|
Mikhail Yangel
Mikhail Kuzmich Yangel (russian: Михаил Кузьмич Янгель; 7 November 1911 – 25 October 1971), was a Soviet engineer born in Irkutsk who was the leading designer in the missile program of the former Soviet Union. Biography Yangel was the grandson of a Russian political prisoner who had been deported to Siberia by the Tsarist regime. Yangel's career started as an aviation engineer, after graduating from Moscow Aviation Institute in 1937. He worked with famous aircraft designers Nikolai Polikarpov and later, Artem Mikoyan. Then he moved to the field of ballistic missiles, where he first was in charge of guidance systems. As Sergei Korolev’s associate, he set up a rocket propulsion centre in Dnepropetrovsk in UkSSR which later formed the basis of his own OKB-586 design bureau in 1954. At first, Yangel’s facility served to mass-produce and further develop intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) in which area Yangel was a pioneer of storeable hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scud Missile
A Scud missile is one of a series of tactical ballistic missiles developed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. It was exported widely to both Second and Third World countries. The term comes from the NATO reporting name attached to the missile by Western intelligence agencies. The Russian names for the missile are the R-11 (the first version), and the R-17 (later R-300) Elbrus (later developments). The name Scud has been widely used to refer to these missiles and the wide variety of derivative variants developed in other countries based on the Soviet design. Scud missiles have been used in combat since the 1970s, mostly in wars in the Middle East. They became familiar to the Western public during the 1991 Persian Gulf War, when Iraq fired dozens at Israel and Saudi Arabia. In Russian service it is being replaced by the 9K720 Iskander. Development The first use of the term ''Scud'' was in the NATO name SS-1b Scud-A, applied to the R-11 Zemlya ballistic missile. The e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guidance System
A guidance system is a virtual or physical device, or a group of devices implementing a controlling the movement of a ship, aircraft, missile, rocket, satellite, or any other moving object. Guidance is the process of calculating the changes in position, velocity, altitude, and/or rotation rates of a moving object required to follow a certain trajectory and/or altitude profile based on information about the object's state of motion. A guidance system is usually part of a Guidance, navigation and control system, whereas navigation refers to the systems necessary to calculate the current position and orientation based on sensor data like those from compasses, GPS receivers, Loran-C, star trackers, inertial measurement units, altimeters, etc. The output of the navigation system, the navigation solution, is an input for the guidance system, among others like the environmental conditions (wind, water, temperature, etc.) and the vehicle's characteristics (i.e. mass, control system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
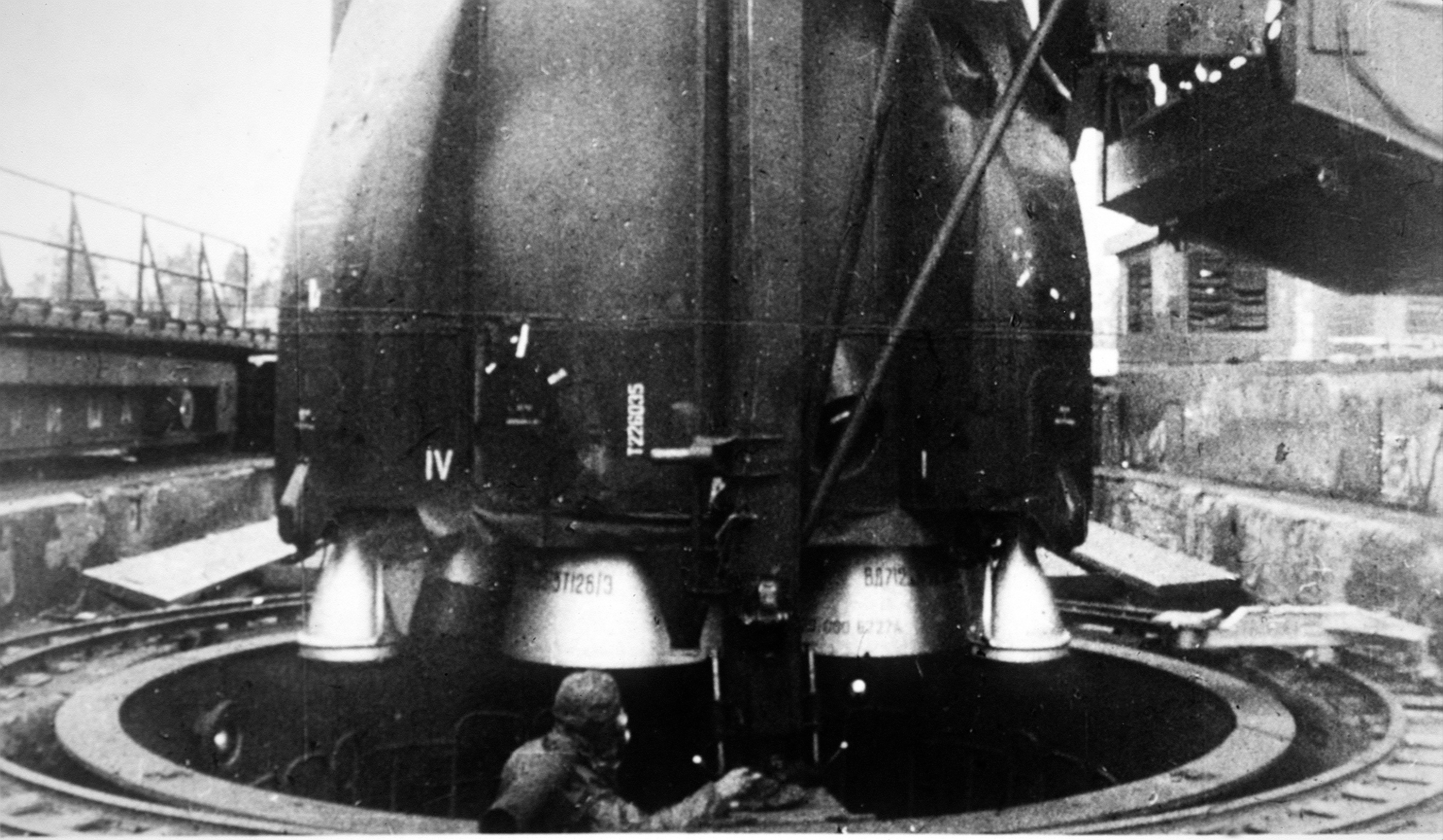
Nedelin Catastrophe
The Nedelin catastrophe or Nedelin disaster was a launch pad accident that occurred on 24 October 1960 at Baikonur test range (of which Baikonur Cosmodrome is a part), during the development of the Soviet R-16 ICBM. As a prototype of the missile was being prepared for a test flight, an explosion occurred when the second stage engine ignited accidentally, killing an unknown number of military and technical personnel working on the preparations. Despite the magnitude of the disaster, news of it was suppressed for many years and the Soviet government did not acknowledge the event until 1989. The disaster is named after Chief marshal of Artillery Mitrofan Ivanovich Nedelin, who was killed in the explosion. As commanding officer of the Soviet Union's Strategic Rocket Forces, Nedelin was the head of the R-16 development program. Launch preparations On 23 October 1960, the prototype R-16 had been installed on launching pad 41 (''russian: стартовая позиция 41 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dnepr (rocket)
The Dnepr rocket (russian: Днепр, translit=Dnepr; uk, Дніпро, translit=Dnipró) was a space launch vehicle named after the Dnieper River. It was a converted ICBM used for launching artificial satellites into orbit, operated by launch service provider ISC Kosmotras. The first launch, on April 21, 1999, successfully placed UoSAT-12, a 350 kg demonstration mini-satellite, into a 650 km circular Low Earth orbit. History The Dnepr was based on the R-36MUTTH Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM)called the ''SS-18 Satan'' by NATOdesigned in the 1970s by the Yuzhnoe Design Bureau in Dnepropetrovsk, Ukrainian SSR. The Dnepr control system was developed and produced by the JSC "Khartron", Kharkiv. The Dnepr was a three-stage rocket using storable hypergolic liquid propellants. The launch vehicles used for satellite launches have been withdrawn from ballistic missile service with the Russian Strategic Rocket Forces and stored for commercial use. A gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsyklon
The Tsyklon (Циклон, "Cyclone", also known as Tsiklon), GRAU index 11K67, was a Soviet-designed expendable launch system, primarily used to put Cosmos satellites into low Earth orbit. It is based on the R-36 intercontinental ballistic missile designed by Mikhail Yangel and made eight launches, with seven successes and one failure. All of its launches were conducted from LC-90 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome. It is sometimes designated Tsyklon-2A, not to be confused with the later Tsyklon-2 rocket. It was introduced in 1967 and was derived from the R-36 ICBM (NATO designation SS-9 Scarp). It was retired in 1969. It made its maiden flight on 27 October 1967. The booster's design was kept secret and no images or film clips of the complete vehicle were released to the public until after the collapse of the Soviet Union, in part because of being used exclusively for military payloads and also because it was derived from an actively serving missile system. After 1991, the plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos (rocket Family)
The Kosmos (also spelled Cosmos, Russian: ) rockets were a series of Soviet and subsequently Russian rockets, derived from the R-12 and R-14 missiles, the best known of which is the Kosmos-3M, which has made over 440 launches. The Kosmos family contained a number of rockets, both carrier rockets and sounding rockets, for orbital and sub-orbital spaceflight respectively. The first variant, the Kosmos-2I, first flew on 27 October 1961. Over 700 Kosmos rockets have been launched overall. Variants Launches See also *R-7 family The R-7 family of rockets (russian: Р-7) is a series of rockets, derived from the Soviet R-7 Semyorka, the world's first ICBM. More R-7 rockets have been launched than any other family of large rockets. When Soviet nuclear warheads became ligh ... References Rocket families Space launch vehicles of the Soviet Union Energia rocket engines {{rocketry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-36 (missile)
The R-36 (russian: Р-36) is a family of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and space launch vehicles ( Tsyklon) designed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. The original R-36 was deployed under the GRAU index 8K67 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-9 Scarp. It was able to carry three warheads and was the first Soviet MRV ( multiple re-entry vehicle) missile. The later version, the R-36M was produced under the GRAU designations 15A14 and 15A18 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-18 Satan. This missile was viewed by certain United States analysts as giving the Soviet Union first strike advantage over the U.S., particularly because of its rapid silo-reload ability, very heavy throw weight and extremely large number of re-entry vehicles. Some versions of the R-36M were deployed with 10 warheads and up to 40 penetration aids and the missile's high throw-weight made it theoretically capable of carrying more warheads or penetration aids. Contemporary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-16 (missile)
The R-16 was the first successful intercontinental ballistic missile deployed by the Soviet Union. In the West it was known by the NATO reporting name SS-7 Saddler, and within Russia, it carried the GRAU index 8K64. Description The missile was 30.4 m long, 3 m in diameter and had a launch weight of 141 tons. The maximum range was 11,000 km with a 5-6 Mt thermonuclear warhead and 13,000 km with a 3 Mt warhead. The missile had a circular error probable (CEP) of 2.7 km. History During development, a massive failure occurred on October 24, 1960, when a prototype rocket exploded on the pad killing at least 78 personnel. After decades of coverup, the government finally revealed this incident, referred to as the Nedelin catastrophe. A fatal accident with the R-9 missile occurred exactly three years later, causing October 24 to be referred to as Baikonur's "Black Day." No launches have been attempted on that date at Baikonur ever since. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-12 Dvina
The R-12 Dvina was a theatre ballistic missile developed and deployed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. Its GRAU designation was 8K63 (8K63U or 8K63У in Cyrillic for silo-launched version), and it was given the NATO reporting name of SS-4 Sandal. The R-12 rocket provided the Soviet Union with the capability to attack targets at medium ranges with a megaton-class thermonuclear warhead and constituted the bulk of the Soviet offensive missile threat to Western Europe. Deployments of the R-12 missile in Cuba caused the Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962. A total of 2335 missiles were produced; all were destroyed in 1993 under the START II treaty. As well as the single-stage ballistic technology, the R-12 Dvina had a two-stage capability that allowed payloads to be placed into low Earth orbit. The Iranian Shahab-4 missile is likely an offshoot of the R-12 Dvina. History Beginning OKB-586 formed from a spin-off of portions of Sergei Korolev's OKB-1 production infrastructur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypergolic Propellant
A hypergolic propellant is a rocket propellant combination used in a rocket engine, whose components spontaneously ignite when they come into contact with each other. The two propellant components usually consist of a fuel and an oxidizer. The main advantages of hypergolic propellants are that they can be stored as liquids at room temperature and that engines which are powered by them are easy to ignite reliably and repeatedly. Common hypergolic propellants are difficult to handle due to their extreme toxicity and/or corrosiveness. In contemporary usage, the terms "hypergol" and "hypergolic propellant" usually mean the most common such propellant combination: dinitrogen tetroxide plus hydrazine and/or its relatives monomethylhydrazine (MMH) and unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH). History In 1935, Hellmuth Walter discovered that hydrazine hydrate was hypergolic with high-test peroxide of 80-83%. He was probably the first to discover this phenomenon, and set to work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercontinental Ballistic Missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. Russia, the United States, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, and North Korea are the only countries known to have operational ICBMs. Early ICBMs had limited precision, which made them suitable for use only against the largest targets, such as cities. They were seen as a "safe" basing option, one that would keep the deterrent force close to home where it would be difficult to attack. Attacks against military targets (especially hardened ones) still demande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OKB-586
Pivdenne Design Office ( uk, Державне конструкторське бюро «Південне» ім. М. К. Янгеля , lit=State design bureau "Southern", named after M. K. Yangel, translit=Derzhavne konstruktorske biuro "Pivdenne" im. M. K. Yanhelia), located in Dnipro, Ukraine, is a designer of satellites and rockets, and formerly of Soviet intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), established by Mikhail Yangel. During Soviet times the bureau's OKB designation was OKB-586. The company is in close co-operation with the PA Pivdenmash multi-product machine-building company, also situated in Dnipro. Pivdenmash is the main manufacturer of the models developed by Pivdenne Design Office. Directors * 1954–1971 Mikhail Yangel * 1971–1991 Vladimir Utkin * 1991–2010 * 2010–2020 Products Current Ballistic missiles * Hrim-2 Orbital launch vehicles * Zenit rocket family ** Zenit-2 ** Zenit-2M ** Zenit-3F ** Zenit-3SL ** Zenit-3SLB * A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |