|
Mazra'a
Mazra'a ( ar, المزرعة, he, מַזְרַעָה) is an Arab town and local council in northern Israel, situated between Acre and Nahariyya east of the Coastal Highway that runs along the Mediterranean coast. The local council was founded in 1896 and was incorporated into the Matte Asher Regional Council in 1982, before proclaiming itself an independent local council again in 1996. In it had a population of . Etymology The Arabic ''al-mazra'a'' (p. ''mazari), meaning "the sown land" or "farm", is a relatively common place name used to refer to cultivated lands outside of and dependent upon a primary settlement.Pringle, 1998, p 30 In Crusader times, the village was known as ''le Mezera'', according to Victor Guérin, while to Arabs in medieval times, it was known as ''al-Mazra'ah''.Guérin, 1880, p 163 History In 1253, during the Crusader era, John Aleman, the Lord of Caesarea, leased Mazra'a to the Hospitalliers. Mazra'a is mentioned in the 1283 treaty between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Aleman
John Aleman (died after 1264) was the Lord of Caesarea (as John II) in the Kingdom of Jerusalem, exercising this right through his wife, Margaret, from at least 1243 until his death. He was the son of Garnier l'Aleman and Pavie de Gibelet, and the older brother of Hugh Aleman. John was active politically and militarily, although less influential than the previous lords of Caesarea had been.John L. Lamonte, "The Lords of Caesarea in the Period of the Crusades", ''Speculum'' 22, 2 (1947): 158–59. His maternal grandmother was Stephanie of Milly. The first reference to John as lord of Caesarea comes in the ''Assizes of Jerusalem'' of John of Ibelin. Therein John writes that his cousin, the lord of Caesarea, refused the bailliage (regency) of the kingdom in 1243, and instead the '' Haute Cour'' gave it to Queen Alice of Cyprus. Since his father-in-law, Lord John of Caesarea, was dead, this is probably a reference to Aleman. In April 1249 he and his wife sold six '' casalia'' near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern District (Israel)
The Northern District ( he, מחוז הצפון, ''Mekhoz HaTzafon''; ar, منطقة الشمال, ''Minṭaqat ash-Shamāl'') is one of Israel's six administrative districts. The Northern District has a land area of 4,478 km2, which increases to 4,638 km2 when both land and water are included. The district capital is Nof HaGalil and the largest city is Nazareth. The Golan Heights has been run as a sub-district of the North District of Israel since the 1981 Golan Heights Law was passed, although the claim is only recognized by the United States while United Nations Security Council Resolution 497 condemns the annexation but does not enforce it. The Golan Heights covers a land area of 1,154 km2 and the remainder of the Northern District covers 3,324 km2 (3,484 km2 including water). Demographics According to the Israeli Central Bureau of Statistics data for 2016: * Total population: 1,390,900 (2016) * Ethnic: ** Arabs: 746,600 (53.7%) ** Jews: 599,700 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
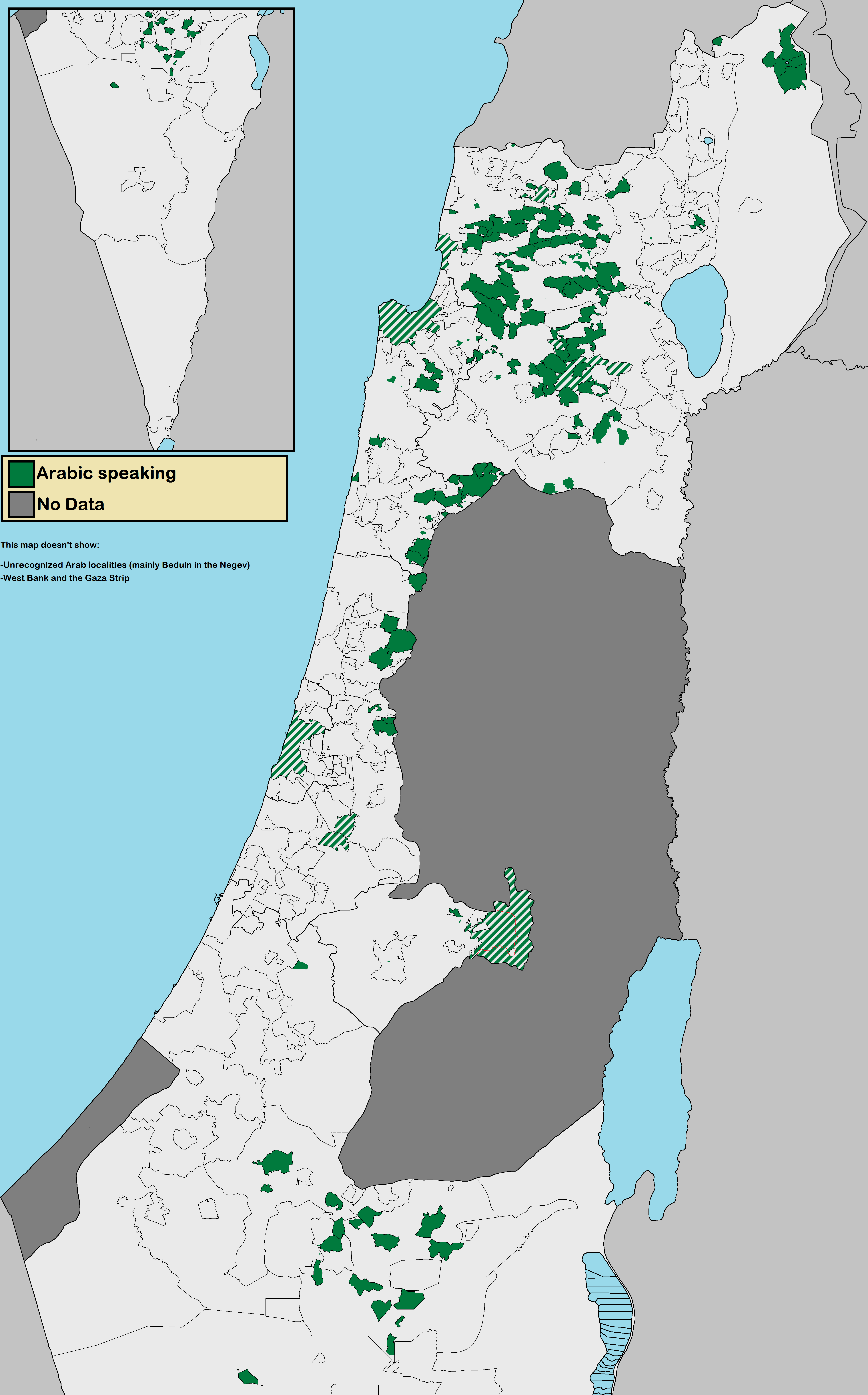
Arab Citizens Of Israel
The Arab citizens of Israel are the largest ethnic minority in the country. They comprise a hybrid community of Israeli citizens with a heritage of Palestinian citizenship, mixed religions (Muslim, Christian or Druze), bilingual in Arabic and Hebrew, and with varying social identities. Self-identification as Palestinian citizens of Israel has sharpened in recent years, alongside distinct identities including Galilee and Negev Bedouin, the Druze people, and Arab Christians and Arab Muslims who do not identify as Palestinians. In Arabic, commonly used terms to refer to Israel's Arab population include 48-Arab ( ar, عرب 48, Arab Thamaniya Wa-Arba'in, label=none) and 48-Palestinian (). Since the Nakba, the Palestinians that have remained within Israel's 1948 borders have been colloquially known as "48-Arabs". In Israel itself, Arab citizens are commonly referred to as Israeli-Arabs or simply as ''Arabs''; international media often uses the term Arab-Israeli to distinguish A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Council (Israel)
Local councils (Hebrew: plural: ''Mo'atzot Mekomiot'' / singular: ''Mo'atza Mekomit,'' Arabic: plural: مجالس محليّة ''Majalis Mahaleea /'' singular: مجلس محلّي ''Majlis Mahalee'') are one of the three types of local government found in Israel, the other two being cities and regional councils. There are 124 local councils in Israel. Local councils should not be confused with local committees, which are lower-level administrative entities. History Local council status is determined by passing a minimum threshold, enough to justify operations as independent municipal units, although not large enough to be declared a city. In general this applies to all settlements of over 2,000 people. The Israeli Interior Minister has the authority of deciding whether a locality is fit to become a municipal council (a city). The minister is then expected to listen to the wishes of the residents of the locality in question, who may wish the locality to remain a local counci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the Muhammad in Islam, main Islamic prophet. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices of Muhammad (''sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (''hadith''). With an estimated population of almost 1.9 billion followers as of 2020 year estimation, Muslims comprise more than 24.9% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each continental landmass stands at: 45% of Islam in Africa, Africa, 25% of Islam in Asia, Asia and Islam in Oceania, Oceania (collectively), 6% of Islam in Europe, Europe, and 1% of the Islam in the Americas, Americas. Addition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahiya
A nāḥiyah ( ar, , plural ''nawāḥī'' ), also nahiya or nahia, is a regional or local type of administrative division that usually consists of a number of villages or sometimes smaller towns. In Tajikistan, it is a second-level division while in Syria, Iraq, Lebanon, Jordan, Xinjiang, and the former Ottoman Empire, where it was also called a '' bucak'', it is a third-level or lower division. It can constitute a division of a '' qadaa'', '' mintaqah'' or other such district-type of division and is sometimes translated as " subdistrict". Ottoman Empire The nahiye ( ota, ناحیه) was an administrative territorial entity of the Ottoman Empire, smaller than a . The head was a (governor) who was appointed by the Pasha. The was a subdivision of a Selçuk Akşin Somel. "Kazâ". ''The A to Z of the Ottoman Empire''. Volume 152 of A to Z Guides. Rowman & Littlefield, 2010. p. 151. and corresponded roughly to a city with its surrounding villages. s, in turn, were divided int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daftar
A ''defter'' (plural: ''defterler'') was a type of tax register and land cadastre in the Ottoman Empire. Description The information collected could vary, but ''tahrir defterleri'' typically included details of villages, dwellings, household heads (adult males and widows), ethnicity/religion (because these could affect tax liabilities/exemptions), and land use. The defter-i hakâni was a land registry, also used for tax purposes. Each town had a defter and typically an officiator or someone in an administrative role to determine whether the information should be recorded. The officiator was usually some kind of learned man who had knowledge of state regulations. The defter was used to record family interactions such as marriage and inheritance. These records are useful for historians because such information allows for a more in-depth understanding of land ownership among Ottomans. This is particularly helpful when attempting to study the daily affairs of Ottoman citizens. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean in South-western Asia,Gasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. }, ), meaning "the eastern place, where the Sun rises". In the 13th and 14th centuries, the term ''levante'' was used for Italian maritime commerce in the Eastern Mediterranean, including Greece, Anatolia, Syria-Palestine, and Egypt, that is, the lands east of Venice. Eventually the term was restricted to the Muslim countries of Syria-Palestine and Egypt. In 1581, England set up the Levant Company to monopolize commerce with the Ottoman Empire. The name ''Levant States'' was used to refer to the French mandate over Syria and Lebanon after World War I. This is pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were intended to recover Jerusalem and its surrounding area from Islamic rule. Beginning with the First Crusade, which resulted in the recovery of Jerusalem in 1099, dozens of Crusades were fought, providing a focal point of European history for centuries. In 1095, Pope Urban II proclaimed the First Crusade at the Council of Clermont. He encouraged military support for Byzantine emperor AlexiosI against the Seljuk Turks and called for an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem. Across all social strata in western Europe, there was an enthusiastic response. The first Crusaders had a variety of motivations, including religious salvation, satisfying feudal obligations, opportunities for renown, and economic or political advantage. Later crusades were c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Kingdom
The Kingdom of Jerusalem ( la, Regnum Hierosolymitanum; fro, Roiaume de Jherusalem), officially known as the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Frankish Kingdom of Palestine,Example (title of works): was a Crusader states, Crusader state that was established in the Levant immediately after the First Crusade. It lasted for almost two hundred years, from the accession of Godfrey of Bouillon in 1099 until the Siege of Acre (1291), siege of Acre in 1291. Its history is divided into two periods with a brief interruption in its existence, beginning with its collapse after the Siege of Jerusalem (1187), siege of Jerusalem in 1187 and its restoration after the Third Crusade in 1192. The original Kingdom of Jerusalem lasted from 1099 to 1187 before being almost entirely overrun by the Ayyubid dynasty, Ayyubid Sultanate under Saladin. Following the Third Crusade, it was re-established in Acre, Israel, Acre in 1192. The re-established state is commonly known as the "Second Kingdom of J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qalaun
( ar, قلاوون الصالحي, – November 10, 1290) was the seventh Bahri Mamluk sultan; he ruled Egypt from 1279 to 1290. He was called (, "Qalāwūn the Victorious"). Biography and rise to power Qalawun was a Kipchak, ancient Turkic people that have since been absorbed into modern Kazakh people, from the Burj Oghlu tribe, who became a mamluk (slave soldier) in the 1240s after being sold to a member of Sultan al-Kamil's household. Qalawun was known as ''al-Alfī'' ("the Thousander"), because as-Salih Ayyub bought him for a thousand dinars of gold. Qalawun initially barely spoke Arabic, but he rose in power and influence and became an emir under Sultan Baibars, whose son, al-Said Barakah, was married to Qalawun's daughter. Baibars died in 1277 and was succeeded by Barakah. In early 1279, as Barakah and Qalawun invaded the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, there was a revolt in Egypt that forced Barakah to abdicate upon his return home. He was succeeded by his brother Sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)


