|
N-Methyltyramine
''N''-Methyltyramine (NMT), also known as 4-hydroxy-''N''-methylphenethylamine, is a human trace amine and natural phenethylamine alkaloid found in a variety of plants.T. A. Smith (1977). "Phenethylamine and related compounds in plants." ''Phytochemistry'' 16 9 – 18. As the name implies, it is the N-methyl analog of tyramine, which is a well-known biogenic trace amine with which NMT shares many pharmacological properties. Biosynthetically, NMT is produced by the N-methylation of tyramine via the action of the enzyme phenylethanolamine ''N''-methyltransferase in humans and tyramine ''N''-methyltransferase in plants. Occurrence N-methyltyramine seems to be quite widely distributed in plants. NMT was isolated as a natural product for the first time, from germinating barley roots, by Kirkwood and Marion in 1950. These chemists found that 600 g of barley, after germination and 10-day growth, yielded 168 mg of N-methyltyramine.S. Kirkwood and L. Marion (1950) ''J. Am. Chem. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyltyramine
Methyltyramine may refer to: * α-Methyltyramine (4-hydroxyamphetamine) * β-Methyltyramine * ''N''-Methyltyramine * 2-Methyltyramine * 3-Methyltyramine * ''O''-Methyltyramine (4-methoxyphenethylamine) {{Chemistry index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trace Amine
Trace amines are an endogenous group of trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) agonists – and hence, monoaminergic neuromodulators – that are structurally and metabolically related to classical monoamine neurotransmitters. Compared to the classical monoamines, they are present in trace concentrations. They are distributed heterogeneously throughout the mammalian brain and peripheral nervous tissues and exhibit high rates of metabolism. Although they can be synthesized within parent monoamine neurotransmitter systems, there is evidence that suggests that some of them may comprise their own independent neurotransmitter systems. Trace amines play significant roles in regulating the quantity of monoamine neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft of monoamine neurons with TAAR1. They have well-characterized presynaptic ''amphetamine-like'' effects on these monoamine neurons via TAAR1 activation; specifically, by activating TAAR1 in neurons they promote the release and preve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
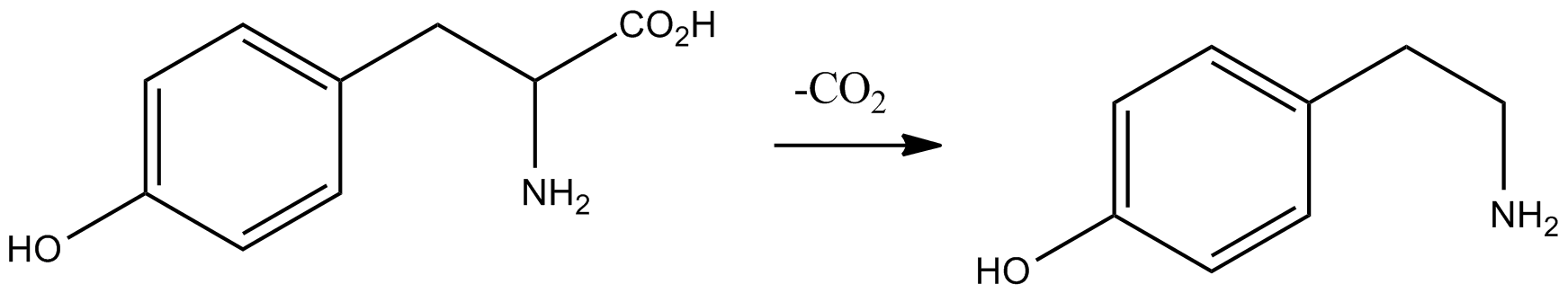
Tyramine
Tyramine ( ) (also spelled tyramin), also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier, resulting in only non-psychoactive peripheral sympathomimetic effects following ingestion. A hypertensive crisis can result, however, from ingestion of tyramine-rich foods in conjunction with the use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Occurrence Tyramine occurs widely in plants and animals, and is metabolized by various enzymes, including monoamine oxidases. In foods, it often is produced by the decarboxylation of tyrosine during fermentation or decay. Foods that are fermented, cured, pickled, aged, or spoiled have high amounts of tyramine. Tyramine levels go up when foods are at room temperature or go past their freshness date. Specific foods containing considerable amounts of tyramine include: * Strong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitter Orange
The bitter orange, sour orange, Seville orange, bigarade orange, or marmalade orange is the hybrid citrus tree species ''Citrus'' × ''aurantium'', and its fruit. It is native to Southeast Asia and has been spread by humans to many parts of the world. It is a cross between the pomelo, '' Citrus maxima'', and the wild type mandarin orange, '' Citrus reticulata''. The bitter orange is used to make essential oil, used in foods, drinks, and pharmaceuticals. The Seville orange is prized for making British orange marmalade. Definition In some proposed systems, the species ''Citrus'' × ''aurantium'' includes not only the bitter orange proper, but all other hybrids between the pomelo and the wild type mandarin, namely the sweet orange, the grapefruit, and all cultivated mandarins. p. 69–70 This article only deals with the bitter orange proper. History The bitter orange, like many cultivated ''Citrus'' species, is a hybrid, in its case of the wild mandarin and pomel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyl Sulfate
Dimethyl sulfate (DMS) is a chemical compound with formula (CH3O)2SO2. As the diester of methanol and sulfuric acid, its formula is often written as ( CH3)2 SO4 or Me2SO4, where CH3 or Me is methyl. Me2SO4 is mainly used as a methylating agent in organic synthesis. Me2SO4 is a colourless oily liquid with a slight onion-like odour. Like all strong alkylating agents, Me2SO4 is toxic. Its use as a laboratory reagent has been superseded to some extent by methyl triflate, CF3SO3CH3, the methyl ester of trifluoromethanesulfonic acid. History Impure dimethyl sulfate was prepared in the early 19th century. J. P. Claesson later extensively studied its preparation. It was investigated for possible use in chemical warfare in World War I in 75% to 25% mixture with methyl chlorosulfonate (CH3ClO3S) called "C-stoff" in Germany, or with chlorosulfonic acid called "Rationite" in France. The esterification of sulfuric acid with methanol was described in 1835: : Production Dimethyl s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorene
Fluorene , or 9''H''-fluorene is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4)2CH2. It forms white crystals that exhibit a characteristic, aromatic odor similar to that of naphthalene. Despite its name, it does not contain the element fluorine, but rather it comes from the violet fluorescence it exhibits. For commercial purposes it is obtained from coal tar, where it was discovered and named by Marcellin Berthelot in 1867. It is insoluble in water and soluble in many organic solvents. Although sometimes classified as a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, the five-membered ring has no aromatic properties. Fluorene is mildly acidic. Synthesis, structure, and reactivity Although fluorene is obtained from coal tar, it can also be prepared by dehydrogenation of diphenylmethane. Alternatively, it can be prepared by the reduction of fluorenone with zinc or hypophosphorous acid– iodine. The fluorene molecule is nearly planar,D. M. Burns, John Iball (1954), ''Molecular Structure of Flu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is encoded by the codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. The one-letter symbol Y was assigned to tyrosine for being alphabetically nearest of those letters available. Note that T was assigned to the structurally simpler threonine, U was avoided for its similarity with V for valine, W was assigned to tryptophan, while X was reserved for undetermined or atypical amino acids. The mnemonic t''Y''rosine was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imine
In organic chemistry, an imine ( or ) is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond (). The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions. Distinction is sometimes made between aldimines and ketimines, derived from aldehydes and ketones, respectively. Structure In imines the five core atoms (C2C=NX, ketimine; and C(H)C=NX, aldimine; X = H or C) are coplanar. Planarity results from the sp2-hybridization of the mutually double-bonded carbon and the nitrogen atoms. The C=N distance is 1.29–1.31 Å for nonconjugated imines and 1.35 Å for conjugated imines. By contrast, C−N distances in amines and nitriles are 1.47 and 1.16 Å respectively. Rotation about the C=N bond is slow. Using NMR spectroscopy, both E–Z notation, ''E'' and ''Z'' isomers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reserpine
Reserpine is a drug that is used for the treatment of hypertension, high blood pressure, usually in combination with a thiazide diuretic or vasodilator. Large clinical trials have shown that combined treatment with reserpine plus a thiazide diuretic reduces mortality of people with hypertension. Although the use of reserpine as a solo drug has declined since it was first approved by the FDA in 1955, the combined use of reserpine and a thiazide diuretic or vasodilator is still recommended in patients who do not achieve adequate lowering of blood pressure with first-line drug treatment alone. The reserpine-hydrochlorothiazide combo pill was the 17th most commonly prescribed of the 43 combination antihypertensive pills available in 2012. The antihypertensive actions of reserpine are largely due to its antinoradrenergic effects, which are a result of its ability to deplete catecholamines (among other monoamine neurotransmitters) from peripheral nervous system, peripheral sympathetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressor
An antihypotensive, also known as a vasopressor, is an agent that raises blood pressure by constricting blood vessels, thereby increasing systemic vascular resistance. This is different from inotropes which increase the force of cardiac contraction. Some substances do both (e.g. dopamine, dobutamine). If low blood pressure is due to blood loss, then preparations increasing volume of blood circulation—plasma-substituting solutions such as colloid and crystalloid solutions (salt solutions)—will raise the blood pressure without any direct vasopressor activity. Packed red blood cells, plasma or whole blood should not be used solely for volume expansion or to increase oncotic pressure of circulating blood. Blood products should only be used if reduced oxygen carrying capacity or coagulopathy is present. Other causes of either absolute (dehydration, loss of plasma via wound/burns) or relative ( third space losses) vascular volume depletion also respond, although blood products are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and by a small number of neurons in the medulla oblongata. It plays an essential role in the fight-or-flight response by increasing blood flow to muscles, heart output by acting on the SA node, pupil dilation response, and blood sugar level. It does this by binding to alpha and beta receptors. It is found in many animals, including humans, and some single-celled organisms. It has also been isolated from the plant '' Scoparia dulcis'' found in Northern Vietnam. Medical uses As a medication, it is used to treat several conditions, including allergic reaction anaphylaxis, cardiac arrest, and superficial bleeding. Inhaled adrenaline may be used to improve the symptoms of croup. It may also be used for asthma when other treatments are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |