|
Nabarro–Herring Creep
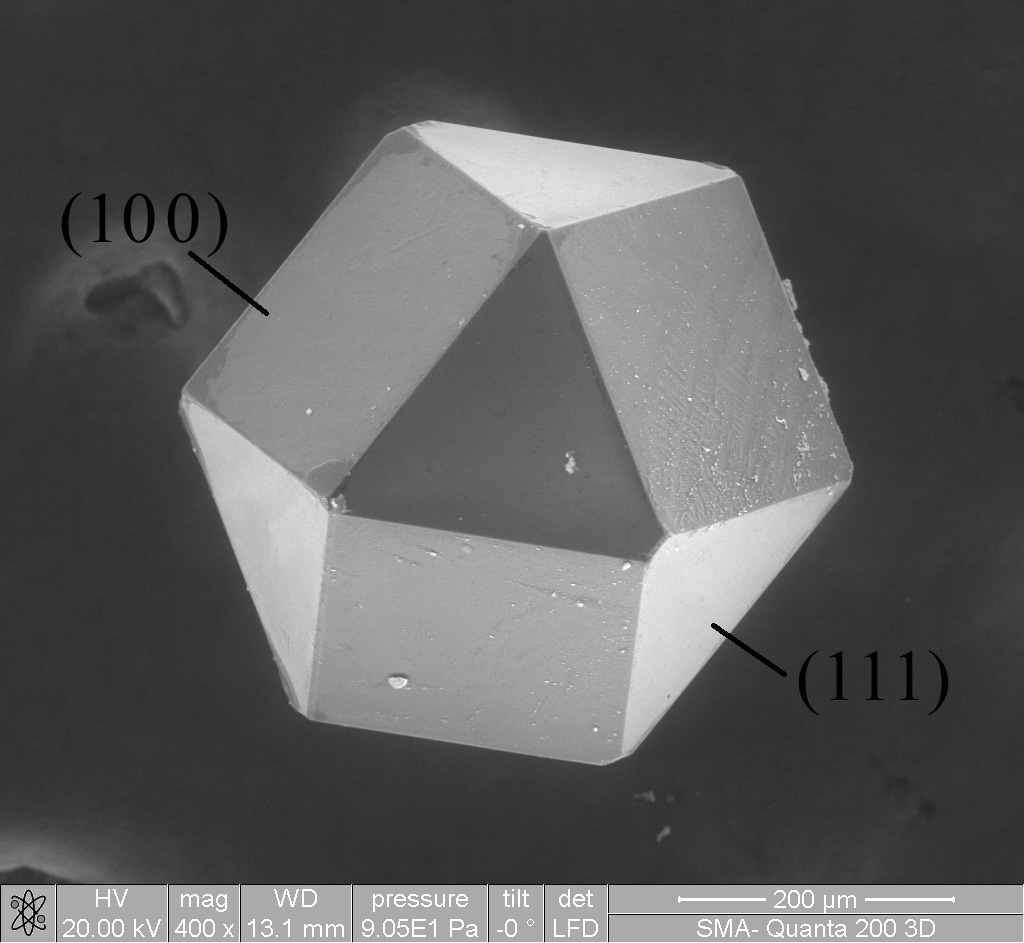
In materials science, Nabarro–Herring creep (NH creep) is a mechanism of deformation of crystalline materials (and amorphous materials) that occurs at low stresses and held at elevated temperatures in fine-grained materials. In Nabarro–Herring creep, atoms diffuse through the crystals, and the rate of creep varies inversely with the square of the grain size so fine-grained materials creep faster than coarser-grained ones. NH creep is solely controlled by diffusional mass transport. This type of creep results from the diffusion of vacancies from regions of high chemical potential at grain boundaries subjected to normal tensile stresses to regions of lower chemical potential where the average tensile stresses across the grain boundaries are zero. Self-diffusion within the grains of a polycrystalline solid can cause the solid to yield to an applied shear stress, the yielding being caused by a diffusional flow of matter within each crystal grain away from boundaries whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Materials Science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field of researching and discovering materials. Materials engineering is an engineering field of finding uses for materials in other fields and industries. The intellectual origins of materials science stem from the Age of Enlightenment, when researchers began to use analytical thinking from chemistry, physics, and engineering to understand ancient, phenomenological observations in metallurgy and mineralogy. Materials science still incorporates elements of physics, chemistry, and engineering. As such, the field was long considered by academic institutions as a sub-field of these related fields. Beginning in the 1940s, materials science began to be more widely recognized as a specific and distinct field of science and engineering, and major technical universities around the world created dedicated schools for its study. Materials scientists emphasize understanding how the history of a material (''processing'') influences its struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycrystalline
A crystallite is a small or even microscopic crystal which forms, for example, during the cooling of many materials. Crystallites are also referred to as grains. Bacillite is a type of crystallite. It is rodlike with parallel longulites. Structure The orientation of crystallites can be random with no preferred direction, called random texture, or directed, possibly due to growth and processing conditions. While the structure of a single crystal is highly ordered and its lattice is continuous and unbroken, amorphous materials, such as glass and many polymers, are non-crystalline and do not display any structures, as their constituents are not arranged in an ordered manner. Polycrystalline structures and paracrystalline phases are in between these two extremes. Polycrystalline materials, or polycrystals, are solids that are composed of many crystallites of varying size and orientation. Most materials are polycrystalline, made of a large number crystallites held together by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coble Creep
In materials science, Coble creep, a form of diffusion creep, is a mechanism for deformation of crystalline solids. Contrasted with other diffusional creep mechanisms, Coble creep is similar to Nabarro–Herring creep in that it is dominant at lower stress levels and higher temperatures than creep mechanisms utilizing dislocation glide. Coble creep occurs through the diffusion of atoms in a material along grain boundaries. This mechanism is observed in polycrystals or along the surface in a single crystal, which produces a net flow of material and a sliding of the grain boundaries. American materials scientist Robert L. Coble first reported his theory of how materials creep across grain boundaries and at high temperatures in alumina. Here he famously noticed a different creep mechanism that was more dependent on the size of the grain. The strain rate in a material experiencing Coble creep is given by \begin \frac \equiv \dot_C &= A_C \frac \fracD_0 \exp\left(-\frac\ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flux
Flux describes any effect that appears to pass or travel (whether it actually moves or not) through a surface or substance. Flux is a concept in applied mathematics and vector calculus which has many applications in physics. For transport phenomena, flux is a vector quantity, describing the magnitude and direction of the flow of a substance or property. In vector calculus flux is a scalar quantity, defined as the surface integral of the perpendicular component of a vector field over a surface. Terminology The word ''flux'' comes from Latin: ''fluxus'' means "flow", and ''fluere'' is "to flow". As '' fluxion'', this term was introduced into differential calculus by Isaac Newton. The concept of heat flux was a key contribution of Joseph Fourier, in the analysis of heat transfer phenomena. His seminal treatise ''Théorie analytique de la chaleur'' (''The Analytical Theory of Heat''), defines ''fluxion'' as a central quantity and proceeds to derive the now well-known expre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boltzmann Constant
The Boltzmann constant ( or ) is the proportionality factor that relates the average relative thermal energy of particles in a ideal gas, gas with the thermodynamic temperature of the gas. It occurs in the definitions of the kelvin (K) and the molar gas constant, in Planck's law of black-body radiation and Boltzmann's entropy formula, and is used in calculating Johnson–Nyquist noise, thermal noise in resistors. The Boltzmann constant has Dimensional analysis, dimensions of energy divided by temperature, the same as entropy and heat capacity. It is named after the Austrian scientist Ludwig Boltzmann. As part of the 2019 revision of the SI, the Boltzmann constant is one of the seven "Physical constant, defining constants" that have been defined so as to have exact finite decimal values in SI units. They are used in various combinations to define the seven SI base units. The Boltzmann constant is defined to be exactly joules per kelvin, with the effect of defining the SI unit ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activation Energy
In the Arrhenius model of reaction rates, activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that must be available to reactants for a chemical reaction to occur. The activation energy (''E''a) of a reaction is measured in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) or kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol). Activation energy can be thought of as a magnitude of the potential barrier (sometimes called the energy barrier) separating minima of the potential energy surface pertaining to the initial and final thermodynamic state. For a chemical reaction to proceed at a reasonable rate, the temperature of the system should be high enough such that there exists an appreciable number of molecules with translational energy equal to or greater than the activation energy. The term "activation energy" was introduced in 1889 by the Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius. Other uses Although less commonly used, activation energy also applies to nuclear reactions and various other physical phenomena. Temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensile Stress
In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity that describes forces present during deformation. For example, an object being pulled apart, such as a stretched elastic band, is subject to ''tensile'' stress and may undergo elongation. An object being pushed together, such as a crumpled sponge, is subject to ''compressive'' stress and may undergo shortening. The greater the force and the smaller the cross-sectional area of the body on which it acts, the greater the stress. Stress has dimension of force per area, with SI units of newtons per square meter (N/m2) or pascal (Pa). Stress expresses the internal forces that neighbouring particles of a continuous material exert on each other, while ''strain'' is the measure of the relative deformation of the material. For example, when a solid vertical bar is supporting an overhead weight, each particle in the bar pushes on the particles immediately below it. When a liquid is in a closed container under pressure, each pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compressive Stress
Compressive stresses are generated in objects when they are subjected to forces that push inward, causing the material to shorten or compress. These stresses occur when an object is squeezed or pressed from opposite directions. In everyday life, compressive stresses are common in many structures and materials. For instance, the weight of a building creates compressive stresses in its walls and foundations. Similarly, when a person stands, the bones in their legs experience compressive stresses due to the weight of the body pushing down. Compressive stresses can lead to deformation if they are strong enough, potentially causing the object to change shape or, in extreme cases, to break. The ability of a material to withstand compressive stresses without failing is known as its compressive strength. When an object is subjected to a force in a single direction (referred to as a uniaxial compression), the compressive stress is determined by dividing the applied force by the cross-sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metals
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. These properties are all associated with having electrons available at the Fermi level, as against nonmetallic materials which do not. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into a wire) and malleable (can be shaped via hammering or pressing). A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polymeric sulfur nitride. The general science of metals is called metallurgy, a subtopic of materials science; aspects of the electronic and thermal properties are also within the scope of condensed matter physics and solid-state chemistry, it is a multidisciplinary topic. In colloquial use materials such as steel alloys are referred to as metals, while others such as polymers, wood or ceramics are nonmetallic materials. A metal conducts electricity at a temperature of absolute z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceramics
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, and brick. The earliest ceramics made by humans were fired clay bricks used for building house walls and other structures. Other pottery objects such as pots, vessels, vases and figurines were made from clay, either by itself or mixed with other materials like silica, hardened by sintering in fire. Later, ceramics were glazed and fired to create smooth, colored surfaces, decreasing porosity through the use of glassy, amorphous ceramic coatings on top of the crystalline ceramic substrates. Ceramics now include domestic, industrial, and building products, as well as a wide range of materials developed for use in advanced ceramic engineering, such as semiconductors. The word '' ceramic'' comes from the Ancient Greek word (), mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strain (mechanics)
In mechanics, strain is defined as relative deformation, compared to a position configuration. Different equivalent choices may be made for the expression of a strain field depending on whether it is defined with respect to the initial or the final configuration of the body and on whether the metric tensor or its dual is considered. Strain has dimension of a length ratio, with SI base units of meter per meter (m/m). Hence strains are dimensionless and are usually expressed as a decimal fraction or a percentage. Parts-per notation is also used, e.g., parts per million or parts per billion (sometimes called "microstrains" and "nanostrains", respectively), corresponding to μm/m and nm/m. Strain can be formulated as the spatial derivative of displacement: \boldsymbol \doteq \cfrac\left(\mathbf - \mathbf\right) = \boldsymbol'- \boldsymbol, where is the identity tensor. The displacement of a body may be expressed in the form , where is the reference position of material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |