|
Méve
Medb (), later spelled Meadhbh (), Méabh(a) () and Méibh (), and often anglicised as Maeve ( ), is Queen regnant, queen of Connacht in the Ulster Cycle of Irish mythology. Her husband in the core stories of the cycle is Ailill mac Máta, although she had several husbands before him who were also List of kings of Connacht, kings of Connacht. She rules from Cruachan (now Rathcroghan, County Roscommon). She is the enemy (and former wife) of Conchobar mac Nessa, king of Ulster, and is best known for starting the ''Táin Bó Cúailnge'' ("The Cattle Raid of Cooley") to steal Ulster's prize stud bull Donn Cúailnge. Medb is strong-willed, ambitious, cunning and promiscuous, and is an archetypal warrior queen. She is believed by some to be a manifestation of the sovereignty goddess.Ó hÓgáin, Dáithí. ''Myth, Legend & Romance: An encyclopaedia of the Irish folk tradition''. Prentice Hall Press, 1991. pp. 294–295Monaghan, Patricia. ''The Encyclopedia of Celtic Mythology and Folk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulster Cycle
The Ulster Cycle (), formerly known as the Red Branch Cycle, is a body of medieval Irish heroic legends and sagas of the Ulaid. It is set far in the past, in what is now eastern Ulster and northern Leinster, particularly counties Armagh, Down and Louth. It focuses on the mythical Ulster king Conchobar mac Nessa and his court at Emain Macha, the hero Cú Chulainn, and their conflict with the Connachta and queen Medb. The longest and most important tale is the epic '' Táin Bó Cúailnge'' (Cattle Raid of Cooley). The Ulster Cycle is one of the four 'cycles' of Irish mythology and legend, along with the Mythological Cycle, the Fianna Cycle and the Kings' Cycle. Ulster Cycle stories The Ulster Cycle stories are set in and around the reign of King Conchobar mac Nessa, who rules the Ulaid from Emain Macha (now Navan Fort near Armagh). The most prominent hero of the cycle is Conchobar's nephew, Cú Chulainn. The Ulaid are most often in conflict with the Connachta, le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Orthography
Irish orthography is the set of conventions used to write Irish. A spelling reform in the mid-20th century led to , the modern standard written form used by the Government of Ireland, which regulates both spelling and grammar. The reform removed inter-dialectal silent letters, simplified some letter sequences, and modernised archaic spellings to reflect modern pronunciation, but it also removed letters pronounced in some dialects but not in others. Irish spelling represents all Irish dialects to a high degree despite their considerable phonological variation, e.g. ("tree") is read in Mayo and Ulster, in Galway, or in Munster. Some words may have dialectal pronunciations not reflected by their standard spelling, and they sometimes have distinct dialectal spellings to reflect this. Alphabet Latin script has been the writing system used to write Irish since the 5th century, when it replaced Ogham, which was used to write Primitive Irish and Old Irish. Prior to the mid- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Louth
County Louth ( ; ) is a coastal Counties of Ireland, county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. Louth is bordered by the counties of County Meath, Meath to the south, County Monaghan, Monaghan to the west, County Armagh, Armagh to the north and County Down, Down to the north-east, across Carlingford Lough. It is the List of Irish counties by area, smallest county in Ireland by land area and the List of Irish counties by population, 17th most populous, with just over 139,100 residents 2022 census of Ireland, as of 2022. The county is named after the village of Louth, County Louth, Louth. Louth County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority for the county. History County Louth is named after the Louth, County Louth, village of Louth, which in turn is named after Lugh, a god of the ancient Irish. Historically, the placename has had various spellings; , , and ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
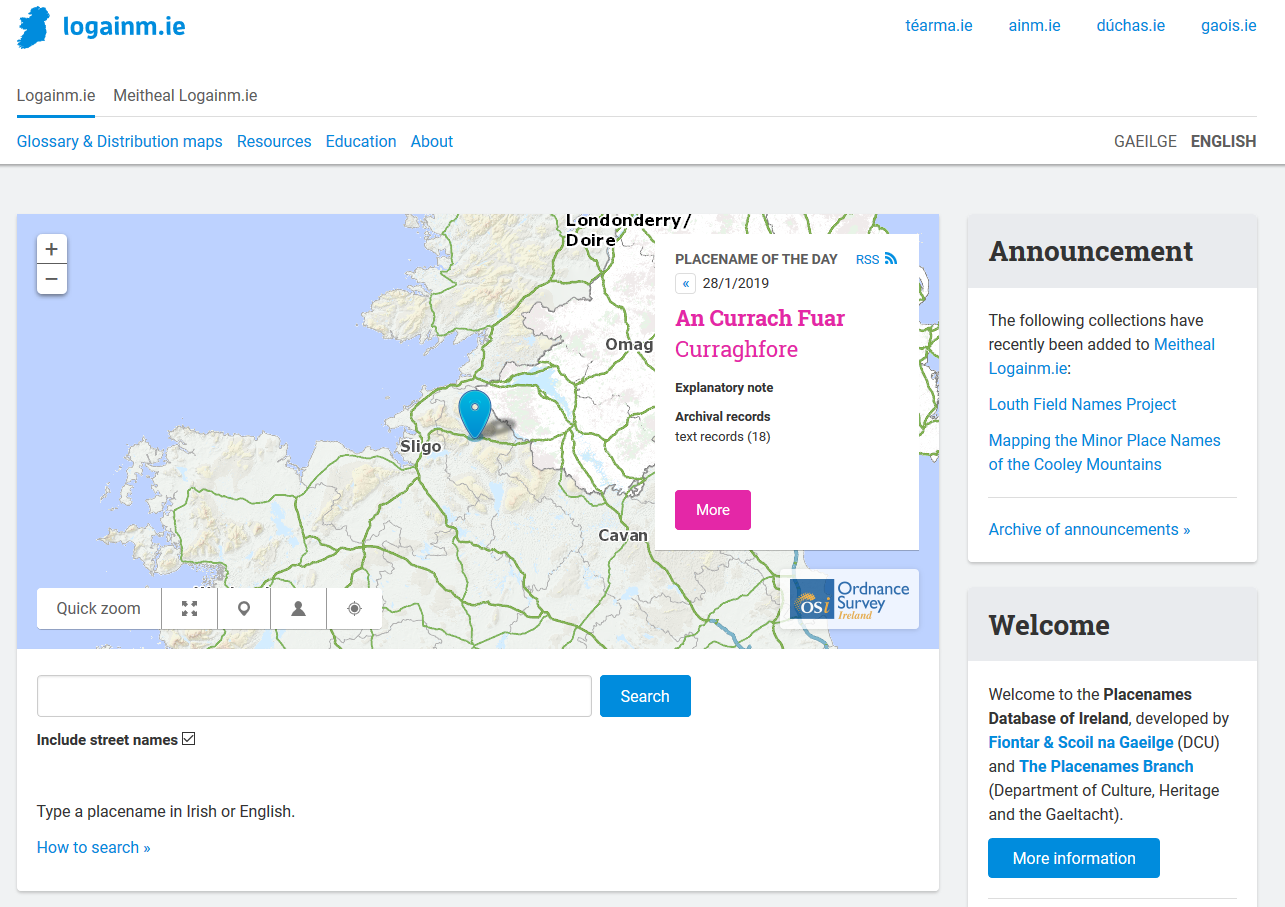
Placenames Database Of Ireland
The Placenames Database of Ireland (), also known as , is a database and archive of place names in Ireland. It was created by Fiontar, Dublin City University in collaboration with the Placenames Branch of the Department of Tourism, Culture, Arts, Gaeltacht, Sport and Media. The website is a public resource primarily aimed at journalists and translators, students and teachers, historians and researchers in genealogy. Placenames Commission and Placenames Branch The Placenames Commission () was established by the Department of Finance in 1946 to advise Ordnance Survey Ireland and the government of what the Irish name of places should be. Although both the 1922 Constitution of the Irish Free State and the current constitution adopted in 1937 recognised Irish as the national language, the law in regard to placenames was carried over from the 19th-century UK statutes which established the Ordnance Survey and Griffith's Valuation, under which only an English-language name had offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Sligo
County Sligo ( , ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Northern and Western Region and is part of the Provinces of Ireland, province of Connacht. Sligo is the administrative capital and largest town in the county. Sligo County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority for the county. The population of the county was 70,198 at the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census. It is noted for Benbulben Mountain, one of Ireland's most distinctive natural landmarks. History The county was officially formed in 1585 by Sir Henry Sidney, Lord Deputy of Ireland, but did not come into effect until the chaos of the Nine Years' War (Ireland), Nine Years' War ended, in 1603. Its boundaries reflect the Ó Conchobhair Sligigh confederation of Lower Connacht () as it was at the time of the Elizabethan conquest. This confederation consisted of the tuatha, or territories, of Cairbre Drom Cliabh, Cairbre Drumcliabh, Tír Fhíacr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Tyrone
County Tyrone (; ) is one of the six counties of Northern Ireland, one of the nine counties of Ulster and one of the thirty-two traditional counties of Ireland. Its county town is Omagh. Adjoined to the south-west shore of Lough Neagh, the county covers an area of , making it the largest of Northern Ireland's six counties by size, and the second largest county in Ulster after Donegal. With a population of 188,383 as of the 2021 census, Tyrone is the 5th most populous county in both Northern Ireland and Ulster, and the 11th most populous county on the island of Ireland. The county derives its name and general geographic location from Tír Eoghain, a Gaelic kingdom under the O'Neill dynasty which existed until the 17th century. Name The name ''Tyrone'' is derived from the Irish , meaning 'land of Eoghan', the name given to the conquests made by the from the provinces of and Ulaid. Historically, it was anglicised as ''Tirowen'' or ''Tyrowen'', which are closer to the Irish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawel Mountain
Sawel Mountain () is the highest peak in the Sperrin Mountains, and the 8th highest in Northern Ireland. It is also the highest mountain in Northern Ireland outside of the Mourne Mountain range located in County Down. Geography To the north of Sawel is County Londonderry and to the south, County Tyrone. The summit is high and is composed of crystalline limestone. Around the peak, there is "montane heathland", with plant life including heather, bilberries and cowberries, although this is being damaged by hillwalking and grazing. Sawel is the source of the River Faughan, a long tributary of the River Foyle. Naming The Irish name of the mountain is a reference to a glen or hollow on the side of Sawel. It was also historically called Slieve Sawel, from the Irish word ''sliabh'' ("mountain"). Plane crash On 5 January 1944 a Royal Navy Stinson Reliant (FK914) of 878 Naval Air Squadron was on a flight from RNAS Eglinton (HMS Gannet) to RNAS Machrihanish (HMS Landrail) when it cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Antrim
County Antrim (named after the town of Antrim, County Antrim, Antrim, ) is one of the six counties of Northern Ireland, located within the historic Provinces of Ireland, province of Ulster. Adjoined to the north-east shore of Lough Neagh, the county covers an area of and has a population of 651,321, as of the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census. County Antrim has a population density of 211 people per square kilometre or 546 people per square mile. It is also one of the thirty-two traditional Counties of Ireland, counties of Ireland. The Glens of Antrim offer isolated rugged landscapes, the Giant's Causeway is a unique landscape and a UNESCO World Heritage Site, Bushmills, County Antrim, Bushmills produces whiskey, and Portrush is a popular seaside resort and night-life area. The majority of Belfast, the capital city of Northern Ireland, is in County Antrim, with the remainder being in County Down. According to the United Kingdom Census 2001, 2001, United Kingdom Census 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulva
In mammals, the vulva (: vulvas or vulvae) comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female sex organ, genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vulval vestibule, vestibule, urinary meatus, vaginal introitus, hymen, and openings of the vestibular glands (Bartholin's gland, Bartholin's and Skene's gland, Skene's). The folds of the outer and inner labia provide a double layer of protection for the vagina (which leads to the uterus). Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support. Blood supply to the vulva comes from the three pudendal arteries. The internal pudendal veins give drainage. Lymphatic vessel#Afferent vessels, Afferent lymph vessels carry lymph away from the vulva to the inguinal lymph nodes. The nerves that supply the vulva are the pudendal nerve, perineal nerve, ilioinguinal nerve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Townland
A townland (; Ulster-Scots: ''toonlann'') is a traditional small land division used in Ireland and in the Western Isles of Scotland, typically covering . The townland system is of medieval Gaelic origin, predating the Norman invasion, and most have Irish-derived names. However, some townland names and boundaries come from Norman manors, plantation divisions, or later creations of the Ordnance Survey.Connolly, S. J., ''The Oxford Companion to Irish History, page 577. Oxford University Press, 2002. ''Maxwell, Ian, ''How to Trace Your Irish Ancestors'', page 16. howtobooks, 2009. Townlands cover the whole island of Ireland, and the total number of inhabited townlands in Ireland was 60,679 in 1911. The total number recognised by the Placenames Database of Ireland as of 2014 was 61,098, including uninhabited townlands. Etymology The term "townland" in English is derived from the Old English word ''tūn'', denoting an enclosure. The term describes the smallest unit of land di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Place Names In Ireland
The vast majority of placenames in Ireland are anglicisations of Irish language names; that is, adaptations of the Irish names to English phonology and spelling. However, some names come directly from the English language, and a handful come from Old Norse and Scots. The study of placenames in Ireland unveils features of the country's history and geography and the development of the Irish language. The name of Ireland itself comes from the Irish name ''Éire'', added to the Germanic word ''land''. In mythology, Éire was an Irish goddess of the land and of sovereignty (see Ériu). In some cases, the official English or anglicised name is wholly different from the official Irish language name. An example is Dublin: its name is derived from the Irish (meaning "black pool"), but its Irish name is (meaning "town of the hurdled ford"). Etymology Names of Irish Gaelic origin For most of the Gaelic period, there were very few towns or large settlements in Ireland. Hence, most pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |