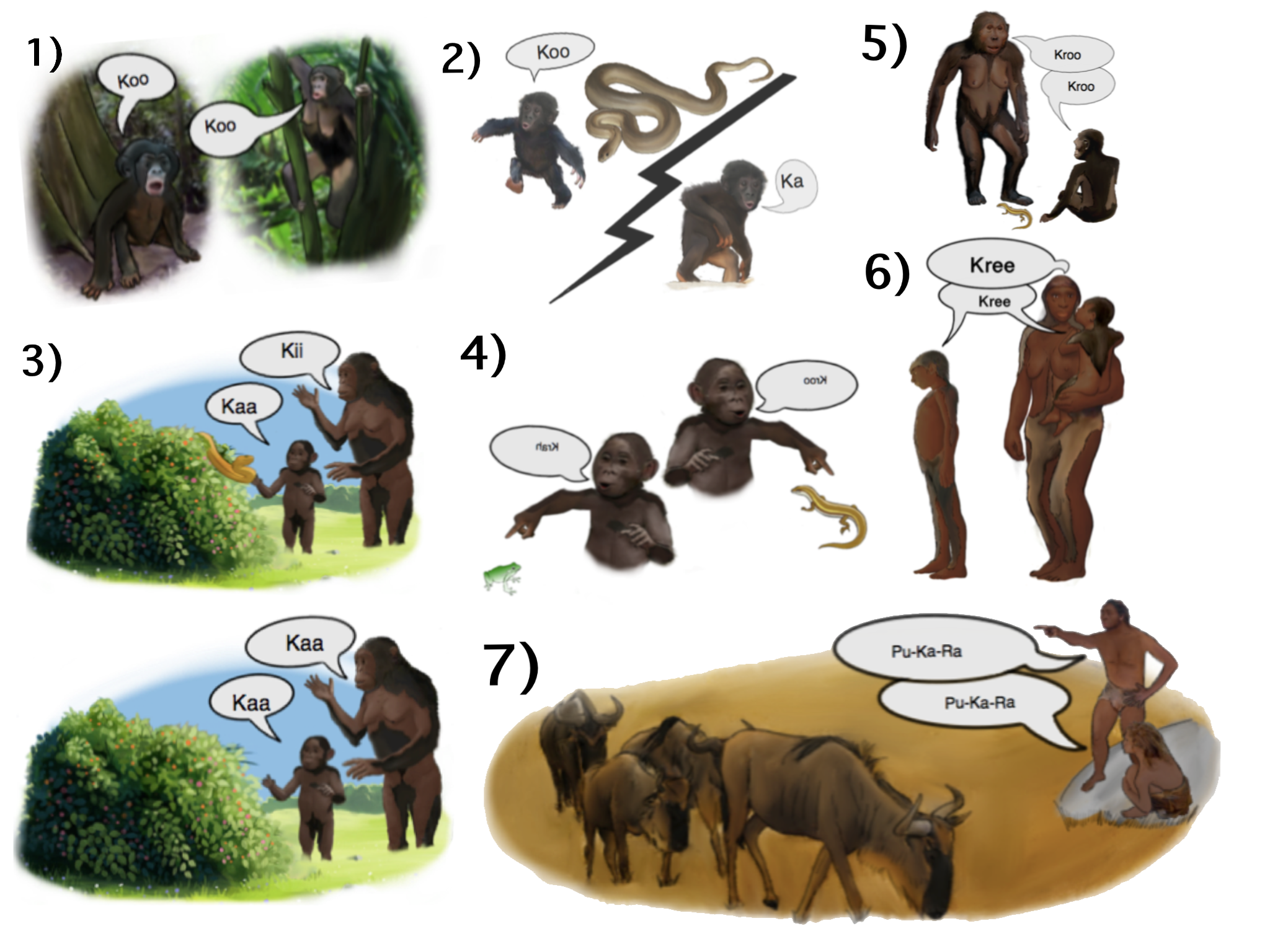
The origin of language, its relationship with human evolution, and its consequences have been subjects of study for centuries. Scholars wishing to study the origins of language draw inferences from evidence such as the fossil record, archaeological evidence, and contemporary language diversity. They may also study language acquisition as well as comparisons between human language and systems of animal communication (particularly other primates). Many argue for the close relation between the origins of language and the origins of modern human behavior, but there is little agreement about the facts and implications of this connection. The shortage of direct, empirical evidence has caused many scholars to regard the entire topic as unsuitable for serious study; in 1866, the Linguistic Society of Paris banned any existing or future debates on the subject, a prohibition which remained influential across much of the Western world until the late twentieth century. Various hypotheses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Content Determination
Content determination is the subtask of natural language generation (NLG) that involves deciding on the information to be communicated in a generated text. It is closely related to the task of document structuring. Example Consider an NLG system which summarises information about sick babies. Suppose this system has four pieces of information it can communicate # The baby is being given morphine via an IV drop # The baby's heart rate shows bradycardia's (temporary drops) # The baby's temperature is normal # The baby is crying Which of these bits of information should be included in the generated texts? Issues There are three general issues which almost always impact the content determination task, and can be illustrated with the above example. Perhaps the most fundamental issue is the ''communicative goal'' of the text, i.e. its ''purpose'' and ''reader''. In the above example, for instance, a doctor who wants to make a decision about medical treatment would probably be most int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatic Image Annotation
Automatic image annotation (also known as automatic image tagging or linguistic indexing) is the process by which a computer system automatically assigns metadata in the form of captioning or keywords to a digital image. This application of computer vision techniques is used in image retrieval systems to organize and locate images of interest from a database. This method can be regarded as a type of multi-class image classification with a very large number of classes - as large as the vocabulary size. Typically, image analysis in the form of extracted feature vectors and the training annotation words are used by machine learning techniques to attempt to automatically apply annotations to new images. The first methods learned the correlations between image features and training annotations. Subsequently, techniques were developed using machine translation to to attempt to translate the textual vocabulary into the 'visual vocabulary,' represented by clustered regions known as ''b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Short-term Memory
Long short-term memory (LSTM) is a type of recurrent neural network (RNN) aimed at mitigating the vanishing gradient problem commonly encountered by traditional RNNs. Its relative insensitivity to gap length is its advantage over other RNNs, hidden Markov models, and other sequence learning methods. It aims to provide a short-term memory for RNN that can last thousands of timesteps (thus "''long'' short-term memory"). The name is made in analogy with long-term memory and short-term memory and their relationship, studied by cognitive psychologists since the early 20th century. An LSTM unit is typically composed of a cell and three gates: an input gate, an output gate, and a forget gate. The cell remembers values over arbitrary time intervals, and the gates regulate the flow of information into and out of the cell. Forget gates decide what information to discard from the previous state, by mapping the previous state and the current input to a value between 0 and 1. A (rounded) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthography
An orthography is a set of convention (norm), conventions for writing a language, including norms of spelling, punctuation, Word#Word boundaries, word boundaries, capitalization, hyphenation, and Emphasis (typography), emphasis. Most national and international languages have an established writing system that has undergone substantial standardization, thus exhibiting less dialect variation than the spoken language. These processes can fossilize pronunciation patterns that are no longer routinely observed in speech (e.g. ''would'' and ''should''); they can also reflect deliberate efforts to introduce variability for the sake of national identity, as seen in Noah Webster's efforts to introduce easily noticeable differences between American and British spelling (e.g. ''honor'' and ''honour''). Orthographic norms develop through social and political influence at various levels, such as encounters with print in education, the workplace, and the state. Some nations have established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (linguistics)
In linguistics, morphology is the study of words, including the principles by which they are formed, and how they relate to one another within a language. Most approaches to morphology investigate the structure of words in terms of morphemes, which are the smallest units in a language with some independent meaning. Morphemes include roots that can exist as words by themselves, but also categories such as affixes that can only appear as part of a larger word. For example, in English the root ''catch'' and the suffix ''-ing'' are both morphemes; ''catch'' may appear as its own word, or it may be combined with ''-ing'' to form the new word ''catching''. Morphology also analyzes how words behave as parts of speech, and how they may be inflected to express grammatical categories including number, tense, and aspect. Concepts such as productivity are concerned with how speakers create words in specific contexts, which evolves over the history of a language. The basic fields of ling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax ( ) is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). Diverse approaches, such as generative grammar and functional grammar, offer unique perspectives on syntax, reflecting its complexity and centrality to understanding human language. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from the ancient Greek word , meaning an orderly or systematic arrangement, which consists of (''syn-'', "together" or "alike"), and (''táxis'', "arrangement"). In Hellenistic Greek, this also specifically developed a use referring to the grammatical order of words, with a slightly altered spelling: . The English term, which first appeared in 1548, is partly borrowed from Latin () and Greek, though the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Realization (linguistics)
In linguistics, realization is the process by which some kind of surface representation is derived from its underlying representation; that is, the way in which some abstract object of linguistic analysis comes to be produced in actual language. Phonemes are often said to be ''realized'' by speech sounds. The different sounds that can realize a particular phoneme are called its allophones. Realization is also a subtask of natural language generation, which involves creating an actual text in a human language (English, French, etc.) from a syntactic representation. There are a number of software packages available for realization, most of which have been developed by academic research groups in NLG. The remainder of this article concerns realization of this kind. Example For example, the following Java code causes the simplenlg systeA Gatt and E Reiter (2009). SimpleNLG: A realisation engine for practical applications. ''Proceedings of ENLG09'/ref> to print out the text ''The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphora (linguistics)
In linguistics, anaphora () is the use of an expression whose interpretation depends upon another expression in context (its antecedent). In a narrower sense, anaphora is the use of an expression that depends specifically upon an antecedent expression and thus is contrasted with cataphora, which is the use of an expression that depends upon a postcedent expression. The anaphoric (referring) term is called an anaphor. For example, in the sentence ''Sally arrived, but nobody saw her'', the pronoun ''her'' is an anaphor, referring back to the antecedent ''Sally''. In the sentence ''Before her arrival, nobody saw Sally'', the pronoun ''her'' refers forward to the postcedent ''Sally'', so ''her'' is now a ''cataphor'' (and an anaphor in the broader, but not the narrower, sense). Usually, an anaphoric expression is a pro-form or some other kind of deictic (contextually dependent) expression. Both anaphora and cataphora are species of endophora, referring to something mentioned elsew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronouns
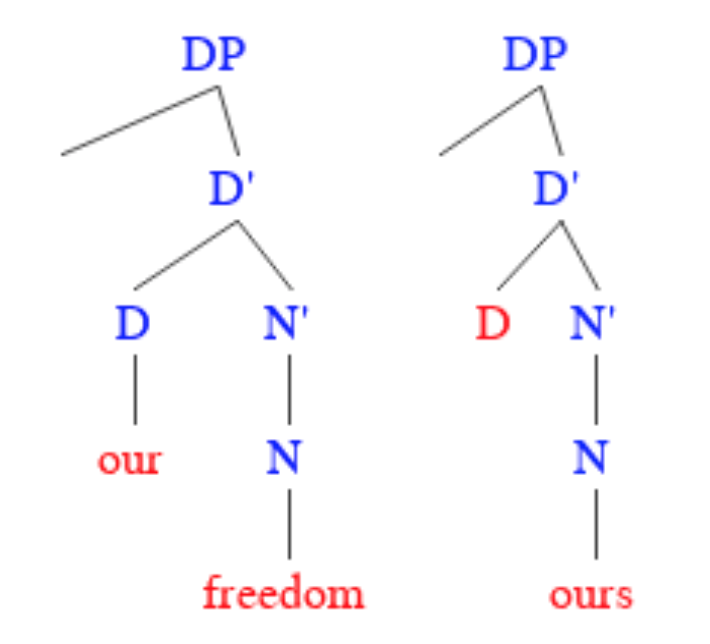
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun ( glossed ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Sub-types include personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive and reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its antecedent, ''that poor man''. The adjective form of the word "pronoun" is "pronominal". A pronominal is also a word or phrase that acts as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Referring Expression
In linguistics, a referring expression (RE) is any noun phrase, or surrogate for a noun phrase, whose function in discourse is to identify some individual object. The technical terminology for ''identify'' differs a great deal from one school of linguistics to another. The most widespread term is probably ''refer'', and a thing identified is a ''referent'', as for example in the work of John Lyons. In linguistics, the study of reference relations belongs to pragmatics, the study of language use, though it is also a matter of great interest to philosophers, especially those wishing to understand the nature of knowledge, perception and cognition more generally. Various devices can be used for reference including determiners, pronouns, proper names. Reference relations can be of different kinds; referents can be in a "real" or imaginary world, or in discourse itself, and they may be singular, plural, or collective. Kinds The kinds of expressions which can refer are: # a noun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Referring Expression Generation
Referring expression generation (REG) is the subtask of natural language generation (NLG) that received most scholarly attention. While NLG is concerned with the conversion of non-linguistic information into natural language, REG focuses only on the creation of referring expressions (noun phrases) that identify specific entities called ''targets''. This task can be split into two sections. The ''content selection'' part determines which set of properties distinguish the intended target and the ''linguistic realization'' part defines how these properties are translated into natural language. A variety of algorithms have been developed in the NLG community to generate different types of referring expressions. Types of referring expressions A referring expression (RE), in linguistics, is any noun phrase, or surrogate for a noun phrase, whose function in discourse is to ''identify'' some individual object (thing, being, event...) The technical terminology for ''identify'' differs a grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |