|
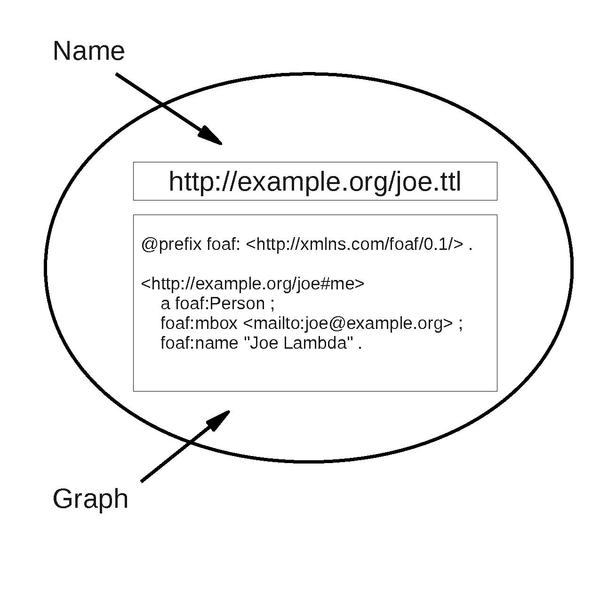
Named Graph
Named graphs are a key concept of Semantic Web architecture in which a set of Resource Description Framework statements (a graph) are identified using a URI, allowing descriptions to be made of that set of statements such as context, provenance information or other such metadata. Named graphs are a simple extension of the RDF data model through which graphs can be created but the model lacks an effective means of distinguishing between them once published on the Web at large. Named graphs and HTTP One conceptualization of the Web is as a graph of document nodes identified with URIs and connected by hyperlink arcs which are expressed within the HTML documents. By doing an HTTP GET on a URI (usually via a Web browser), a somehow-related document may be retrieved. This "follow your nose" approach also applies to RDF documents on the Web in the form of Linked Data, where typically an RDF syntax is used to express data as a series of statements, and URIs within the RDF point to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resource Description Framework
The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a method to describe and exchange graph data. It was originally designed as a data model for metadata by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). It provides a variety of syntax notations and formats, of which the most widely used is Turtle ( Terse RDF Triple Language). RDF is a directed graph composed of triple statements. An RDF graph statement is represented by: (1) a node for the subject, (2) an arc from subject to object, representing a predicate, and (3) a node for the object. Each of these parts can be identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI). An object can also be a literal value. This simple, flexible data model has a lot of expressive power to represent complex situations, relationships, and other things of interest, while also being appropriately abstract. RDF was adopted as a W3C recommendation in 1999. The RDF 1.0 specification was published in 2004, and the RDF 1.1 specification in 2014. SPARQL is a standard query ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Browser
A web browser, often shortened to browser, is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers can also display content stored locally on the user's device. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, smartwatches and consoles. As of 2024, the most used browsers worldwide are Google Chrome (~66% market share), Safari (~16%), Edge (~6%), Firefox (~3%), Samsung Internet (~2%), and Opera (~2%). As of 2023, an estimated 5.4 billion people had used a browser. Function The purpose of a web browser is to fetch content and display it on the user's device. This process begins when the user inputs a Uniform Resource Locator (URL), such as ''https://en.wikipedia.org/'', into the browser's address bar. Virtually all URLs on the Web start with either ''http:'' or ''h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TriX (syntax)
TriX ( Triples in XML) is a serialization format for RDF (Resource Description Framework) graphs. It is an XML format for serializing Named Graphs and RDF Datasets which offers a compact and readable alternative to the XML-based RDF/XML syntax. It was jointly created by HP Labs and Nokia Nokia Corporation is a Finnish multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications industry, telecommunications, technology company, information technology, and consumer electronics corporation, originally established as a pulp mill in 1 .... It is suggested that those digital artifacts dependent of the serialization format need means to verify immutability, or digital artifacts including datasets, code, texts, and images are not verifiable nor permanent. Embedding cryptographic hash values to applied URIs has been suggested for structured data files such as nano-publications. Member registration required. Example https://example.org/Bob https://example.org/wife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-Quads
N-Triples is a format for storing and transmitting data. It is a line-based, plain text serialisation format for RDF (Resource Description Framework) graphs, and a subset of the Turtle (Terse RDF Triple Language) format. N-Triples should not be confused with Notation3 which is a superset of Turtle. N-Triples was primarily developed by Dave Beckett at the University of Bristol and Art Barstow at the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). N-Triples was designed to be a simpler format than Notation3 and Turtle, and therefore easier for software to parse and generate. However, because it lacks some of the shortcuts provided by other RDF serialisations (such as CURIEs and nested resources, which are provided by both RDF/XML and Turtle) it can be onerous to type out large amounts of data by hand, and difficult to read. Usage There is very little variation in how an RDF graph can be represented in N-Triples. This makes it a very convenient format to provide "model answers" foRDF test suit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arity
In logic, mathematics, and computer science, arity () is the number of arguments or operands taken by a function, operation or relation. In mathematics, arity may also be called rank, but this word can have many other meanings. In logic and philosophy, arity may also be called adicity and degree. In linguistics, it is usually named valency. Examples In general, functions or operators with a given arity follow the naming conventions of ''n''-based numeral systems, such as binary and hexadecimal. A Latin prefix is combined with the -ary suffix. For example: * A nullary function takes no arguments. ** Example: f()=2 * A unary function takes one argument. ** Example: f(x)=2x * A binary function takes two arguments. ** Example: f(x,y)=2xy * A ternary function takes three arguments. ** Example: f(x,y,z)=2xyz * An ''n''-ary function takes ''n'' arguments. ** Example: f(x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n)=2\prod_^n x_i Nullary A constant can be treated as the output of an operation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turtle (syntax)
In computing, Terse RDF Triple Language (Turtle) is a syntax and file format for expressing data in the Resource Description Framework (RDF) data model. Turtle syntax is similar to that of SPARQL, an RDF query language. It is a common data format for storing RDF data, along with N-Triples, JSON-LD and RDF/XML. RDF represents information using semantic triples, which comprise a subject, predicate, and object. Each item in the triple is expressed as a Web URI. Turtle provides a way to group three URIs to make a triple, and provides ways to abbreviate such information, for example by factoring out common portions of URIs. For example, information about Huckleberry Finn could be expressed as: <http://example.org/books/Huckleberry_Finn> <http://example.org/relation/author> <http://example.org/person/Mark_Twain> . History Turtle was defined by Dave Beckett as a subset of Tim Berners-Lee and Dan Connolly's Notation3 (N3) language, and a superset of the minima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPARQL
SPARQL (pronounced ":wikt:sparkle, sparkle", a recursive acronym for SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language) is an RDF query language—that is, a Semantic Query, semantic query language for databases—able to retrieve and manipulate data stored in Resource Description Framework, Resource Description Framework (RDF) format. It was made a standard by the ''RDF Data Access Working Group'' (DAWG) of the World Wide Web Consortium, and is recognized as one of the key technologies of the semantic web. On 15 January 2008, SPARQL 1.0 was acknowledged by W3C as an official recommendation, and SPARQL 1.1 in March, 2013. SPARQL allows for a query to consist of triplestore, triple patterns, logical conjunction, conjunctions, logical disjunction, disjunctions, and optional software design pattern, patterns. Implementations for multiple programming languages exist. There exist tools that allow one to connect and semi-automatically construct a SPARQL query for a SPARQL endpoint, for exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tim Berners-Lee
Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee (born 8 June 1955), also known as TimBL, is an English computer scientist best known as the inventor of the World Wide Web, the HTML markup language, the URL system, and HTTP. He is a professorial research fellow at the University of Oxford and a professor emeritus at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Berners-Lee proposed an information management system on 12 March 1989 and implemented the first successful communication between a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) client and Server (computing), server via the Internet in mid-November. He devised and implemented the first Web browser and Web server and helped foster the Web's subsequent development. He is the founder and emeritus director of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), which oversees the continued development of the Web. He co-founded (with Rosemary Leith) the World Wide Web Foundation. In April 2009, he was elected as Foreign Associate of the National Academy of Sciences. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linked Data
In computing, linked data is structured data which is interlinked with other data so it becomes more useful through semantic queries. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP, RDF and URIs, but rather than using them to serve web pages only for human readers, it extends them to share information in a way that can be read automatically by computers. Part of the vision of linked data is for the Internet to become a global database. Tim Berners-Lee, director of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), coined the term in a 2006 design note about the Semantic Web project. Linked data may also be open data, in which case it is usually described as Linked Open Data. Principles In his 2006 "Linked Data" note, Tim Berners-Lee outlined four principles of linked data, paraphrased along the following lines: #Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) should be used to name and identify individual things. #HTTP URIs should be used to allow these things to be looked up, interpreted, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTTP
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, where hypertext documents include hyperlinks to other resources that the user can easily access, for example by a Computer mouse, mouse click or by tapping the screen in a web browser. Development of HTTP was initiated by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN in 1989 and summarized in a simple document describing the behavior of a client and a server using the first HTTP version, named 0.9. That version was subsequently developed, eventually becoming the public 1.0. Development of early HTTP Requests for Comments (RFCs) started a few years later in a coordinated effort by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), with work later moving to the IETF. HTTP/1 was finalized and fully documented (as version 1.0) in 1996 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TriX (serialization Format)
TriX ( Triples in XML) is a serialization format for RDF (Resource Description Framework) graphs. It is an XML format for serializing Named Graphs and RDF Datasets which offers a compact and readable alternative to the XML-based RDF/XML syntax. It was jointly created by HP Labs and Nokia Nokia Corporation is a Finnish multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications industry, telecommunications, technology company, information technology, and consumer electronics corporation, originally established as a pulp mill in 1 .... It is suggested that those digital artifacts dependent of the serialization format need means to verify immutability, or digital artifacts including datasets, code, texts, and images are not verifiable nor permanent. Embedding cryptographic hash values to applied URIs has been suggested for structured data files such as nano-publications. Member registration required. Example https://example.org/Bob https://example.org/wife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |