|
National Defense Reserve Fleet
The National Defense Reserve Fleet (NDRF) consists of Ship, ships of the United States, mostly Merchant ship, merchant vessels, that have been Reserve fleet, mothballed but can be activated within 20 to 120 days to provide shipping during national military emergencies, or non-military emergencies such as commercial shipping crises. The NDRF is managed by the United States Department of Transportation, U.S. Department of Transportation's United States Maritime Administration, Maritime Administration (MARAD). It is distinct from the United States Navy reserve fleets, which consist largely of Naval ship, naval vessels. NDRF vessels are at the fleet sites at James River, Virginia (James River, Reserve Fleet, James River Reserve Fleet); Beaumont, Texas, Beaumont, Texas (Beaumont Reserve Fleet); and Suisun Bay, California (Suisun Bay Reserve Fleet); and at designated outported berths. Former anchorage sites included Stony Point, New York, Stony Point, New York (Hudson River Reserve Fle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson River Reserve Fleet
The Hudson River Reserve Fleet, formally the Hudson River National Defense Reserve Fleet and popularly the Mothball Fleet, was established by act of Congress in 1946 as a component of the National Defense Reserve Fleet. It was first located off Tarrytown, New York, on the Hudson River, one of eight anchorages in the United States to provide a sizable reserve of merchant ships to support any military need arising. History Establishment The Hudson River Reserve Fleet was established in the wake of World War II to provide an anchorage and place of maintenance for a part of the enormous numbers of combat vessels and transports surplussed by the return of peace. Originally anchored at Tarrytown, New York, it was moved further north on the Hudson River on April 30, 1946, to Jones Point at the foot of Dunderberg Mountain. The fleet was anchored in ten rows, extending from the fleet office at the Jones Point dock several miles to the south to the Boulderberg House at Tomkins Cove. Sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suisun Fleet BB61
Suisun may refer to: People * Suisun people Places *Suisun Bay * Suisun City, California ** Suisun–Fairfield station *Suisun Marsh Located in northern California, the Suisun Marsh ( ) has been referred to as the largest brackish water marsh on west coast of the United States of America. The marsh land is part of a tidal estuary, and subject to tidal ebb and flood. The marsh ... * Suisun Valley AVA, wine region Ships * USS ''Suisun'' {{disambig, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ready Reserve Force Ships
Ready Reserve Force (RRF) ships of the National Defense Reserve Fleet are owned, crewed, and maintained by the civilian United States Maritime Administration, but come under control of the Military Sealift Command when activated. The MSC Sealift Program's Surge Project Office is responsible for RRF activities. Ready Reserve Force ships By location Baltimore, MD * SS Wright (T-AVB-3), SS ''Wright'' (T-AVB-3) – SS Wright is part of the RRF, but is dedicated to USMC aviation logistics support. * MV Cape Wrath (T-AKR-9962), MV ''Cape Wrath'' (T-AKR-9962) * MV Cape Washington (T-AKR-9961), MV ''Cape Washington'' (T-AKR-9961) * USNS_Pomeroy , USNS ''Pomeroy ''(T-AKR-316) * MV_Charles_L._Gilliland , MV ''Charles L. Gilliland'' (T-AKR-298) * MV_Gary_I._Gordon , MV ''Gary I Gordan'' (T-AKR-296) * USNS_Watson , USNS ''Watson'' (T-AKR-310) Beaumont Reserve Fleet * MV Cape Victory (T-AKR-9701), MV ''Cape Victory'' (T-AKR-9701) * MV Cape Vincent (T-AKR-9666), MV ''Cape Vincent'' (T- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (1 November 1955 – 30 April 1975) was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) and South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam) and their allies. North Vietnam was supported by the Soviet Union and China, while South Vietnam was supported by the United States and other anti-communist nations. The conflict was the second of the Indochina wars and a proxy war of the Cold War between the Soviet Union and US. The Vietnam War was one of the postcolonial wars of national liberation, a theater in the Cold War, and a civil war, with civil warfare a defining feature from the outset. Direct United States in the Vietnam War, US military involvement escalated from 1965 until its withdrawal in 1973. The fighting spilled into the Laotian Civil War, Laotian and Cambodian Civil Wars, which ended with all three countries becoming Communism, communist in 1975. After the defeat of the French Union in the First Indoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin Crisis Of 1961
The Berlin Crisis of 1961 () was the last major European political and military incident of the Cold War concerning the status of the German capital city, Berlin, and of History of Germany (1945–90), post–World War II Germany. The crisis culminated in the city's ''de facto'' Partition (politics), partition with the East Germany, East German erection of the Berlin Wall. The Berlin Crisis of 1961 was the second attempt by Premier of the Soviet Union, Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev to change the status of Berlin by demanding the withdrawal of all armed forces from the city and stopping the mass exodus of East Germans fleeing to the West. After the failure of his first Berlin Crisis of 1958–1959, ultimatum in 1958, Khrushchev renewed his demands at the 1961 Vienna summit, this time challenging the newly inaugurated U.S. President John F. Kennedy, John F. Kennedy. When talks broke down and no agreement was reached, in August 1961 East German leader Walter Ulbricht, with Khru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
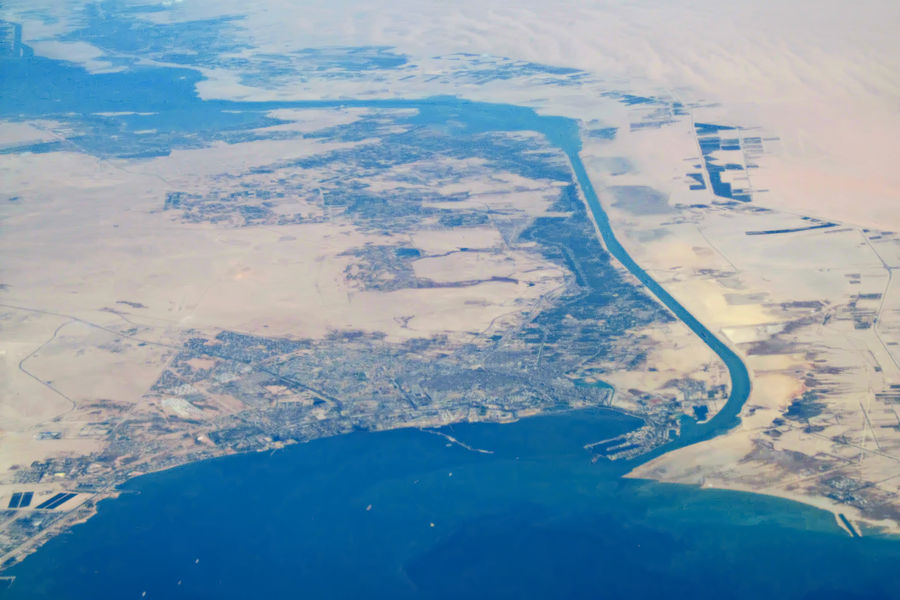
Suez Canal
The Suez Canal (; , ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, Indo-Mediterranean, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia (and by extension, the Sinai Peninsula from the rest of Egypt). The canal is a key trade route between Europe and Asia. In 1858, French diplomat Ferdinand de Lesseps formed the Suez Canal Company, Compagnie de Suez for the express purpose of building the canal. Construction of the canal lasted from 1859 to 1869. The canal officially opened on 17 November 1869. It offers vessels a direct route between the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic and northern Indian Ocean, Indian oceans via the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea, avoiding the South Atlantic and southern Indian oceans and reducing the journey distance from the Arabian Sea to London by approximately , to 10 days at or 8 days at . The canal extends from the northern terminus of Port Said to the southern terminus of Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is an executive department of the United States federal government that aims to meet the needs of commercial farming and livestock food production, promotes agricultural trade and production, works to assure food safety, protects natural resources, fosters rural communities and works to end hunger in the United States and internationally. It is headed by the secretary of agriculture, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the president's Cabinet. The current secretary is Brooke Rollins, who has served since February 13, 2025. Approximately 71% of the USDA's $213 billion budget goes towards nutrition assistance programs administered by the Food and Nutrition Service (FNS). The largest component of the FNS budget is the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (formerly known as the 'Food Stamp' program), which is the cornerstone of USDA's nutrition assistance. The United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean War
The Korean War (25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953) was an armed conflict on the Korean Peninsula fought between North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea; DPRK) and South Korea (Republic of Korea; ROK) and their allies. North Korea was supported by China and the Soviet Union, while South Korea was supported by the United Nations Command (UNC) led by the United States. The conflict was one of the first major proxy wars of the Cold War. Fighting ended in 1953 with an armistice but no peace treaty, leading to the ongoing Korean conflict. After the end of World War II in 1945, Korea, which had been a Korea under Japanese rule, Japanese colony for 35 years, was Division of Korea, divided by the Soviet Union and the United States into two occupation zones at the 38th parallel north, 38th parallel, with plans for a future independent state. Due to political disagreements and influence from their backers, the zones formed their governments in 1948. North Korea was led by Kim Il S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
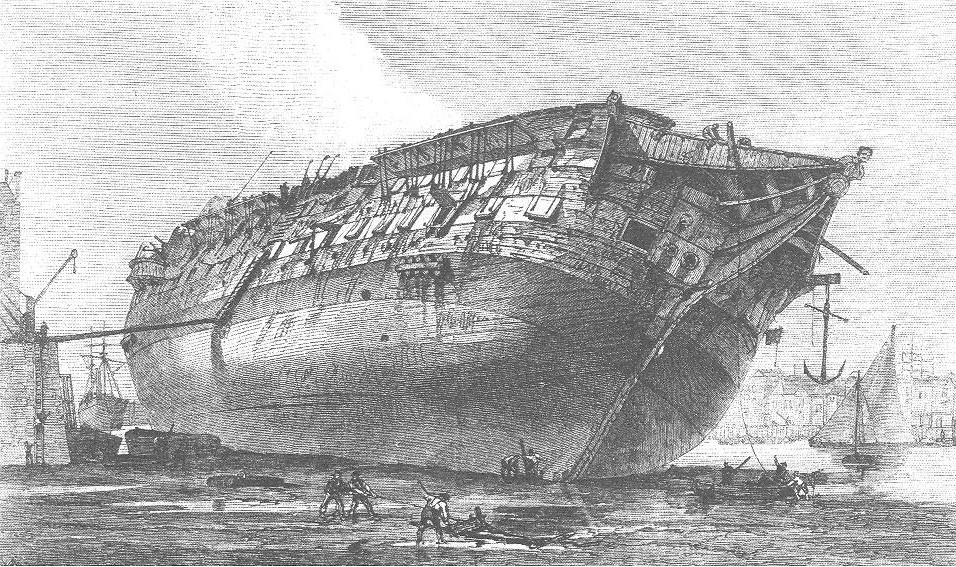
Ship Breaking
Ship breaking (also known as ship recycling, ship demolition, ship scrapping, ship dismantling, or ship cracking) is a type of ship disposal involving the breaking up of ships either as a source of Interchangeable parts, parts, which can be sold for re-use, or for the extraction of raw materials, chiefly scrap. Modern ships have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years before corrosion, Fatigue (material), metal fatigue and a lack of parts render them uneconomical to operate. Ship-breaking allows the materials from the ship, especially steel, to be recycled and made into new products. This lowers the demand for mined iron ore and reduces energy use in the steelmaking process. Fixtures and other equipment on board the vessels can also be reused. While ship-breaking is sustainable, there are concerns about its use by poorer countries without stringent environmental legislation. It is also labour-intensive, and considered one of the world's most dangerous industries. In 2012, roughly 1,250 oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olympia, Washington
Olympia is the capital city of the U.S. state of Washington. It had a population of 55,605 at the 2020 census, making it the state of Washington's 23rd-most populous city. Olympia is the county seat of Thurston County, and the central city for a metropolitan statistical area of 298,758, the fifth-largest in Washington state. Located 50 miles southwest of Seattle, Olympia anchors the South Puget Sound region of Western Washington. The Squaxin and other Coast Salish peoples inhabited the southern Puget Sound region prior to the arrival of European and American settlers in the 19th century. The Treaty of Medicine Creek was signed in 1854 and followed by the Treaty of Olympia in 1856; these two treaties forced the Squaxin to relocate to an Indian reservation. Olympia was declared the capital of the Washington Territories (later the state of Washington) in 1853 and incorporated as a town on January 28, 1859. It became a city in 1882. Aside from its role in the state governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |