|
Myriocin
Myriocin, also known as antibiotic ISP-1 and thermozymocidin, is a non-proteinogenic amino acid derived from the entomopathogenic fungus, ''Isaria sinclairii''. Myriocin is a very potent inhibitor of serine palmitoyltransferase, the first step in sphingosine biosynthesis. Due to this property, it is used in biochemical research as a tool for depleting cells of sphingolipids. Myriocin was shown to inhibit the proliferation of an IL-2-dependent mouse cytotoxic T cell line. Myriocin possesses immunosuppressant activity. It is reported to be 10- to 100-fold more potent than ciclosporin. The multiple sclerosis drug fingolimod was derived from myriocin by using structure–activity relationship The structure–activity relationship (SAR) is the relationship between the chemical structure of a molecule and its biological activity. This idea was first presented by Alexander Crum Brown and Thomas Richard Fraser at least as early as 1868. Th ... studies to determine the parts of the mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Immunosuppressant
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent the activity of the immune system. Classification Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified into five groups: * glucocorticoids * cytostatics * antibodies * drugs acting on immunophilins * other drugs Glucocorticoids In pharmacologic (supraphysiologic) doses, glucocorticoids, such as prednisone, dexamethasone, and hydrocortisone are used to suppress various allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune disorders. They are also administered as posttransplantory immunosuppressants to prevent the acute transplant rejection and graft-versus-host disease. Nevertheless, they do not prevent an infection and also inhibit later reparative processes. Immunosuppressive mechanism Glucocorticoids suppress cell-mediated immunity. They act by inhibiting gene expression of cytokines including Interleukin 1 (IL-1), IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Isaria Sinclairii
''Isaria sinclairii'' is a species of entomopathogenic fungus mostly infecting the underground nymphs of cicadas. It produces myriocin, from which the synthetic drug fingolimod, a treatment for multiple sclerosis, was developed. Taxonomy ''Isaria sinclairii'' is the name of the anamorph; the teleomorph is ''Cordyceps sinclairii'', Cordycipitaceae. The species was first described in 1855 by Miles Joseph Berkeley from specimens collected in the garden of Archdeacon William Williams at Tūranga, Poverty Bay. It was moved to the genus '' Isaria'' in 1923 by Curtis Gates Lloyd. Ecology ''Isaria sinclairii'' is a fungus which attacks insects, including cicada larvae. The larvae typically die just beneath the soil surface, and the fungus produces white tufts which grow up from the soil and release powdery white spores. ''I. sinclairii'' is found from Asia (particularly China, Japan, and Korea) through to New Zealand. In New Zealand it attacks cicadas of the genera '' Amphipsalta'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
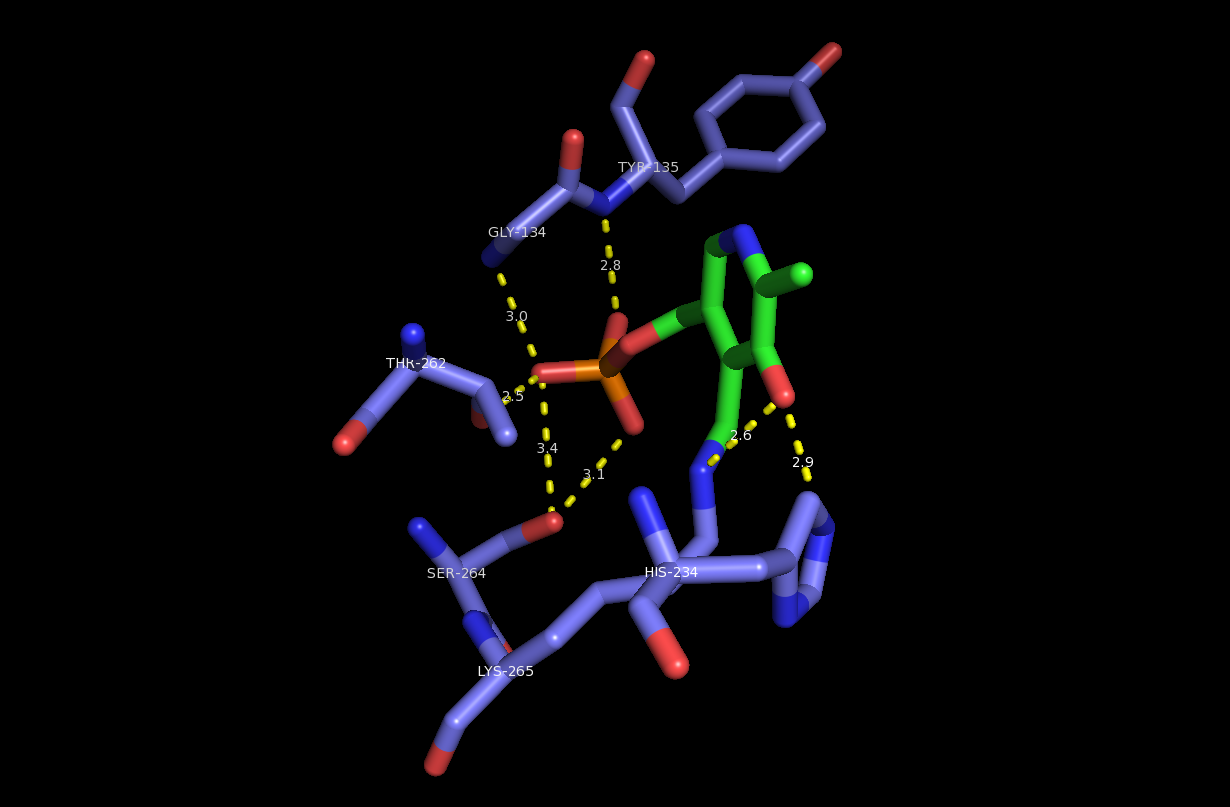
Fingolimod
Fingolimod, sold under the brand name Gilenya, is an immunomodulating medication, used for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Fingolimod is a sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator, which sequesters lymphocytes in lymph nodes, preventing them from contributing to an autoimmune reaction. It has been reported to reduce the rate of relapses in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis by approximately one-half over a two-year period. Medical uses Fingolimod is used in the treatment of the relapsing form of multiple sclerosis. Its effect in those with primary progressive multiple sclerosis is not clear. It may also be used in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Adverse effects The most common side effects of fingolimod have been head colds, headache, increased gamma-glutamyl transfer (≤15%), diarrhea (13%), nausea (13%), abdominal pain (11%) and fatigue. A few cases of skin cancer have been reported, which has also been reported in patients taking natalizuma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Non-proteinogenic Amino Acid
In biochemistry, non-coded or non-proteinogenic amino acids are distinct from the 22 proteinogenic amino acids (21 in eukaryotesplus formylmethionine in eukaryotes with prokaryote organelles like mitochondria), which are naturally encoded in the genome of organisms for the assembly of proteins. However, over 140 non-proteinogenic amino acids occur naturally in proteins and thousands more may occur in nature or be synthesized in the laboratory. Chemically synthesized amino acids can be called unnatural amino acids. Unnatural amino acids can be synthetically prepared from their native analogs via modifications such as amine alkylation, side chain substitution, structural bond extension cyclization, and isosteric replacements within the amino acid backbone. Many non-proteinogenic amino acids are important: * intermediates in biosynthesis, * in post-translational formation of proteins, * in a physiological role (e.g. components of bacterial cell walls, neurotransmitters and toxins), * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Entomopathogenic Fungus
Entomopathogenic fungi are parasitic unicellular or multicellular microorganisms belonging to the kingdom of Fungi, that can infect and seriously disable or kill insects. Pathogenicity for insects is widely distributed in the kingdom of fungi and occur in six fungal phyla (Ascomycota, Oomycetes, Basidiomycota, Chytridiomycota, Zygomycota, and Microsporidia). It plays a vital ecological role in controlling insect populations by impacting 19 out of 30 known insect orders. Some fungal entomopathogens are opportunistic whereas some have evolved into highly specific pathogens of insects. Mode of infection Unlike many other insect pathogens (entomopathogenic viruses, nematodes, or bacteria), most entomopathogenic fungi do not require entry through ingestion or oral intake and instead directly attack the insect cuticle and penetrate the insect body through the exoskeleton. These fungi use a broad spectrum of virulence factors such as adhesins (to attach to insect cuticles), lytic enzym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Serine Palmitoyltransferase
In enzymology, a serine ''C''-palmitoyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction: :palmitoyl-CoA + -serine \rightleftharpoons CoA + 3-dehydro--sphinganine + CO2 Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are palmitoyl-CoA and -serine, whereas its 3 products are CoA, 3-dehydro--sphinganine, and CO2. This reaction is a key step in the biosynthesis of sphingosine which is a precursor of many other sphingolipids. This enzyme participates in sphingolipid metabolism. It employs one cofactor, pyridoxal phosphate. Nomenclature This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those acyltransferases transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups. The systematic name of this enzyme class is palmitoyl-CoA:L-serine ''C''-palmitoyltransferase (decarboxylating). Other names in common use include: * serine palmitoyltransferase, * SPT, 3-oxosphinganine synthetase, and * acyl-CoA:serine C-2 acyltransferase decarboxylating. Structure Serine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sphingosine
Sphingosine (2-amino-4-trans-octadecene-1,3-diol) is an 18-carbon amino alcohol with an unsaturated hydrocarbon chain, which forms a primary part of sphingolipids, a class of cell membrane lipids that include sphingomyelin, an important phospholipid. Functions Sphingosine can be phosphorylated in vivo via two kinases, sphingosine kinase type 1 and sphingosine kinase type 2. This leads to the formation of sphingosine-1-phosphate, a potent signaling lipid. Sphingolipid metabolites, such as ceramides, sphingosine and sphingosine-1-phosphate, are lipid signaling molecules involved in diverse cellular processes. Biosynthesis Sphingosine is synthesized from palmitoyl CoA and serine in a condensation required to yield dihydrosphingosine. Dehydrosphingosine is then reduced by NADPH to dihydrosphingosine (sphinganine), acylated to dihydroceramide and finally oxidized by FAD to ceramide. Sphingosine is then solely formed via degradation of sphingolipid in the lysosome. Gal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sphingolipid
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids containing a backbone of sphingoid bases, which are a set of aliphatic amino alcohols that includes sphingosine. They were discovered in brain extracts in the 1870s and were named after the mythological sphinx because of their enigmatic nature. These compounds play important roles in signal transduction and cell recognition. Sphingolipidoses, or disorders of sphingolipid metabolism, have particular impact on neural tissue. A sphingolipid with a terminal hydroxyl group is a ceramide. Other common groups bonded to the terminal oxygen atom include phosphocholine, yielding a sphingomyelin, and various sugar monomers or dimers, yielding cerebrosides and globosides, respectively. Cerebrosides and globosides are collectively known as glycosphingolipids. Structure The long-chain bases, sometimes simply known as sphingoid bases, are the first non-transient products of '' de novo'' sphingolipid synthesis in both yeast and mammals. These co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Interleukin 2
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is an interleukin, which is a type of cytokine signaling molecule forming part of the immune system. It is a 15.5–16 Dalton (unit), kDa protein that regulates the activities of white blood cells (leukocytes, often lymphocytes) that are responsible for immunity. IL-2 is part of the body's immune response, natural response to microbial infection, and in discriminating between foreign ("non-self") and "self". IL-2 mediates its effects by binding to IL-2 receptors, which are expressed by lymphocytes. The major sources of IL-2 are activated T helper cell, CD4+ T cells and activated CD8+ T cells, CD8+ T cells. Put shortly the function of IL-2 is to stimulate the growth of helper, cytotoxic and regulatory T cells. IL-2 receptor IL-2 is a member of a specific family of cytokines, each member of which has a Helix bundle#Four-helix bundles, four alpha helix bundle; this cytokine family also includes Interleukin-4, IL-4, Interleukin 7, IL-7, Interleukin 9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
T Cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface receptor, cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: Cytotoxic T cell, CD8+ "killer" (cytotoxic) and T helper cell, CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ciclosporin
Ciclosporin, also spelled cyclosporine and cyclosporin, is a calcineurin inhibitor, used as an immunosuppressant medication. It is taken Oral administration, orally or intravenously for rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, Crohn's disease, nephrotic syndrome, eczema, and in organ transplants to prevent transplant rejection, rejection. It is also used as eye drops for keratoconjunctivitis sicca (dry eyes). Common side effects include high blood pressure, headache, kidney problems, increased hair growth, and vomiting. Other severe side effects include an increased risk of infection, liver problems, and an increased risk of lymphoma. Blood levels of the medication should be checked to decrease the risk of side effects. Use during pregnancy may result in preterm birth; however, ciclosporin does not appear to cause birth defects. Ciclosporin is believed to work by decreasing the function of lymphocytes. It does this by forming a complex with cyclophilin to block the phosphatase act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, cognitive disability, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Symptoms include double vision, vision loss, eye pain, muscle weakness, and loss of Sensation (psychology), sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In relapsing forms of MS, symptoms may disappear completely between attacks, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. In progressive forms of MS, bodily function slowly deteriorates once symptoms manifest and will steadily worsen if left untreated. While its cause is unclear, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |