|
Modifications (genetics)
The term Modifications in genetics refers to both naturally occurring and engineered changes in DNA. Incidental, or natural mutations occur through errors during replication and repair, either spontaneously or due to environmental stressors. Intentional modifications are done in a laboratory for various purposes, developing hardier seeds and plants, and increasingly to treat human disease. The use of gene editing technology remains controversial. Genetic Modifications (Incidental and Intentional) Modifications are changes in an individual's DNA due to incidental mutation or intentional genetic modification using various biotechnologies. Although confusion exists between the terms "modification" and "mutation" as they are often used interchangeably, modification differentiates itself from mutation because it acts as an umbrella term, encompassing both definitions of mutation and genetic engineering. Both of these subcategorizations result in a change affect an organism's obervable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultimate s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fitness Landscape ...
Fitness may refer to: * Physical fitness, a state of health and well-being of the body * Fitness (biology), an individual's ability to propagate its genes * Fitness (cereal), a brand of breakfast cereals and granola bars * ''Fitness'' (magazine), a women's magazine, focusing on health and exercise * Fitness and figure competition, a form of physique training, related to bodybuilding * Fitness approximation, a method of function optimization evolutionary computation or artificial evolution methodologies * Fitness function, a particular type of objective function in mathematics and computer science * "Fitness", a 2018 song by Lizzo See also * FitNesse, a web server, a wiki, and a software testing tool *Survival of the fittest "Survival of the fittest" is a phrase that originated from Darwinian evolutionary theory as a way of describing the mechanism of natural selection. The biological concept of fitness is defined as reproductive success. In Darwinian terms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro Fertilisation
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperm in vitro ("in glass"). The process involves monitoring and stimulating an individual's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) from their ovaries and letting sperm fertilise them in a culture medium in a laboratory. After the fertilised egg (zygote) undergoes embryo culture for 2–6 days, it is transferred by catheter into the uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy. IVF is a type of assisted reproductive technology used for infertility treatment, gestational surrogacy, and, in combination with pre-implantation genetic testing, avoiding transmission of genetic conditions. A fertilised egg from a donor may implant into a surrogate's uterus, and the resulting child is genetically unrelated to the surrogate. Some countries have banned or otherwise regulate the availability of IVF treatment, giving rise to fertility tourism. Restrict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applications Of Combinatorial Gene Circuit Optimization Strategies
Application may refer to: Mathematics and computing * Application software, computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks ** Application layer, an abstraction layer that specifies protocols and interface methods used in a communications network * Function application, in mathematics and computer science Processes and documents * Application for employment, a form or forms that an individual seeking employment must fill out * College application, the process by which prospective students apply for entry into a college or university * Patent application, a document filed at a patent office to support the grant of a patent Other uses * Application (virtue), a characteristic encapsulated in diligence * Topical application, the spreading or putting of medication to body surfaces See also * * Apply In mathematics and computer science, apply is a function that applies a function to arguments. It is central to programming languages derived from lambda calculu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetically Modified Bacteria
Genetically modified bacteria were the first organisms to be modified in the laboratory, due to their simple genetics. These organisms are now used for several purposes, and are particularly important in producing large amounts of pure human proteins for use in medicine. History The first example of this occurred in 1978 when Herbert Boyer, working at a University of California laboratory, took a version of the human insulin gene and inserted into the bacterium ''Escherichia coli'' to produce synthetic "human" insulin. Four years later, it was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Research Bacteria were the first organisms to be genetically modified in the laboratory, due to the relative ease of modifying their chromosomes. This ease made them important tools for the creation of other GMOs. Genes and other genetic information from a wide range of organisms can be added to a plasmid and inserted into bacteria for storage and modification. Bacteria are cheap, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
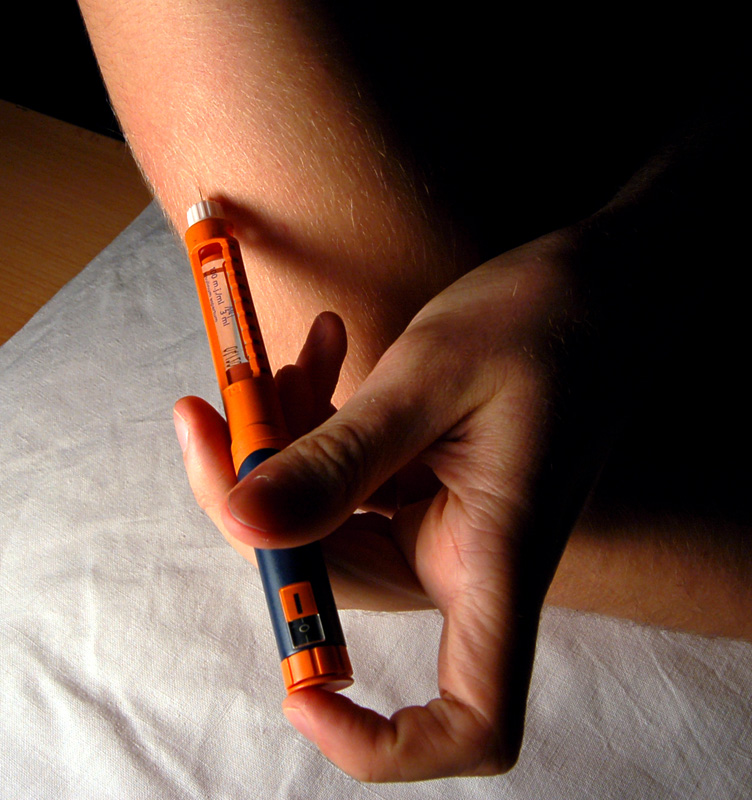
Insulin (medication)
As a medication, insulin is any pharmaceutical preparation of the protein hormone insulin that is used to treat high blood glucose. Such conditions include type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and complications of diabetes such as diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic states. Insulin is also used along with glucose to treat hyperkalemia (high blood potassium levels). Typically it is given by injection under the skin, but some forms may also be used by injection into a vein or muscle. There are various types of insulin, suitable for various time spans. The types are often all called ''insulin'' in the broad sense, although in a more precise sense, insulin is identical to the naturally occurring molecule whereas insulin analogues have slightly different molecules that allow for modified time of action. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2020, regular human insulin was the 307th most commonly prescribed med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyloid-beta Precursor Protein
Amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP) is an integral membrane protein expressed in many tissues and concentrated in the synapses of neurons. It functions as a cell surface receptor and has been implicated as a regulator of synapse formation, neural plasticity, antimicrobial activity, and iron export. It is coded for by the gene ''APP'' and regulated by substrate presentation. APP is best known as the precursor molecule whose proteolysis generates amyloid beta (Aβ), a polypeptide containing 37 to 49 amino acid residues, whose amyloid fibrillar form is the primary component of amyloid plaques found in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients. Genetics Amyloid-beta precursor protein is an ancient and highly conserved protein. In humans, the gene ''APP'' is located on chromosome 21 and contains 18 exons spanning 290 kilobases. Several alternative splicing isoforms of APP have been observed in humans, ranging in length from 639 to 770 amino acids, with certain isoforms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years. The cause of Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an allele of APOE. Other risk factors include a history of head injury, clinical depression, and high blood pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. Malaria is caused by single-celled microorganisms of the ''Plasmodium'' group. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into a person's blood. The parasites travel to the liver where they mature and reproduce. Five species of ''Plasmodium'' can infect and be spread by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin Subunit Beta
Hemoglobin subunit beta (beta globin, β-globin, haemoglobin beta, hemoglobin beta) is a globin protein, coded for by the ''HBB'' gene, which along with alpha globin ( HBA), makes up the most common form of haemoglobin in adult humans, hemoglobin A (HbA). It is 147 amino acids long and has a molecular weight of 15,867 Da. Normal adult human HbA is a heterotetramer consisting of two alpha chains and two beta chains. HBB is encoded by the ''HBB'' gene on human chromosome 11. Mutations in the gene produce several variants of the proteins which are implicated with genetic disorders such as sickle-cell disease and beta thalassemia, as well as beneficial traits such as genetic resistance to malaria. At least 50 disease-causing mutations in this gene have been discovered. Gene locus HBB protein is produced by the gene ''HBB'' which is located in the multigene locus of β-globin locus on chromosome 11, specifically on the short arm position 15.4. Expression of beta globin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders typically inherited from a person's parents. The most common type is known as sickle cell anaemia. It results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red blood cells. This leads to a rigid, sickle-like shape under certain circumstances. Problems in sickle cell disease typically begin around 5 to 6 months of age. A number of health problems may develop, such as attacks of pain (known as a sickle cell crisis), anemia, swelling in the hands and feet, bacterial infections and stroke. Long-term pain may develop as people get older. The average life expectancy in the developed world is 40 to 60 years. Sickle cell disease occurs when a person inherits two abnormal copies of the β-globin gene (''HBB'') that makes haemoglobin, one from each parent. This gene occurs in chromosome 11. Several subtypes exist, depending on the exact mutation in each haemoglobin gene. An attack can be set off by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charles Darwin popularised the term "natural selection", contrasting it with artificial selection, which in his view is intentional, whereas natural selection is not. Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and their offspring can inherit such mutations. Throughout the lives of the individuals, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment. Because individuals with certain variants of the trait tend to survive and reproduce more than individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |