|
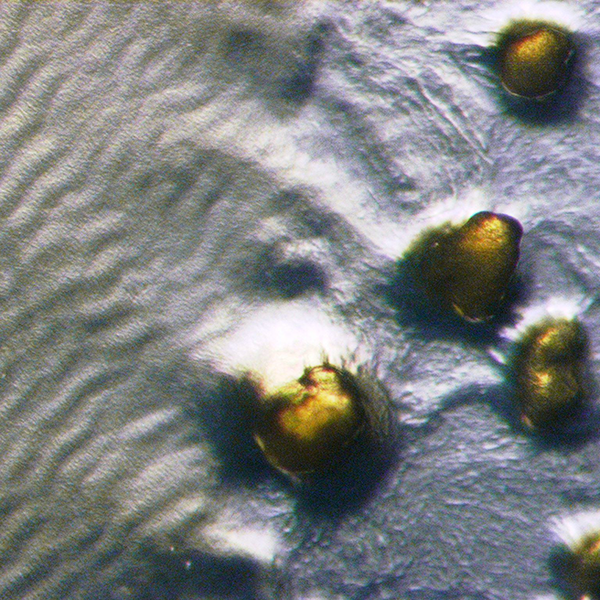
Myxobacteria
The myxobacteria ("slime bacteria") are a group of bacteria that predominantly live in the soil and feed on insoluble organic substances. The myxobacteria have very large genomes relative to other bacteria, e.g. 9–10 million nucleotides except for '' Anaeromyxobacter'' and ''Vulgatibacter''. One species of myxobacteria, ''Minicystis rosea'', has the largest known bacterial genome with over 16 million nucleotides. The second largest is another myxobacteria '' Sorangium cellulosum''. Myxobacteria can move by gliding. They typically travel in '' swarms'' (also known as ''wolf packs''), containing many cells kept together by intercellular molecular signals. Individuals benefit from aggregation as it allows accumulation of the extracellular enzymes that are used to digest food; this in turn increases feeding efficiency. Myxobacteria produce a number of biomedically and industrially useful chemicals, such as antibiotics, and export those chemicals outside the cell. Myxobacteria a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stigmatella Aurantiaca
''Stigmatella aurantiaca'' is a member of myxobacteria, a group of gram-negative bacteria with a complex developmental life cycle. Classification The bacterial nature of this organism was recognized by Thaxter in 1892, who grouped it among the ''Chrondromyces''. It had been described several times before, but had been misclassified as a member of the '' fungi imperfecti''. More recent investigations have shown that, contrary to Thaxter's classification, this organism is not closely related to ''Chrondromyces'', and ''Stigmatella'' is currently recognized as a separate genus. Of the three major subgroups of the myxobacteria, Myxococcus, Nannocystis, and Chrondromyces, ''Stigmatella'' is most closely aligned with Myxococcus. Life cycle ''S. aurantiaca'', like other myxobacterial species, has a complex life cycle including social gliding (swarming), fruiting body formation, and predatory feeding behaviors. The bacteria do not swim, but glide on surfaces leaving slime trail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myxococcus Xanthus
''Myxococcus xanthus'' is a gram-negative, bacillus (or rod-shaped) species of myxobacteria that is typically found in the top-most layer of soil. These bacteria lack flagella; rather, they use pili for motility. ''M. xanthus'' is well-known for its predatory behavior on other microorganisms. These bacteria source carbon from lipids rather than sugars. They exhibit various forms of self-organizing behavior in response to environmental cues. Under normal conditions with abundant food, they exist as predatory, saprophytic single-species biofilm called a swarm, highlighting the importance of intercellular communication for these bacteria. Under starvation conditions, they undergo a multicellular development cycle. Microbiology Morphology ''M. xanthus'' appear as gram-negative rods without flagella. These rods have an average length of 7 microns and width of 0.5 microns. It utilizes type IV pilus (T4P) to move in a "gliding" manner, crawling along a surface. As a colony or sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorangium Cellulosum
''Sorangium cellulosum'' is a soil-dwelling Gram-negative bacterium of the group myxobacteria. It is motile and shows gliding motility. Under stressful conditions this motility, as in other myxobacteria, the cells congregate to form fruiting bodies and differentiate into myxospores. These congregating cells make isolation of pure culture and colony counts on agar medium difficult as the bacterium spread and colonies merge. It has an unusually-large genome of 13,033,779 base pairs, making it the largest bacterial genome sequenced to date by roughly 4 Mb. Ecology ''S. cellulosum'' is found in soils, animal feces, and tree bark. The bacterium is a saprophyte deriving its nutrition from cellulose aerobically. It is a prolific producer of secondary fungicides and bactericides that reduce competition in soil environments. In lab samples, ''S. cellulosum'' grows on agar medium only when certain cell densities are plated. Quorum-sensing allows Sorangium to grow in communities suff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pxr SRNA
Pxr sRNA is a regulatory RNA which downregulates genes responsible for the formation of fruiting bodies in ''Myxococcus xanthus''. Fruiting bodies are aggregations of myxobacteria formed when nutrients are scarce, the fruiting bodies permit a small number of the aggregated colony to transform into stress-resistant spores. Pxr exists in two forms: Pxr-L (a long form) and Pxr-S which is shorter. The short form was found to be expressed in cells during growth but is rapidly repressed during starvation. This finding implies that Pxr-S is specifically responsible for inhibiting the fruiting body development during cell growth when nutrients are abundant. Pxr homologs have only been found in one other taxon, namely ''Stigmatella aurantiaca''. Homologs were not found in any other myxobacteria (such as '' Sorangium cellulosum'' or ''Anaeromyxobacter dehalogenans'') which suggests the Pxr RNA gene may have a recent evolutionary origin in the sub-clade Myxococcales. PxR sRNA folds into 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
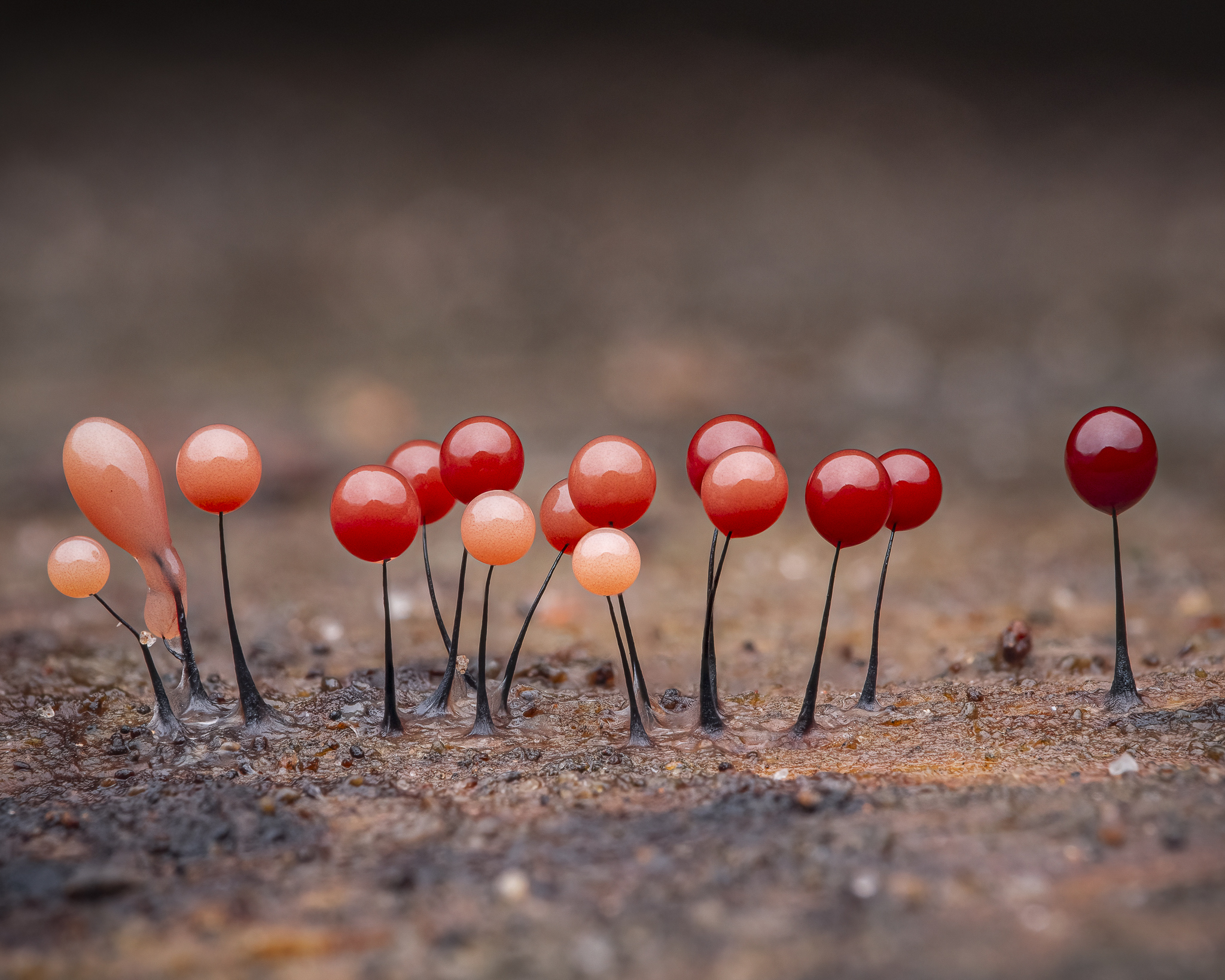
Slime Mold
Slime mold or slime mould is an informal name given to a polyphyletic assemblage of unrelated eukaryotic organisms in the Stramenopiles, Rhizaria, Discoba, Amoebozoa and Holomycota clades. Most are near-microscopic; those in the Myxogastria form larger plasmodial slime molds visible to the naked eye. The slime mold life cycle includes a free-living single-celled stage and the formation of spores. Spores are often produced in macroscopic multicellular or multinucleate fruiting bodies that may be formed through aggregation or fusion; aggregation is driven by chemical signals called acrasins. Slime molds contribute to the decomposition of dead vegetation; some are parasitic. Most slime molds are terrestrial and free-living, typically in damp shady habitats such as in or on the surface of rotting wood. Some myxogastrians and protostelians are aquatic or semi-aquatic. The phytomyxea are parasitic, living inside their plant hosts. Geographically, slime molds are cosmopo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all life, forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a Cell membrane, membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning 'small room'. Most cells are only visible under a light microscope, microscope. Cells Abiogenesis, emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of Self-replication, replication, protein synthesis, and cell motility, motility. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possess a Cell nucleus, nucleus, and prokaryotic, prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled, such as amoebae, or multicellular organism, multicellular, such as some algae, plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles including Mitochondrion, mitochondria, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multicellular Organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- and partially multicellular, like slime molds and social Amoeba, amoebae such as the genus ''Dictyostelium''. Multicellular organisms arise in various ways, for example by cell division or by aggregation of many single cells. Colonial organisms are the result of many identical individuals joining together to form a colony (biology), colony. However, it can often be hard to separate colonial protists from true multicellular organisms, because the two concepts are not distinct; colonial protists have been dubbed "pluricellular" rather than "multicellular". There are also macroscopic organisms that are multinucleate though technically unicellular, such as the Xenophyophorea that can reach 20 cm. Evolutionary history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Gliding
Gliding motility is a type of translocation used by microorganisms that is independent of propulsive structures such as flagella, pili, and fimbriae. Gliding allows microorganisms to travel along the surface of low aqueous films. The mechanisms of this motility are only partially known. Twitching motility also allows microorganisms to travel along a surface, but this type of movement is jerky and uses pili as its means of transport. Bacterial gliding is a type of gliding motility that can also use pili for propulsion. The speed of gliding varies between organisms, and the reversal of direction is seemingly regulated by some sort of internal clock. For example the apicomplexans are able to travel at fast rates between 1–10 μm/s. In contrast '' Myxococcus xanthus'' bacteria glide at a rate of 0.08 μm/s. Types of motility Bacterial gliding is a process of motility whereby a bacterium can move under its own power. Generally, the process occurs whereby the bacteriu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myxococcaceae
Myxococcaceae is a family of gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria. The family Myxococcaceae is encompassed within the myxobacteria ("slime bacteria"). The family is ubiquitously found in soils, marine, and freshwater environments. Production of compounds with medical uses by Myxococcaceae makes them useful in human health fields. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Morphology and Behavior Cells can be motile with gliding and swarming behavior. The vegetative cell shape in the Myxococcaceae family is long rods, which vary in size between members. The most common fruiting body morphs are soft hump and knob shaped with possible colors of yellow, peach, white, or orange depending on species. Myxococcaceae are spore producing bacteria and are delineated by their spore shape. The myxospores are oval to round and are optically refractive. Quoru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulgatibacteraceae
Vulgatibacteraceae is a monotypic family of bacteria in the order Myxococcales, containing one species in one genus; ''Vulgatibacter incomptus''. The bacteria were first isolated from soil samples from Yakushima in 2014. The bacteria of this family are motile rods, and, like all myxococcota, are gram-negative. The one species, ''Vulgatibacter incomptus'' (initially designated strain B00001T) is believed to be most closely related to the species '' Cystobacter armeniaca'' and ''Anaeromyxobacter dehalogenans.'' See also * List of bacterial orders * List of bacteria genera This article lists the genera of the bacteria Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, ... References {{Taxonbar, from1=Q26307000, from2=Q26306993, from3=Q26700331 Myxococcota Monotypic bacteria genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |