|
Myszaków
Myszaków is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Zagórów, within Słupca County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. It lies approximately south-west of Zagórów, south of Słupca, and south-east of the regional capital Poznań. One of the battles of the Polish January Uprising against the Russian Empire was fought near the village in 1863. There is a mass grave of the Polish insurgents in the village. Notable people * Stanisław Kostanecki (1860–1910), one of the most renown Polish organic chemists *Kazimierz Kostanecki (1863–1940), Polish physician, anatomist, cytologist, murdered by the Germans in the Sachsenhausen concentration camp * (1866–1941), Polish economist, rector of the University of Warsaw The University of Warsaw (, ) is a public university, public research university in Warsaw, Poland. Established on November 19, 1816, it is the largest institution of higher learning in the country, offering 37 different fields of st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gmina Zagórów
__NOTOC__ Gmina Zagórów is an urban-rural gmina (administrative district) in Słupca County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. Its seat is the town of Zagórów, which lies approximately south of Słupca and east of the regional capital Poznań. The gmina covers an area of , and as of 2006 its total population is 9,073 (out of which the population of Zagórów amounts to 2,932, and the population of the rural part of the gmina is 6,141). The gmina contains part of the protected area called Warta Landscape Park. Villages Apart from the town of Zagórów, Gmina Zagórów contains the villages and settlements of Adamierz, Anielewo, Augustynów, Bukowe, Chruściki, Długa Górka, Drzewce, Grabina, Grądzeń, Huta Łukomska, Imielno, Kirchol, Kopojno, Kopojno-Parcele, Kościołków, Koszelewska Łąka, Łazińsk Drugi, Łazińsk Pierwszy, Łazy, Łomów, Łukom, Mariantów, Michalinów near Oleśnica, Michalinów near Trąbczyn, Myszaków, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zagórów
Zagórów is a town in Słupca County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in central Poland, with 2,985 inhabitants (2010). History The town's name is of Old Polish origin and comes from the word ''zagór''. The oldest known mention of the settlement comes from a document from 1240. Zagórów received town rights from King Władysław II Jagiełło in 1407, however, these rights were implemented only in 1445. It was a private church town, administratively located in the Konin County in the Kalisz Voivodeship in the Greater Poland Province of the Polish Crown. The town suffered as a result of the 17th-century Polish–Swedish wars. It was annexed by Prussia during the Second Partition of Poland in 1793. After the successful Greater Poland uprising of 1806, it was regained by Poles and included within the short-lived Duchy of Warsaw. After the duchy's dissolution, it passed to the Russian Partition of Poland in 1815. Polish insurgents were active in the area during the January Uprising ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazimierz Kostanecki
Professor Kazimierz Kostanecki (25 December 1863, Myszaków – 11 January 1940, Sachsenhausen concentration camp) was a Polish physician, anatomist, and cytologist. Since 1892 he was a professor of comparative and descriptive anatomy at the Jagiellonian University in Kraków under the military partitions of Poland. He held his post until 1935 in the reborn Second Polish Republic. During this time he also served as Dean of the Faculty of Medicine, and between 1913 and 1916 was the Rector (academia), Rector of the Jagiellonian University. He is considered the father of the Kraków school of anatomy due to his many scientific discoveries and accomplishments. Kostanecki is the author of 62 scientific publications in Polish, English, German, and French. During his work in Berlin and Giessen he conducted research in the field of comparative anatomy of throat and palate, and the anatomy of the neck and head. He also described all the muscles associated with the Ear trumpet and, as the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanisław Kostanecki
Stanisław Kostanecki (born 16 April 1860 in Myszaków, now in Poland then Kingdom of Prussia – 15 November 1910 in Würzburg) was a Polish organic chemist, professor who pioneered in vegetable dye chemistry e.g. curcumin Curcumin is a bright yellow chemical produced by plants of the ''Curcuma longa'' species. It is the principal curcuminoid of turmeric (''Curcuma longa''), a member of the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It is sold as a herbal supplement, cosmetic .... He is best known for discovering Kostanecki acylation, which was named after him. In 1896, he developed the theory of dyes and studied the natural vegetable dyes. Among his many students were scientists Kazimierz Funk and Wiktor Lampe. References 1860 births 1910 deaths Polish organic chemists 19th-century Prussian people {{Chemist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Słupca
Słupca is a town in Greater Poland Voivodeship, central Poland, and the seat of Słupca County. It has 13,773 inhabitants (2018). History History of Słupca dates back to the Middle Ages. On November 15, 1290 Polish Duke Przemysł II granted Słupca town rights. In 1296 Słupca's town privileges were renewed; this time Słupca was granted a range of new privileges. It is inhabited by about 1000 people. On November 11, 1314 King Władysław I the Elbow-high granted Slupca a privilege to establish a Mint (facility), mint and produce coins. Since 1314 it was located in the Kalisz Voivodeship (1314–1793), Kalisz Voivodeship of the Polish Kingdom. In 1331 the town was raided and burned down by the Teutonic Knights. A defensive wall of the length of 1100 meters was constructed between 1375 and 1382. During the Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466) the town of Slupca sent 20 knights so as other 9 biggest towns of Greater Poland did. By the end of 15th century Słupca was inhabited by ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Warsaw
The University of Warsaw (, ) is a public university, public research university in Warsaw, Poland. Established on November 19, 1816, it is the largest institution of higher learning in the country, offering 37 different fields of study as well as 100 specializations in humanities, Engineering, technical, and natural sciences. The University of Warsaw consists of 126 buildings and educational complexes with over 18 faculties: biology, chemistry, medicine, journalism, political science, philosophy, sociology, physics, geography, regional studies, geology, history, applied linguistics, philology, Polish language, pedagogy, economics, law, public administration, psychology, applied social sciences, management, mathematics, computer science, and mechanics. Among the university's notable alumni are heads of state, prime ministers, Nobel Prize laureates, including Joseph Rotblat, Sir Joseph Rotblat and Olga Tokarczuk, as well as several historically important individuals in their res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sachsenhausen Concentration Camp
Sachsenhausen () or Sachsenhausen-Oranienburg was a German Nazi concentration camp in Oranienburg, Germany, used from 1936 until April 1945, shortly before the defeat of Nazi Germany in May later that year. It mainly held political prisoners throughout World War II. Prominent prisoners included Joseph Stalin's oldest son, Yakov Dzhugashvili; assassin Herschel Grynszpan; Paul Reynaud, the penultimate prime minister of the French Third Republic; Francisco Largo Caballero, prime minister of the Second Spanish Republic during the Spanish Civil War; the wife and children of the Albrecht, Duke of Bavaria, crown prince of Bavaria; Ukrainian nationalist leader Stepan Bandera; and several enemy soldiers and political dissidents. Sachsenhausen was a labour camp, outfitted with several subcamps, a gas chamber, and a medical experimentation area. Prisoners were treated inhumanely, fed inadequately, and killed openly. After World War II, when Oranienburg was in the Soviet Occupation Zone, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughly one-sixth of the world's landmass, making it the list of largest empires, third-largest empire in history, behind only the British Empire, British and Mongol Empire, Mongol empires. It also Russian colonization of North America, colonized Alaska between 1799 and 1867. The empire's 1897 census, the only one it conducted, found a population of 125.6 million with considerable ethnic, linguistic, religious, and socioeconomic diversity. From the 10th to 17th centuries, the Russians had been ruled by a noble class known as the boyars, above whom was the tsar, an absolute monarch. The groundwork of the Russian Empire was laid by Ivan III (), who greatly expanded his domain, established a centralized Russian national state, and secured inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
January Uprising
The January Uprising was an insurrection principally in Russia's Kingdom of Poland that was aimed at putting an end to Russian occupation of part of Poland and regaining independence. It began on 22 January 1863 and continued until the last insurgents were captured by the Russian forces in 1864. It was the longest-lasting insurgency in partitioned Poland. The conflict engaged all levels of society and arguably had profound repercussions on contemporary international relations and ultimately transformed Polish society. A confluence of factors rendered the uprising inevitable in early 1863. The Polish nobility and urban bourgeois circles longed for the semi-autonomous status they had enjoyed in Congress Poland before the previous insurgency, a generation earlier in 1830, and youth encouraged by the success of the Italian independence movement urgently desired the same outcome. Russia had been weakened by its Crimean adventure and had introduced a more liberal attitude in its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
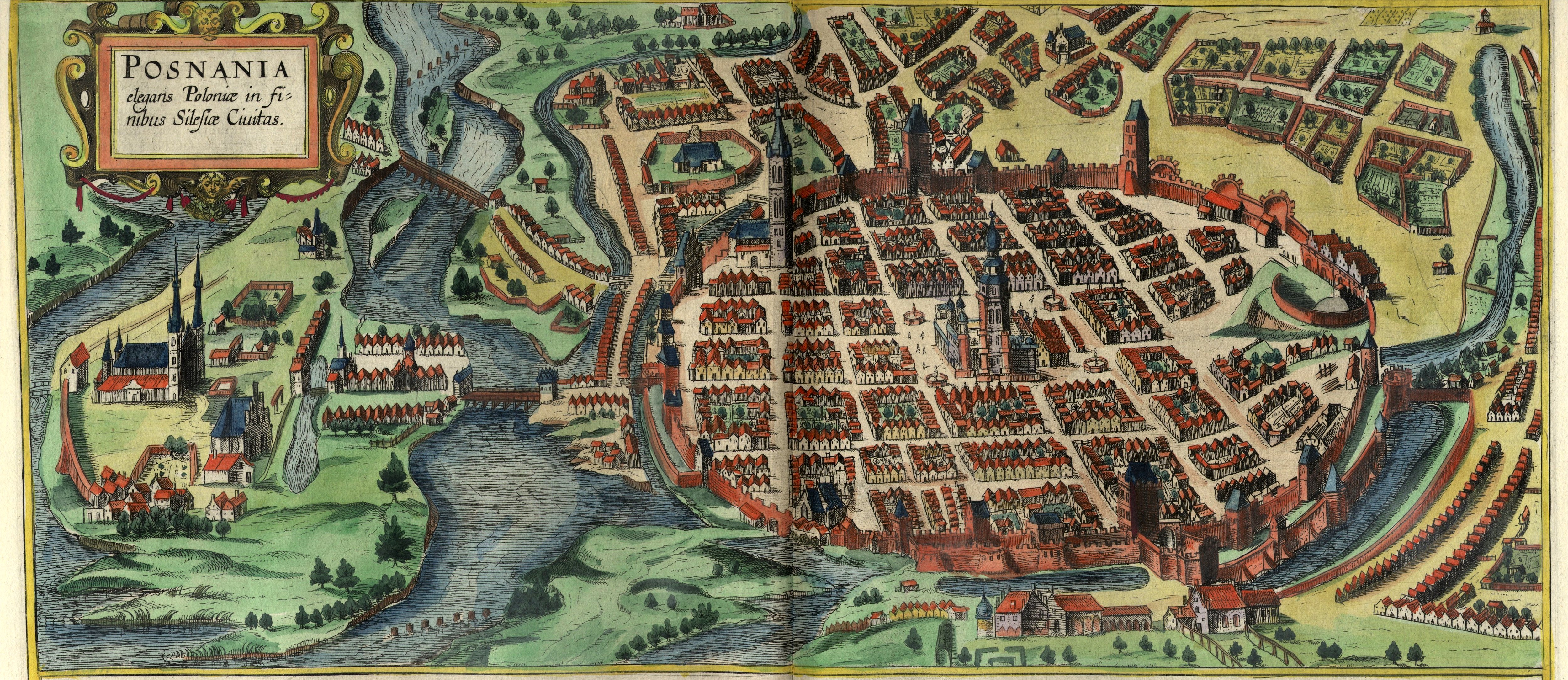
Poznań
Poznań ( ) is a city on the Warta, River Warta in west Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business center and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's Fair, Poznań, Saint John's Fair (''Jarmark Świętojański''), traditional St. Martin's croissant, Saint Martin's croissants and a local dialect. Among its most important heritage sites are the Renaissance in Poland, Renaissance Old Town, Poznań Town Hall, Town Hall and Poznań Cathedral. Poznań is the fifth-largest List of cities and towns in Poland#Cities, city in Poland. As of 2023, the city's population is 540,146, while the Poznań metropolitan area (''Metropolia Poznań'') comprising Poznań County and several other communities is inhabited by over 1.029 million people. It is one of four historical capitals of medieval Poland and the ancient capital of the Greater Poland region, currently the administrative capital of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivodeships Of Poland
A voivodeship ( ; ; plural: ) is the highest-level Administrative divisions of Poland, administrative division of Poland, corresponding to a province in many other countries. The term has been in use since the 14th century and is commonly translated into English as "province". The administrative divisions of Poland, Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998, which went into effect on 1 January 1999, reduced the number of voivodeships to sixteen. These 16 replaced the 49 subdivisions of the Polish People's Republic, former voivodeships that had existed from 1 July 1975, and bear a greater resemblance (in territory, but not in name) to the voivodeships that existed between 1950 and 1975. Today's voivodeships are mostly named after historical and geographical regions, while those prior to 1998 generally took their names from the cities on which they were centered. The new units range in area from under (Opole Voivodeship) to over (Masovian Voivodeship), and in population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |