|
Msiri
Msiri (c. 1830 – December 20, 1891) founded and ruled the Yeke Kingdom (also called the Garanganze or Garenganze kingdom) in south-east Katanga (now in DR Congo) from about 1856 to 1891. His name is sometimes spelled 'M'Siri' in articles in French. Other variants are "Mziri", "Msidi", and "Mushidi"; and his full name was Mwenda Msiri Ngelengwa Shitambi.''Mwami Msiri, King of Garanganze''. Retrieved 8 February 2007. Msiri's origins and rise to power From Tabora to Katanga Msiri was a Nyamwezi from in modern-day |
Msiri 1830 1891
Msiri (c. 1830 – December 20, 1891) founded and ruled the Yeke Kingdom (also called the Garanganze or Garenganze kingdom) in south-east Katanga Province, Katanga (now in DR Congo) from about 1856 to 1891. His name is sometimes spelled 'M'Siri' in articles in French. Other variants are "Mziri", "Msidi", and "Mushidi"; and his full name was Mwenda Msiri Ngelengwa Shitambi.''Mwami Msiri, King of Garanganze''. Retrieved 8 February 2007. Msiri's origins and rise to power From Tabora to Katanga Msiri was a Nyamwezi people, Nyamwezi from Tabora in modern-day Tanzania and a trader, like his father Kalasa, involved in the copper, Ivory trade, ivory and Arab slave, East African slave trade controlled by the Sultan of Zanzibar and his Arabs, Arab and Swahili people, Swahili agents. The ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeke Kingdom
The Yeke Kingdom (also called the ''Garanganze'' or ''Garenganze'' kingdom) of the Garanganze people in Katanga, DR Congo, was short-lived, existing from about 1856 to 1891 under one king, Msiri, but it became for a while the most powerful state in south-central Africa, controlling a territory of about half a million square kilometres. The Yeke Kingdom also controlled the only trade route across the continent from east to west, since the Kalahari Desert and Lozi Kingdom in the south and the Congo rainforest in the north blocked alternative routes. It achieved this control through natural resources and force of arms—Msiri traded Katanga's copper principally, but also slaves and ivory, for gunpowder and firearms—and by alliances through marriage. The most important alliances were with Portuguese–Angolans in the Benguela area, with Tippu Tip in the north and with Nyamwezi and Swahili traders in the east, and indirectly with the Sultan of Zanzibar who controlled the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria De Fonseca
Maria de Fonseca was the Great Wife, great wife of Msiri, the powerful warrior-king of Katanga Province, Katanga, at the time when the Stairs Expedition arrived in 1891 to take possession of the territory for the Belgium, Belgian King Leopold II of Belgium, Leopold II, with or without Msiri's consent.Joseph A. Moloney: ''With Captain Stairs to Katanga''. S. Low, Marston & Company, London, 1893. Msiri typically cemented alliances with trading partners by marriage. Maria was the daughter of mixed Portuguese-African parents from Angola, and was also the sister of Coimbra, the first trader to supply him with gunpowder from the west coast, the key to Msiri's power. In 1891, Maria was about forty-five years old and Msiri, about sixty, and had been ruler of Katanga for thirty years. When treaty negotiations with Msiri reached stalemate, Christian de Bonchamps, third officer of the expedition, proposed capturing Msiri and holding him hostage. Msiri typically had 300 armed warriors at hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazembe
Kazembe is a traditional kingdom in modern-day Zambia, Southeastern Congo. For more than 250 years, Kazembe has been an influential kingdom of the Kiluba- Chibemba, speaking the language of the Eastern Luba- Lunda people of south-central Africa (also known as the Luba, Luunda, Eastern Luba-Lunda, and Luba-Lunda-Kazembe). Its position on trade routes in a well-watered, relatively fertile and well-populated area of forestry, fishery and agricultural resources drew expeditions by traders and explorers (such as Scottish missionary David LivingstoneDavid Livingstone and Horace Waller (ed.) (1874) ''The Last Journals of David Livingstone in Central Africa from 1865 to his Death''. Two volumes, John Murray.) who called it variously Kasembe, Cazembe and Casembe. Known by the title Mwata or Mulopwe, now equivalent to 'Paramount Chief', the chieftainship with its annual Mutomboko festival stands out in the Luapula Valley and Lake Mweru in present-day Zambia, though its history in coloni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
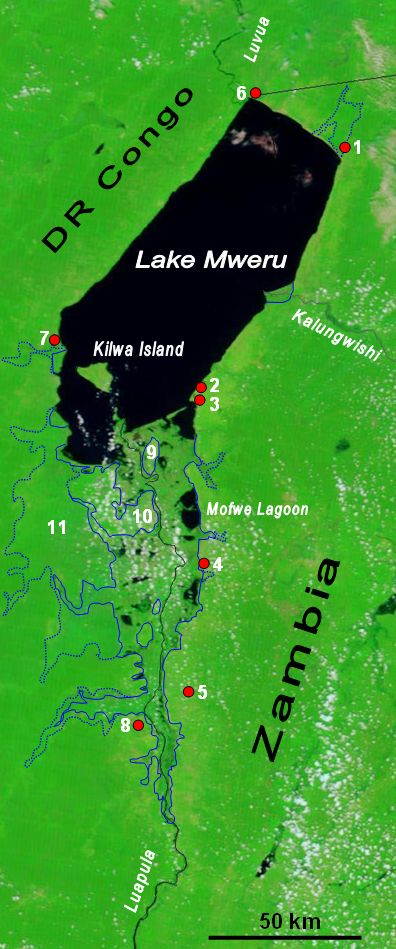
Lake Mweru
Lake Mweru (also spelled ''Mwelu'', ''Mwero'') is a freshwater lake on the longest arm of Africa's second-longest river, the Congo. Located on the border between Zambia and Democratic Republic of the Congo, it makes up of the total length of the Congo, lying between its Luapula River (upstream) and Luvua River (downstream) segments.Google Earth accessed 29 March 2007. When in flood Lake Bangweulu and its swamps may temporarily have a larger area, but not a larger volume. Mweru means 'lake' in a number of Bantu languages, so it is often referred to as just 'Mweru'.The ''Northern Rhodesia Journal'' online at NZRAM.org: J B W Anderson: "Kilwa Island and the Luapula." Vol II, No. 3 pp87–88 (1954) Physical geography Mweru is mainly fed by the Luapula River, which comes in through swamps from the south, and the Kalungwishi River from the east. At its north end the lake is drained by the Luvua River, which flows in a northwesterly direction to join the Lualaba River and thence to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luba People
The Luba people or Baluba are an ethno-linguistic group indigenous to the south-central region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The majority of them live in this country, residing mainly in Katanga, Kasai and Maniema. The Baluba Tribe consist of many sub-groups or clans who speak various dialects of Luba (e.g. Kiluba, Tshiluba) and other languages, such as Swahili. The Baluba developed a society and culture by about the 400s CE, later developing a well-organised community in the Upemba Depression known as the Baluba in Katanga confederation. Luba society consisted of miners, smiths, woodworkers, potters, crafters, and people of various other professions. Kingdoms of the Savanna: The Luba and Lunda Empires Alexander Ives Bortolot (2003), Department of Art History and Archaeology, Columb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katanga Province
Katanga was one of the four large provinces created in the Belgian Congo in 1914. It was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo between 1966 and 2015, when it was split into the Tanganyika Province, Tanganyika, Haut-Lomami, Lualaba Province, Lualaba, and Haut-Katanga provinces. Between 1971 and 1997 (during the rule of Mobutu Sese Seko when Congo was known as Zaire), its official name was Shaba Province. Katanga's area encompassed . Farming and ranching are carried out on the Katanga Plateau. The eastern part of the province is considered to be a rich mining region, which supplies cobalt, copper, tin, radium, uranium, and diamonds. The region's former capital, Lubumbashi, is the second-largest city in the Congo. History Copper mining in Katanga dates back over 1,000 years, and mines in the region were producing standard-sized ingots of copper for international transport by the end of the 10th century CE. In the 1890s, the province was beleaguered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to the south; Zambia to the southwest; and Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west. Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa's highest mountain, is in northeastern Tanzania. According to the United Nations, Tanzania has a population of million, making it the most populous country located entirely south of the equator. Many important hominid fossils have been found in Tanzania, such as 6-million-year-old Pliocene hominid fossils. The genus Australopithecus ranged across Africa between 4 and 2 million years ago, and the oldest remains of the genus ''Homo'' are found near Lake Olduvai. Following the rise of '' Homo erectus'' 1.8 million years ago, humanity spread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Rhodesia Journal
The ''Northern Rhodesia Journal'', often referred to simply as "NRJ", was produced between 1950 and 1965, by the Northern Rhodesian Government Printer, to record some of the early history of Northern Rhodesia. It is one of the most important sources of historical information on Zambia before and during its colonial era, up to its independence from the United Kingdom. Format The Journal is quarto in size. The first two volumes comprised six "Numbers" each, and the page numbering started with 1 for each Number. For the remaining four volumes (the first three of which also had six Numbers) the pages in each volume were numbered continuously, started with page 1 in Number 1 of each volume. The final volume (VI) had but three Numbers, the pages numbered continuously, started with page 1 in Number 1, and, as it was produced after Independence, was titled The ''Zambia Northern Rhodesia Journal''. Purpose From the "Editorial" of the first issue:- ''The difficulty is to state in a succi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horace Waller (activist)
Horace Waller (1833–1896) was an English anti-slavery activist, missionary and clergyman. He was known as a writer on Africa, evangelical Christian, close associate of David Livingstone and others involved in central and east African mission and exploration work, and advocate of British imperial expansion. Life Born in London, Waller was educated under Dr. Wadham at Brook Green. He was for some time in business, in London, as a stockbroker. With the Universities' Mission to Central Africa (UMCA), Waller went out in 1861 to the regions recently visited by David Livingstone and Sir John Kirk. For a period he worked with Charles Frederick Mackenzie, bishop of Central Africa, and was associated with Livingstone in the Zambesi River and Shire Highlands districts. Returning to England after the death of Mackenzie in 1862, Waller was in 1867 ordained by the bishop of Rochester to the curacy of St. John, Chatham; in 1870 he moved to the vicarage of Leytonstone, Essex, and in 1874 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Livingstone
David Livingstone (; 19 March 1813 – 1 May 1873) was a Scottish physician, Congregationalist, and pioneer Christian missionary with the London Missionary Society, an explorer in Africa, and one of the most popular British heroes of the late 19th-century Victorian era. David was the husband of Mary Moffat Livingstone, from the prominent 18th Century missionary family, Moffat. He had a mythic status that operated on a number of interconnected levels: Protestant missionary martyr, working-class "rags-to-riches" inspirational story, scientific investigator and explorer, imperial reformer, anti-slavery crusader, and advocate of British commercial and colonial expansion. Livingstone's fame as an explorer and his obsession with learning the sources of the Nile River was founded on the belief that if he could solve that age-old mystery, his fame would give him the influence to end the East African Arab–Swahili slave trade. "The Nile sources", he told a friend, "are valuabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luapula River
The Luapula River is a section of Africa's second-longest river, the Congo. It is a transnational river forming for nearly all its length part of the border between Zambia and the DR Congo. It joins Lake Bangweulu (wholly in Zambia) to Lake Mweru (shared between the two countries) and gives its name to the Luapula Province of Zambia.Terracarta/International Travel Maps, Vancouver Canada: "Zambia, 2nd edition", 2000 Source and upper Luapula The Luapula drains Lake Bangweulu and its swamps into which flows the Chambeshi River, the source of the Congo. There is no single clear channel connecting the two rivers and the lake, but a mass of shifting channels, lagoons and swamps, as the explorer David Livingstone found to his cost. (He died exploring the area, and one of his last acts was to question Chief Chitambo about the course of the Luapula.)Blaikie, William Garden (1880): ''The Personal Life Of David Livingstone''Project Gutenberg Ebook #13262 release date: August 23, 2004.D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |