|
Malassezia Sympodialis
''Malassezia sympodialis'' is a species in the genus ''Malassezia''. It is characterized by a pronounced lipophily, unilateral, percurrent or sympodial budding and an irregular, corrugated cell wall ultrastructure. It is one of the most common species found on the skin of healthy and diseased individuals. It is considered to be part of the skin's normal human microbiota and begins to colonize the skin of humans shortly after birth. ''Malassezia sympodialis'', often has a symbiotic or commensal relationship with its host, but it can act as a pathogen causing a number of different skin diseases, such as atopic dermatitis. History In 1846, Karl Ferdinand Eichstedt was the first to identify the association of fungi with pityriasis versicolor, a common infection associated with the genus ''Malassezia''. The name applied to the fungal agent responsible shifted multiple times over the next 150 years until the genus ''Pityrosporum'' was settled upon for the teleomorph, and ''Malassezia' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malassezia
''Malassezia'' (formerly known as ''Pityrosporum'') is a genus of fungi. It is the sole genus in family Malasseziaceae, which is the only family in order Malasseziales, itself the single member of class Malasseziomycetes. ''Malassezia'' species are naturally found on the skin surfaces of many animals, including humans. In occasional opportunistic infections, some species can cause hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation on the trunk and other locations in humans. Allergy tests for these fungi are available. Systematics Due to progressive changes in their nomenclature, some confusion exists about the naming and classification of ''Malassezia'' yeast species. Work on these yeasts has been complicated because they require specific growth media and grow very slowly in laboratory culture. ''Malassezia'' were originally identified by the French scientist Louis-Charles Malassez in the late nineteenth century. Raymond Sabouraud identified a dandruff-causing organism in 1904 and called i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innate Immune System
The innate, or nonspecific, immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the dominant immune system response found in plants, fungi, insects, and primitive multicellular organisms (see Beyond vertebrates).. The major functions of the innate immune system are to: * recruit immune cells to infection sites by producing chemical factors, including chemical mediators called cytokines * activate the complement cascade to identify bacteria, activate cells, and promote clearance of antibody complexes or dead cells * identify and remove foreign substances present in organs, tissues, blood and lymph, by specialized white blood cells * activate the adaptive immune system through antigen presentation * act as a physical and chemical barrier to infectious agents; via physical measures such as skin and chemical measures such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidiomycota
Basidiomycota () is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya (often referred to as the "higher fungi") within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Basidiomycota includes these groups: mushrooms, puffballs, stinkhorns, bracket fungi, other polypores, jelly fungi, boletes, chanterelles, earth stars, smuts, bunts, rusts, mirror yeasts, and ''Cryptococcus'', the human pathogenic yeast. Basidiomycota are filamentous fungi composed of hyphae (except for basidiomycota-yeast) and reproduce sexually via the formation of specialized club-shaped end cells called basidia that normally bear external meiospores (usually four). These specialized spores are called basidiospores. However, some Basidiomycota are obligate asexual reproducers. Basidiomycota that reproduce asexually (discussed below) can typically be recognized as members of this division by gross similarity to others, by the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otitis
Otitis is a general term for inflammation or infection, inner ear infection, middle ear infection of the ear, in both humans and other animals. When infection is present, it may be viral or bacterial. When inflammation is present due to fluid build up in the middle ear and infection is not present it is considereOtitis media with effusion It is subdivided into the following: * ''Otitis externa'', external otitis, or "swimmer's ear", involves the outer ear and ear canal. In external otitis, we see tenderness in the pinna—i.e., the outer ear hurts when touched or pulled. * ''Otitis media'', or middle ear infection, involves the middle ear. In otitis media, the ear is infected or clogged with fluid behind the ear drum, in the normally air-filled middle-ear space. This is the most common infection and very common in babies below 6 months. This condition sometimes requires a surgical procedure called ''myringotomy'' and tube insertion. * ''Otitis interna'', or labyrinthitis, involve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malassezia Furfur
''Malassezia furfur'' (formerly known as ''Pityrosporum ovale'' in its hyphal form) is a species of yeast (a type of fungus) that is naturally found on the skin surfaces of humans and some other mammals. It is associated with a variety of dermatological conditions caused by fungal infections, notably seborrhoeic dermatitis and tinea versicolor. As an opportunistic pathogen, it has further been associated with dandruff, malassezia folliculitis, pityriasis versicolor (alba), and malassezia intertrigo, as well as catheter-related fungemia and pneumonia in patients receiving hematopoietic transplants. The fungus can also affect other animals, including dogs. Background ''Malassezia furfur'' is a fungus that lives on the superficial layers of the dermis. It generally exists as a commensal organism forming a natural part of the human skin microbiota, but it can gain pathogenic capabilities when morphing from a yeast to a hyphal form during its life cycle, through unknown molecular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
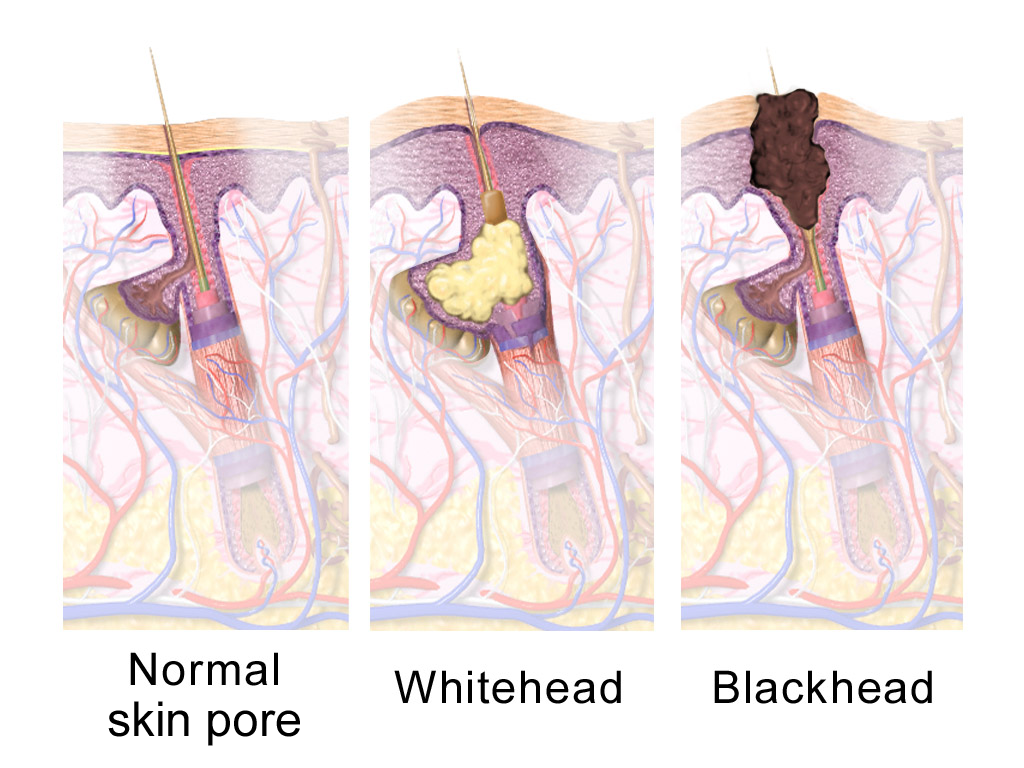
Sebaceous Glands
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipple, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipple. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals. Structure Location Sebaceous glands are found throughout all areas of the skin, except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There are two types of sebaceous glands, those connected to hair follicles and those that exist independently. Sebaceous glands are found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malassezia Globosa
''Malassezia globosa'' is a species of yeast-like fungus. Cause of dandruff and dermatitis In 2007, it was discovered that the responsible agent is a scalp specific fungus, ''Malassezia globosa'' (previously thought to be '' Malassezia furfur''), that metabolizes triglycerides present in sebum by the expression of lipase, resulting in a lipid byproduct: oleic acid. Identification of ''Malassezia'' on skin has been aided by the application of molecular or DNA-based techniques. These investigations show that the ''Malassezia'' species causing most skin disease in humans, including the most common cause of dandruff and seborrhoeic dermatitis, is ''M. globosa'' (though ''M. restricta'' is also involved). The skin rash of tinea versicolor (''pityriasis versicolor'') is also due to infection by this fungus. As the fungus requires fat to grow, it is most common in areas with many sebaceous glands: on the scalp, face, and upper part of the body. When the fungus grows too rapidly, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pityriasis Versicolor
Pityriasis commonly refers to flaking (or scaling) of the skin. The word comes from the Greek πίτυρον "bran". Classification Types include: * Pityriasis alba * Pityriasis lichenoides chronica * Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta * Pityriasis rosea ** Pityriasis circinata * Pityriasis rubra pilaris * Pityriasis versicolor * Dandruff, historically called ''Pityriasis capitis'' * Pityriasis amiantacea See also * Desquamation * List of cutaneous conditions Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against t ... References External links Dermatologic terminology {{cutaneous-condition-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrhoeic dermatitis, sometimes inaccurately referred to as seborrhoea, is a long-term skin disorder. Symptoms include red, scaly, greasy, itchy, and inflamed skin. Areas of the skin rich in oil-producing glands are often affected including the scalp, face, and chest. It can result in social or self-esteem problems. In babies, when the scalp is primarily involved, it is called cradle cap. Dandruff is a milder form of the condition without inflammation. The cause is unclear but believed to involve a number of genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors include poor immune function, Parkinson's disease, and alcoholic pancreatitis. The condition may worsen with stress or during the winter. The ''Malassezia'' yeast is believed to play a role. It is not a result of poor hygiene. Diagnosis is typically based on the symptoms. The condition is not contagious. The typical treatment is antifungal cream and anti-inflammatory agents. Specifically, ketoconazole or ciclopirox are effe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattern Recognition Receptors
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) play a crucial role in the proper function of the innate immune system. PRRs are germline-encoded host sensors, which detect molecules typical for the pathogens. They are proteins expressed, mainly, by cells of the innate immune system, such as dendritic cells, macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils and epithelial cells, to identify two classes of molecules: pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), which are associated with microbial pathogens, and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which are associated with components of host's cells that are released during cell damage or death. They are also called primitive pattern recognition receptors because they evolved before other parts of the immune system, particularly before adaptive immunity. PRRs also mediate the initiation of antigen-specific adaptive immune response and release of inflammatory cytokines. The microbe-specific molecules that are recognized by a given PRR are called p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrophils
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in different animals. They are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow and differentiated into subpopulations of neutrophil-killers and neutrophil-cagers. They are short-lived and highly mobile, as they can enter parts of tissue where other cells/molecules cannot. Neutrophils may be subdivided into segmented neutrophils and banded neutrophils (or bands). They form part of the polymorphonuclear cells family (PMNs) together with basophils and eosinophils. The name ''neutrophil'' derives from staining characteristics on hematoxylin and eosin ( H&E) histological or cytological preparations. Whereas basophilic white blood cells stain dark blue and eosinophilic white blood cells stain bright red, neutrophils stain a neutral pink. Normally, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |