|
Mount Bonnell
Mount Bonnell , also known as Covert Park, is a prominent point alongside the Lake Austin portion of the Colorado River (Texas), Colorado River in Austin, Texas. It has been a popular tourist destination since the 1850s. The mount provides a vista for viewing the city of Austin, Lake Austin, and the surrounding hills. It was designated a Recorded Texas Historic Landmark in 1969, bearing Marker number 6473, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2015. Geography Mount Bonnell is located at 30.3210°N, 97.7736°W (World Geodetic System, WGS 84 datum (geodesy), datum). The mount is often described as the highest point in Austin, with the elevation at its peak about 775 feet above mean sea level (AMSL). If Mount Bonnell ever held this distinction, it was only because the city limits did not include the next summit to the north, Mount Barker, which has an elevation of about 840 feet above mean sea level (AMSL) But, City of Austin records indicate the city annexed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Austin
Lake Austin, formerly Lake McDonald, is a water reservoir on the Colorado River in Austin, Texas. The reservoir was formed in 1939 by the construction of Tom Miller Dam by the Lower Colorado River Authority. Lake Austin is one of the seven Highland Lakes created by the LCRA, and is used for flood control, electrical power generation, and recreation. Hydrology Lake Austin is a part of Texas' Colorado River; it begins below Mansfield Dam and is principally fed by the outflow of Lake Travis. The lake meanders generally from northwest to southeast, with few significant tributaries; the largest are Bull Creek, entering from the north near where Loop 360 spans the lake at the Pennybacker Bridge, and Bee Creek, entering from the west just above Tom Miller Dam, where the lake ends. Its outflow through Tom Miller Dam then becomes the principal inflow for Lady Bird Lake. Lake Austin is maintained as a constant-level lake by releases of water from Lake Travis upstream. The other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balcones Fault
The Balcones Fault or Balcones Fault Zone is an area of largely normal faulting Edwards Aquifer in the U.S. state of Texas that runs roughly from the southwest part of the state near Del Rio to the north-central region near Dallas along Interstate 35. The Balcones Fault zone is made up of many smaller features, including normal faults, grabens, and horsts. One of the obvious features is the Mount Bonnell Fault. The location of the fault zone may be related to the Ouachita Mountains, formed 300 million years ago during a continental collision. Although long since worn away in Texas, the roots of these ancient mountains still exist, buried beneath thousands of feet of sediment. These buried Ouachita Mountains J.S. Aber may still be an area of weakness that becomes a preferred site for faulting when stress exists in the Earth's crust. The Balcones Fault has remained inactive for nearly 15 million years, with the last activity being during the Neogene period. This ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
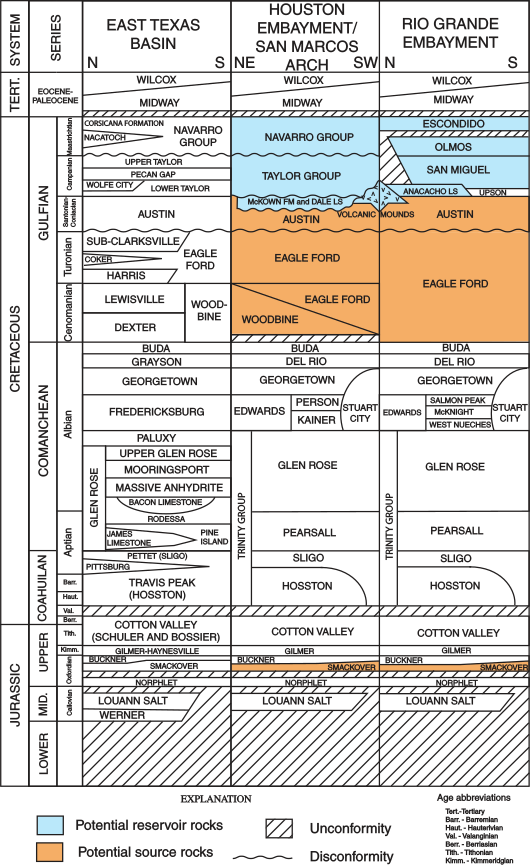
Del Rio Clay
The Del Rio Clay is a geologic formation in Texas. It preserves fossils dating back to the Cretaceous period. A stratigraphic column at the Mount Bonnell location starts with the Lower Cretaceous Trinity Group overlain by the Edwards Group and the Georgetown Formation. Upper Cretaceous formations follow, starting with the Del Rio Clay, Buda Limestone, and then the Eagle Ford Group. Formations within the Trinity Group include the Hammett Formation, Cow Creek Formation, Hensel Formation, and Lower and Upper Glen Rose Formation. The Upper Cretaceous rock units confine the Edwards Aquifer within the Edwards Group and Georgetown Formation. See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Texas * Paleontology in Texas Paleontology in Texas refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Texas. Author Marian Murray has remarked that "Texas is as big for fossils as it is for everything else." Some of the most imp ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation (geology)
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by Abraham Gottlob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia and An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgetown Formation
The Georgetown Formation is a geologic formation in Mexico and the United States. It preserves fossils dating back to the Cretaceous period. A stratigraphic column at the Mount Bonnell location starts with the Lower Cretaceous Trinity Group overlain by the Edwards Group and the Georgetown Formation. Upper Cretaceous formations follow, starting with the Del Rio Clay, Buda Limestone, and then the Eagle Ford Group. Formations within the Trinity Group include the Hammett Formation, Cow Creek Formation, Hensel Formation, and Lower and Upper Glen Rose Formation. The Hammett and the lower portion of the Upper Glen Rose act as confining units (or aquitard) for the Middle Trinity Aquifer. The Upper Glen Rose contains the Upper Trinity Aquifer, which appears to have intra-aquifer groundwater flow with the Edwards Aquifer as water levels are at the same elevation. Formations within the Edwards Group include the Kainier Formation and the Person Formation. The Upper Cretaceous roc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edwards Group
The Edwards Group is a geologic group in Texas. It preserves fossils dating back to the Cretaceous period. A stratigraphic column at the Mount Bonnell Fault location starts with the Lower Cretaceous Trinity Group overlain by the Edwards Group. Upper Cretaceous formations follow, starting with the Del Rio Clay, Buda Limestone, and then the Eagle Ford Group. Formations within the Edwards Group include the Kainer Formation and the Person Formation. The Kainer Formation includes the Dolomitic, Kirschberg, and Grainstone Members. See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Texas * Paleontology in Texas * Edwards Aquifer The Edwards Aquifer is one of the most prolific artesian aquifers in the world. Located on the eastern edge of the Edwards Plateau in the U.S. state of Texas, it is the source of drinking water for two million people, and is the primary water s ... References * Cretaceous geology of Texas {{Cretaceous-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinity Group (geologic Formation)
The Trinity Group is a group (sequence of rock strata) in the Lower Cretaceous lithostratigraphy of Texas, Arkansas, Mississippi, Louisiana and Oklahoma. It is named for the Trinity River of Texas. A stratigraphic column at the Mount Bonnell Fault location starts with the Lower Cretaceous Trinity Group overlain by the Edwards Group. Upper Cretaceous formations follow, starting with the Del Rio Clay, Buda Limestone, and then the Eagle Ford Group. Formations within the Trinity Group include the Hammett Formation, Cow Creek Formation, Hensel Formation, and Lower and Upper Glen Rose Formation. The Hammett and the lower portion of the Upper Glen Rose act as confining units (or aquitard) for the Middle Trinity Aquifer. The Upper Glen Rose contains the Upper Trinity Aquifer, which appears to have intra-aquifer groundwater flow with the Edwards Aquifer The Edwards Aquifer is one of the most prolific artesian aquifers in the world. Located on the eastern edge of the Edwards P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Cretaceous
Lower may refer to: *Lower (surname) *Lower Township, New Jersey *Lower Receiver (firearms) *Lower Wick Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is situated about five miles south west of Dursley, eighteen miles southwest of Gloucester and fifteen miles northeast of Bristol. Lower Wick is within the civil ... Gloucestershire, England See also * Nizhny {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphic Column
A stratigraphic column is a representation used in geology and its subfield of stratigraphy to describe the vertical location of rock units in a particular area. A typical stratigraphic column shows a sequence of sedimentary rocks, with the oldest rocks on the bottom and the youngest on top. In areas that are more geologically complex, such as those that contain intrusive rocks, faults, and/or metamorphism, stratigraphic columns can still indicate the relative locations of these units with respect to one another. However, in these cases, the stratigraphic column must either be a structural column, in which the units are stacked with respect to how they are observed in the field to have been moved by the faults, or a time column, in which the units are stacked in the order in which they were formed. Stratigraphy is a branch of geology that concerns the order and relative position of geologic strata and their relationship to the geologic time scale. The relative time sequencing req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outcrop
An outcrop or rocky outcrop is a visible exposure of bedrock or ancient superficial deposits on the surface of the Earth. Features Outcrops do not cover the majority of the Earth's land surface because in most places the bedrock or superficial deposits are covered by soil and vegetation and cannot be seen or examined closely. However, in places where the overlying cover is removed through erosion or tectonic uplift, the rock may be exposed, or ''crop out''. Such exposure will happen most frequently in areas where erosion is rapid and exceeds the weathering rate such as on steep hillsides, mountain ridges and tops, river banks, and tectonically active areas. In Finland, glacial erosion during the last glacial maximum (ca. 11000 BC), followed by scouring by sea waves, followed by isostatic uplift has produced many smooth coastal and littoral outcrops. Bedrock and superficial deposits may also be exposed at the Earth's surface due to human excavations such as quarrying and build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |