|
Minerotrophic
Minerotrophic refers to environments that receive nutrients primarily through groundwater that flows through mineral-rich soils or rock,Environment Canada (2014). Ontario wetland evaluation system: Northern Manual, 1st edition, version 3.2. Queen’s printer for Ontario. or surface water flowing over land. Minerotrophic, “minerogenous”, and “geogenous” are now often used interchangeably, although the latter two terms refer primarily to hydrological systems, while the former refers to nutrient dynamics. The hydrologic process behind minerotrophic wetlands results in water that has acquired dissolved chemicals which raise the nutrient levels and reduce the acidity. This in turn affects vegetation assemblages and diversity in the wetland in question.Brinson, M. M. (1993). A Hydrogeomorphic Classification for Wetlands. ''Environmental Laboratory (U.S.) & Engineer Research and Development Center (U.S.).'' Retrieved from https://erdc-library.erdc.dren.mil/jspui/bitstream/11681/6483/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ombrotrophic
Ombrotrophic ("cloud-fed"), from Ancient Greek ὄμβρος (''ómvros'') meaning "rain" and τροφή (''trofí'') meaning "food"), refers to Soil, soils or vegetation which receive all of their water and nutrients from precipitation, rather than from streams or springs. Such environments are hydrology, hydrologically isolated from the surrounding landscape, and since rain is acidic and very low in Plant nutrition, nutrients, they are home to organisms tolerant of acidic, low-nutrient environments. The vegetation of ombrotrophic peatlands is often bog, dominated by ''Sphagnum'' mosses. The hydrology of these environments are directly related to their climate, as precipitation is the water and nutrient source, and temperatures dictate how quickly water evaporates from these systems. Ombrotrophic circumstances may occur even in landscapes composed of limestone or other nutrient-rich substrates – for example, in high-rainfall areas, limestone boulders may be capped by acidic om ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The primary factor that distinguishes wetlands from terrestrial land forms or Body of water, water bodies is the characteristic vegetation of aquatic plants, adapted to the unique anoxic hydric soils. Wetlands are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as home to a wide range of plant and animal species. Methods for assessing wetland functions, wetland ecological health, and general wetland condition have been developed for many regions of the world. These methods have contributed to wetland conservation partly by raising public awareness of the functions some wetlands provide. Wetlands occur naturally on every continent. The water in wetlands is either freshwater, brackish or seawater, saltwater. The main w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is called a hydrologist. Hydrologists are scientists studying earth or environmental science, civil or environmental engineering, and physical geography. Using various analytical methods and scientific techniques, they collect and analyze data to help solve water related problems such as environmental preservation, natural disasters, and water management. Hydrology subdivides into surface water hydrology, groundwater hydrology (hydrogeology), and marine hydrology. Domains of hydrology include hydrometeorology, surface hydrology, hydrogeology, drainage-basin management, and water quality, where water plays the central role. Oceanography and meteorology are not included because water is only one of many important aspects within those fields. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcifuge
A calcifuge is a plant that does not tolerate alkaline (basic) soil. The word is derived from the Latin 'to flee from chalk'. These plants are also described as ericaceous, as the prototypical calcifuge is the genus ''Erica'' (heaths). It is not the presence of carbonate or hydroxide ions ''per se'' that these plants cannot tolerate, but the fact that under alkaline conditions, iron becomes less soluble. Consequently, calcifuges grown on alkaline soils often develop the symptoms of iron deficiency, ''i.e.'' interveinal chlorosis of new growth. There are many horticultural plants which are calcifuges, most of which require an 'ericaceous' compost with a low pH, composed principally of ''Sphagnum'' moss peat. A plant that thrives in lime-rich soils is known as a calcicole. Examples Order Ericales Ericaceae *''Andromeda polifolia'' *''Calluna'' (common heather) *''Cassiope lycopodioides'' *''Daboecia'' *'' Enkianthus campanulatus'' *''Erica'' (but not '' E. carnea'' or '' E. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcicole
A calcicole, calciphyte or calciphile is a plant that thrives in lime rich soil. The word is derived from the Latin 'to dwell on chalk'. Under acidic conditions, aluminium becomes more soluble and phosphate less. As a consequence, calcicoles grown on acidic soils often develop the symptoms of aluminium toxicity, i.e. necrosis, and phosphate deficiency, i.e. anthocyanosis (reddening of the leaves) and stunting. A plant that thrives in acid soils is known as a calcifuge. A plant thriving on sand (which may be acidic or calcic) is termed psammophilic or arenaceous (see also arenite). Examples of calcicole plants * Ash trees (''Fraxinus'' spp.) * Honeysuckle (''Lonicera'') * ''Buddleja'' * Lilac (''Syringa'') * Beet * ''Clematis'' * ''Sanguisorba minor'' * Some European orchids * Some succulent plants genera ''Sansevieria'' and ''Titanopsis'' or cacti genus ''Thelocactus ''Thelocactus'' is a genus of flowering plants in the cactus family Cactaceae. Members of the genus are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Everglades
The Everglades is a natural region of tropical climate, tropical wetlands in the southern portion of the U.S. state of Florida, comprising the southern half of a large drainage basin within the Neotropical realm. The system begins near Orlando, Florida, Orlando with the Kissimmee River, which discharges into the vast but shallow Lake Okeechobee. Water leaving the lake in the wet season forms a slow-moving river wide and over long, flowing southward across a limestone shelf to Florida Bay at the southern end of the state. The Everglades experiences a wide range of weather patterns, from frequent flooding in the wet season to drought in the dry season. Throughout the 20th century, the Everglades suffered significant loss of habitat and environmental degradation. Human habitation in the southern portion of the Florida peninsula dates to 15,000 years ago. Before European colonization, the region was dominated by the native Calusa and Tequesta tribes. With Spanish colonizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
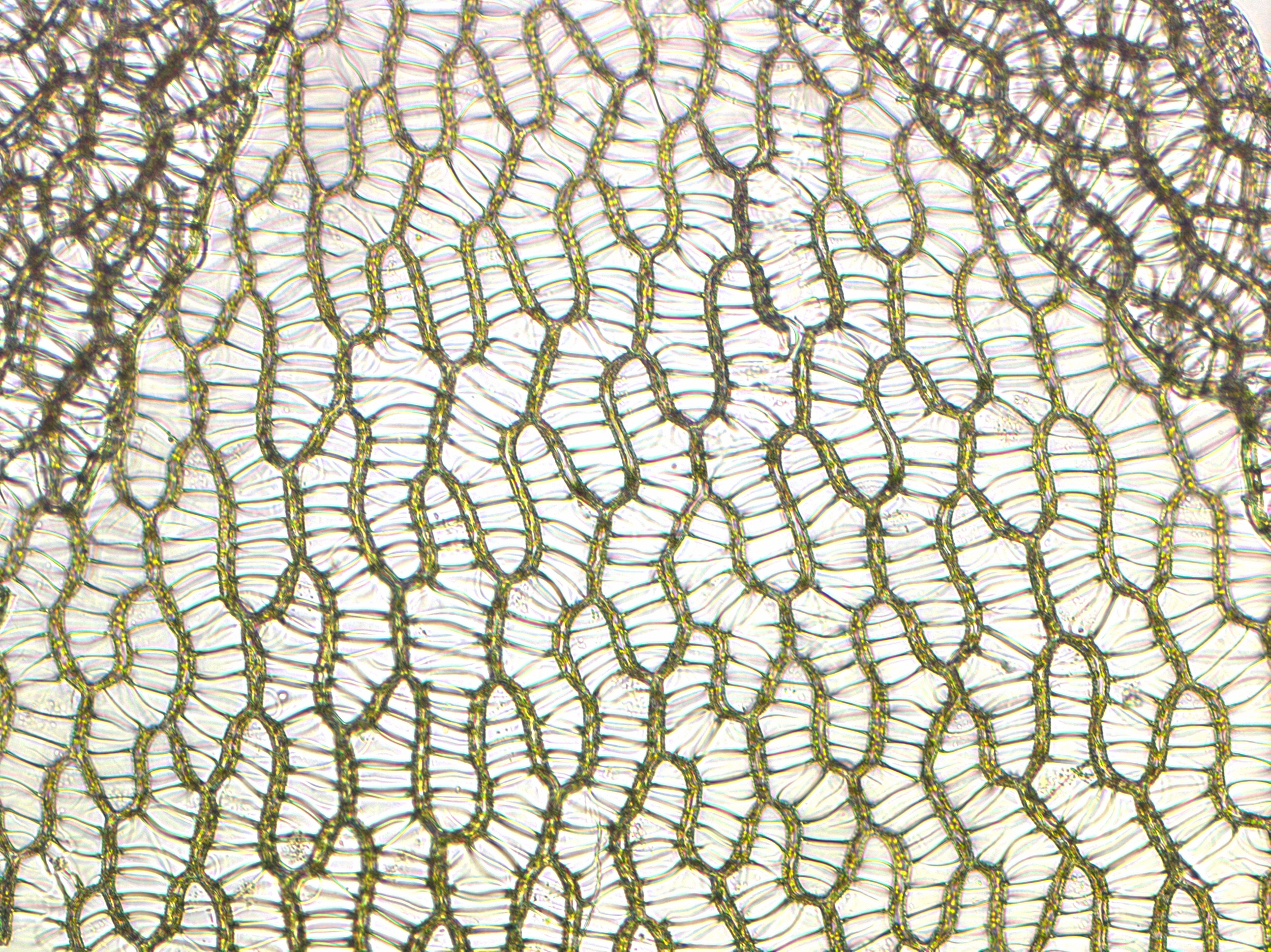
Sphagnum
''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, peat moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store water, since both living and dead plants can hold large quantities of water inside their cells; plants may hold 16 to 26 times as much water as their dry weight, depending on the species.Bold, H. C. 1967. Morphology of Plants. second ed. Harper and Row, New York. p. 225-229. The empty cells help retain water in drier conditions. As sphagnum moss grows, it can slowly spread into drier conditions, forming larger mires, both raised bogs and blanket bogs. Thus, sphagnum can influence the composition of such habitats, with some describing sphagnum as 'habitat manipulators'. These peat accumulations then provide habitat for a wide array of peatland plants, including sedges and Calcifuges, ericaceous shrubs, as well as orchids and carnivorous plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carex
''Carex'' is a vast genus of more than 2,000 species of grass-like plants in the family Cyperaceae, commonly known as sedges (or seg, in older books). Other members of the family Cyperaceae are also called sedges, however those of genus ''Carex'' may be called true sedges, and it is the most species-rich genus in the family. The study of ''Carex'' is known as caricology. Description All species of ''Carex'' are perennial, although some species, such as '' C. bebbii'' and '' C. viridula'' can fruit in their first year of growth, and may not survive longer. They typically have rhizomes, stolons or short rootstocks, but some species grow in tufts (caespitose). The culm – the flower-bearing stalk – is unbranched and usually erect. It is usually distinctly triangular in section. The leaves of ''Carex'' comprise a blade, which extends away from the stalk, and a sheath, which encloses part of the stalk. The blade is normally long and flat, but may be folded, inrolled, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amblystegiaceae
Amblystegiaceae is a family of mosses. It includes 20 to 30 genus, genera with a total of up to 150 species.Amblystegiaceae. Flora of North America. Volume 28. They occur nearly worldwide, growing in tropical, temperate, and subpolar regions. These mosses are small to large in size and are yellow, green, or brown in color. Some are aquatic and some terrestrial. Most occur in wet habitat types. Many occur in substrates with a basic pH, but some grow in neutral to acidic substrates.Watson, L., and Dallwitz, M.J. 2005 onwards The Moss Families of the British Isles. Version: 21 June 2009. Genera Genera include: *''Acrocladium''[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficient carbon sink on the planet, because peatland plants capture carbon dioxide (CO2) naturally released from the peat, maintaining an equilibrium. In natural peatlands, the "annual rate of biomass production is greater than the rate of decomposition", but it takes "thousands of years for peatlands to develop the deposits of , which is the average depth of the boreal orthernpeatlands", which store around 415 gigatonnes (Gt) of carbon (about 46 times 2019 global CO2 emissions). Globally, peat stores up to 550 Gt of carbon, 42% of all soil carbon, which exceeds the carbon stored in all other vegetation types, including the world's forests, although it covers just 3% of the land's surface. ''Sphagnum'' moss, also called peat moss, is one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swamp
A swamp is a forested wetland.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in creating this environment. Swamps vary in size and are located all around the world. The water of a swamp may be fresh water, brackish water, or seawater. Freshwater swamps form along large rivers or lakes where they are critically dependent upon rainwater and seasonal flooding to maintain natural water level fluctuations.Hughes, F.M.R. (ed.). 2003. The Flooded Forest: Guidance for policy makers and river managers in Europe on the restoration of floodplain forests. FLOBAR2, Department of Geography, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK. 96 p. Saltwater swamps are found along tropical and subtropical coastlines. Some swamps have hammock (ecology), hammocks, or dry-land protrusions, covered by aquatic vegetation, or vegetation that tolerates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
