|
Naré Maghann Konaté
Naré Maghann Konaté was a 12th-century faama (king) of the Mandinka people, in what is today Mali. He was the father of Sundiata Keita, founder of the Mali Empire, and a character in the oral tradition of the Epic of Sundiata.Takacs, Sarolta Anna; Cline Eric H.,"The Ancient World." Volumes 1-5. Routledge (2015), p. 68,(retrieved 29 April 2024)Fauvelle, François-Xavier, "Les masques et la mosquée - L empire du Mâli XIIIe XIVe siècle." (Contributor: François-Xavier Fauvelle), CNRS editions (2022), p. 19,(retrieved 29 April 2024)Editors: Conrad, David C.; Condé, Djanka Tassey, "Sunjata: A West African Epic of the Mande Peoples." Hackett Publishing (2004), pp. xxxv, xxii, 202, The Epic of Sundiata In the Epic of Sundiata, Naré Maghann Konaté (also called Farako Manko Farakonken, Maghan Kon Fatta or Maghan the Handsome) was a Mandinka king who one day received a divine hunter at his court. The hunter predicted that if Konaté married an ugly woman, she would give him a son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faama
Faama is a Mandinka word meaning "father," "leader," or "king". It was commonly used within the area of pre-imperial Mali. The title spread into areas conquered by Mali and was later used by the Bamana Empire and the Wassoulou Empire of Samori Toure and non-Mandinka groups in the Kenedougou Empire. Both ''faama'' and '' mansa'' are word for king, but ''faama'' is a martial ruler and ''mansa'' is a mystic ruler. See also *Mali Empire * Kenedougou Empire *Wassoulou Empire *Bamana Empire *Keita Dynasty The Keita dynasty ruled pre-imperial and imperial Mali from the 11th century into the early 17th century. It was a Muslim dynasty, and its rulers claimed descent from Bilal ibn Rabah. The early history is entirely unknown, outside of legends and ... * Kabadougou Kingdom References Bamana Mali Empire History of Africa Royal titles Faamas {{africa-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sosso
The Sosso Empire, also written as Soso or Susu, or alternatively Kaniaga, was kingdom of West Africa that originated as a vassal of the Ghana Empire before breaking away and conquering their former overlords. Inhabited by the Soninke ancestors of the modern-day Sosso people, it was centered in the region south of Wagadou and north of Beledougou. The empire peaked under the reign of Soumaoro Kante, who was defeated by the rising Mali Empire of Sundiata Keita. Etymology To the inhabitants of the Manding region, the term 'Kaniaga' referred to all the Soninke-inhabited lands, including Wagadou, Bakhounou, Kingui, Guidioume, Diafounou, Guidimakha and Gajaaga, stretching from the upper Senegal river to Mema. 'Kaniaga' is sometimes also used to refer to the Kingdom of Diarra, a state that was the vassal of Ghana, Sosso, and eventually the Mali Empire. The term 'Sosso' may come from the word for horse, as the kingdom had a monopoly on the horse trade vis-a-vis its southern nei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
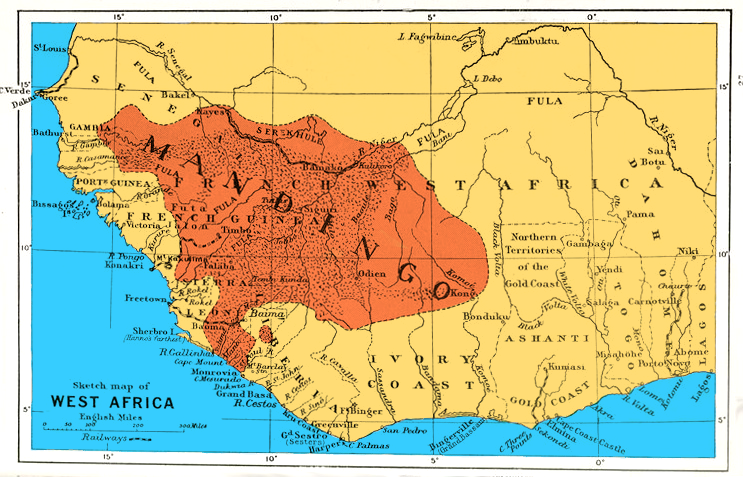
Mandinka
Mandinka, Mandika, Mandinkha, Mandinko, or Mandingo may refer to: Media * Mandingo (novel), ''Mandingo'' (novel), a bestselling novel published in 1957 * Mandingo (film), ''Mandingo'' (film), a 1975 film based on the eponymous 1957 novel * ''Mandingo (play)'', a play by Jack Kirkland * Mandinka (song), "Mandinka" (song), by Sinead O'Connor from her 1987 album ''The Lion and the Cobra'' People * Mandingo people of Sierra Leone * Mandingo Wars (1883–1898), between France and the Wassoulou Empire of the Mandingo * Mandinka language, a Manding language of West Africa, belonging to the Mande subgroup of the Niger-Congo language family * Mandinka people of West Africa * Wassoulou Empire, also known as the Mandinka Empire * Madinkhaya, an eastern variant of the Syriac alphabet * Mandingo, a Stereotypes_of_African_Americans#Mandingo, stereotype of African American men Other use * Mandingo fight, gladiator-like combat to the death by black slaves See also * Manding (disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th-century Births
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longmans
Longman, also known as Pearson Longman, is a publishing company founded in 1724 in London, England, which is owned by Pearson PLC. Since 1968, Longman has been used primarily as an imprint by Pearson's Schools business. The Longman brand is also used for the Longman Schools in China and the '' Longman Dictionary''. History Beginnings The Longman company was founded by Thomas Longman (1699 – 18 June 1755), the son of Ezekiel Longman (died 1708), a gentleman of Bristol. Thomas was apprenticed in 1716 to John Osborn, a London bookseller, and at the expiration of his apprenticeship married Osborn's daughter. In August 1724, he purchased the stock and household goods of William Taylor, the first publisher of ''Robinson Crusoe'', for 9s 6d. Taylor's two shops in Paternoster Row, London, were known respectively as the ''Black Swan'' and the ''Ship'', premises at that time having signs rather than numbers, and became the publishing house premises. Longman entered int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djibril Tamsir Niane
Djibril Tamsir Niane (9 January 1932 – 8 March 2021) was a Guinean historian, playwright, and short story writer. Biography Born in Conakry, Guinea, his secondary education was in Senegal and his degree from the University of Bordeaux. He was an honorary professor of Howard University and the University of Tokyo. He is noted for introducing the Epic of Sundiata, about Sundiata Keita (ca. 1217–1255), founder of the Mali Empire, to the Western world in 1960 by translating the story told to him by Djeli Mamoudou Kouyate, a griot or traditional oral historian. He also edited Volume IV —Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century— of the UNESCO '' General History of Africa'' and participated in other UNESCO projects. He was the father of the late model Katoucha Niane (1960–2008). Niane died in Dakar, Senegal on 8 March 2021, at age 89, from COVID-19 during the COVID-19 pandemic in Senegal. Bibliography Recherches sur l'Empire du Mali au Moyen Age(D.E.S.), suivi d Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Mali
Mali is located in West Africa. The history of the territory can be divided into multiple periods: * Pre-Imperial Mali, before the 13th century, * The era of the Mali Empire, and * The Songhai Empire, from the 13th to the 16th centuries The present borders of Mali touch historical French Sudanese borders that were established in 1891. These boundaries are colonial, grouping regions from the Sudan and Saharan zones. As a result, Mali is a multiethnic country, with the Mandé peoples forming a significant portion of the population. Mali's history is deeply shaped by its strategic role in Trans-Saharan trade, connecting West Africa with the Maghreb. The city of Timbuktu is representative of this legacy; located on the southern edge of the Sahara near the Niger River. It became a major hub of commerce, scholarship, and culture from the 13th century onward. This growth was particularly pronounced during the rise of the Mali Empire, followed by the expansion of the Songhai Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keita Dynasty
The Keita dynasty ruled pre-imperial and imperial Mali from the 11th century into the early 17th century. It was a Muslim dynasty, and its rulers claimed descent from Bilal ibn Rabah. The early history is entirely unknown, outside of legends and myths. The first Keita ''mansa'' was Sundiata Keita. This is when Mari Jata is crowned and Keita becomes a clan name. A couple of generations after him, his great-nephew, Mansa Musa Keita I of Mali, made a celebrated pilgrimage to Mecca. The dynasty remained a major power in West Africa from the early 13th century until the breakup of the Mali Empire around 1610. Rivals from within the clan founded smaller kingdoms within contemporary Mali and Guinea. Of the members of these modern "daughter dynasties", the late politician Modibo Keita and the musician Salif Keita are arguably the most famous. Legendary Ancestors According to Muslim tradition, Bilal ibn Rabah was a freed slave, possibly of Abyssinian descent, who accepted Islam and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indiana University Press
Indiana University Press, also known as IU Press, is an academic publisher founded in 1950 at Indiana University that specializes in the humanities and social sciences. Its headquarters are located in Bloomington, Indiana. IU Press publishes approximately 100 new books annually, in addition to 38 academic journals, and maintains a current catalog comprising some 2,000 titles. Indiana University Press primarily publishes in the following areas: African, African American, Asian, cultural, Jewish, Holocaust, Middle Eastern studies, Russian and Eastern European, and women's and gender studies; anthropology, film studies, folklore, history, bioethics, music, paleontology, philanthropy, philosophy, and religion. IU Press undertakes extensive regional publishing under its Quarry Books imprint. History IU Press began in 1950 as part of Indiana University's post-war growth under President Herman B Wells. Bernard Perry, son of Harvard philosophy professor Ralph Barton Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soumaoro Kanté
Soumaoro Kanté (also known as Sumaworo Kanté or Sumanguru Kanté) was a 13th-century king of the Sosso people. Seizing Koumbi Saleh, the capital of the recently defunct Ghana Empire, Soumaoro Kanté proceeded to conquer several neighboring states, including the Mandinka people in what is now Mali. However, the Mandinka prince Sundiata Keita built a coalition of smaller kingdoms to oppose him at the Battle of Kirina (c. 1235.), defeating the Sosso and leaving Sundiata's new Mali Empire dominant in the region. Whether or not any of the deeds attributed to him actually happened as such, or even whether Kante existed at all, is debated by historians. Traditional oral histories provide a wide variety of information, some of which is contradictory and much that is obviously mythical. Biography Soumaoro Kanté is portrayed as a villainous sorcerer-king in the national epic of Mali, the Epic of Sundiata. After his defeat at Kirina, he flees into the mountains of Koulikoro, where he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sogolon Condé
Sogolon Wulen Condé Akyeampong, Emmanuel Kwaku; and Gates, Jr., Professor Henry Louis; "Dictionary of African Biography, Volumes 1-6." (contributors and editors: Emmanuel Kwaku Akyeampong, Professor Henry Louis Gates, Jr.), OUP USA (2012), p. 330,(retrieved 22 April 2024) (Gambian English: Sogolon Konte/Konteh) of Dò ni Kiri, commonly known as Sogolon Condé (in Malian French), was a 13th-century princess of Imperial Mali, and one of the prominent women portrayed in the Epic of Sundiata. Her trials and tribulations are well preserved in the epic. She was the second wife of Faama (''King'') Naré Maghann Konaté, and mother of Mansa Sundiata Keita, founder of the Mali Empire in the 13th century. According to Bamba Suso and Banna Kanute, Sogolong's father was Sankarang Madiba Konte, also known as Faa Ganda (probably Sangaran Madiba Konte, king of Sankaran, according to Conrad and Frank),Suso, Bamba; and Kanute, Banna; "Sunjata: Gambian Versions of the Mande Epic." (translat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandinka People
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, The Gambia, southern Senegal and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the List of ethnic groups of Africa, largest ethnolinguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family, which are a ''lingua franca'' in much of West Africa. They are predominantly Subsistence agriculture, subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali. The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |